Snowflake is a prominent cloud data platform known for scalable data warehousing and analytics. Its architecture separates storage from compute and supports deployment across multiple clouds, appealing to enterprises worldwide. However, shifting business needs, such as cost control, cloud ecosystem alignment, and specialized analytics, lead many organizations to consider Snowflake competitors.
In this article, you will find an in-depth comparison of leading Snowflake alternatives in 2026. We also provide a structured decision framework to guide platform selection, an objective scoring rubric, and practical advice on migrating from Snowflake.
Key Takeaways
- Snowflake is a leading cloud warehouse, but strong alternatives include Google BigQuery, Amazon Redshift, Databricks, Azure Synapse, and Teradata. Each offers different strengths in cost model, ecosystem integration, and workload focus.
- The right platform depends on your primary use case. BI-heavy teams may prefer Snowflake or BigQuery, ML-driven teams may lean toward Databricks, and AWS-native environments often choose Redshift.
- Pricing structures differ significantly. Credit-based models, serverless compute, and reserved capacity options can materially impact long-term cost.
- Migration between warehouses requires more than data transfer. Pipelines, transformation logic, governance rules, and historical consistency must be preserved.
- A warehouse does not normalize marketing APIs or align KPIs. Improvado acts as the ingestion and transformation layer, standardizing schemas, aligning metric definitions, and delivering governed, warehouse-ready datasets regardless of a DWH you choose.
What Is Snowflake and Why Consider Competitors in 2026?
Snowflake is a cloud-native data platform designed for large-scale data warehousing and analytics across AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP). Its key innovation is the decoupling of storage and compute, enabling independent scaling based on workload demand.
Additional features include support for high concurrency, automated query optimization, and secure data sharing without duplication.
Despite these strengths, organizations may evaluate competitors due to several factors:
- Cost management: Snowflake’s consumption-based pricing can become costly with unpredictable or large-scale workloads.
- Vendor diversification: Avoiding reliance on a single cloud vendor or platform.
- Feature specialization: Requirements for deeper machine learning integration, real-time analytics, or hybrid big data capabilities.
- Cloud ecosystem preferences: Need for seamless integration with a particular cloud provider’s native services.
- Performance optimization: Workloads that benefit from platforms optimized for specific use cases or architectures.

Snowflake Competitors in 2026: Features, Pricing, and Tradeoffs
Assessing alternatives helps align platform choice with business objectives, technical needs, and budget considerations. Here are some of the prominent Snowflake alternatives to consider.
1. Google BigQuery
Google BigQuery is a fully managed, serverless data warehouse built on Google Cloud Platform. It separates storage and compute automatically and scales resources based on workload.
Users run standard SQL queries without provisioning or maintaining infrastructure. BigQuery is optimized for large-scale analytical processing and supports structured and semi-structured data formats, including JSON and Avro.
Best for: Organizations operating primarily on Google Cloud that require elastic scaling, strong integration with GCP services, and embedded AI capabilities through BigQuery ML and Vertex AI. It is well suited for large analytical workloads, marketing data processing, and machine learning model training directly inside the warehouse.
Pricing: Pay-as-you-go for storage and queries, with optional flat-rate pricing for predictable costs.
Tradeoffs:
- Query costs can increase quickly without partitioning and clustering.
- Cold or infrequent queries may experience latency.
- Complex workloads require performance tuning and workload management.
- BigQuery operates exclusively within GCP, which can constrain multi-cloud or hybrid architectures.
2. Amazon Redshift
Amazon Redshift is a fully managed, cluster-based data warehouse built within the AWS ecosystem. It uses a massively parallel processing (MPP) architecture and supports both provisioned clusters and a serverless deployment model. Redshift Spectrum extends querying to data stored in Amazon S3, enabling lakehouse-style analytics without duplicating storage.
Compared to Snowflake, Redshift relies more heavily on cluster configuration and node sizing. Snowflake separates storage and compute more transparently, while Redshift typically requires more active workload management and capacity planning.
Best for: Organizations standardized on AWS that require tight integration with services such as S3, AWS Glue, IAM, and SageMaker. It suits teams running complex analytical queries and blending warehouse data with data lake assets inside the AWS environment.
Pricing: Hourly node-based rates with reserved instance discounts.
Tradeoffs:
- Redshift operates exclusively within AWS, limiting multi-cloud strategies.
- Workload scaling and concurrency management may require manual tuning in provisioned clusters.
- Cost predictability can fluctuate under variable workloads without careful query optimization and resource planning.
3. Microsoft Azure Synapse Analytics
Azure Synapse Analytics is a unified analytics platform within the Microsoft Azure ecosystem. It combines enterprise data warehousing, big data processing, data integration, and pipeline orchestration in a single environment. It supports both provisioned SQL pools for predictable performance and serverless SQL pools for on-demand querying over data stored in Azure Data Lake.
Compared to Snowflake, Synapse provides tighter integration with the broader Microsoft stack, including Azure Data Factory, Power BI, and Azure Machine Learning. Snowflake typically offers simpler compute scaling and cross-cloud deployment, while Synapse emphasizes ecosystem integration and hybrid data scenarios.
Best for: Organizations standardized on Azure that require deep integration with Microsoft services and a combined SQL and big data architecture.
Pricing: Pay-per-query and reserved capacity options.
Tradeoffs:
- The extensive feature set can complicate configuration.
- Some users report concurrency limitations, especially in serverless pools, and a steeper learning curve compared to competitors.
- The learning curve is steeper compared to more specialized, single-purpose warehouse platforms.
4. Databricks Lakehouse Platform
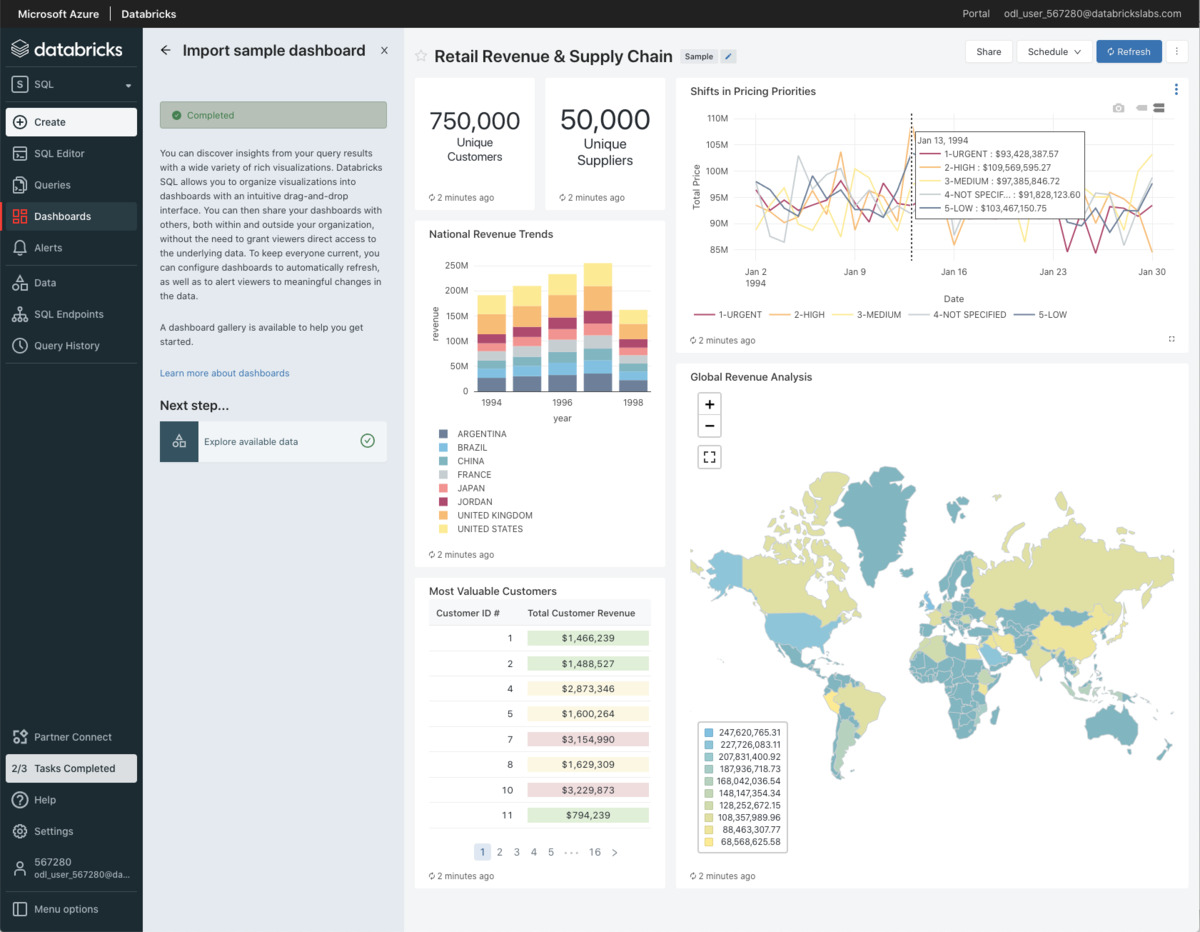
Databricks is a cloud-based lakehouse platform built on Apache Spark and Delta Lake. It unifies data engineering, streaming pipelines, machine learning, and SQL analytics in one environment. Instead of separating data lakes and warehouses, Databricks layers structured governance and ACID transactions on top of object storage.
Compared to Snowflake, Databricks is more engineering-centric. It provides deeper control over distributed processing, real-time streaming, and machine learning workflows.
Databricks is often chosen when advanced modeling and large-scale data transformation are core requirements.
Best for: Organizations with strong data engineering and data science teams that require real-time ingestion, large-scale transformation, and integrated machine learning pipelines.
Pricing: Compute consumption-based, varying with workload and collaboration features.
Tradeoffs:
- Platform complexity is higher than traditional data warehouses.
- Performance and cost optimization require Spark expertise.
- For straightforward BI and reporting workloads, operational overhead may exceed the value delivered.
5. Teradata Vantage
Teradata Vantage is an enterprise analytics platform that supports deployment across AWS, Azure, GCP, and on-prem environments. The platform integrates traditional data warehousing with advanced analytics, including in-database machine learning and workload management.
Compared to Snowflake, Teradata emphasizes deep enterprise control, hybrid deployment flexibility, and legacy system continuity. Teradata is often selected by organizations with existing Teradata estates or highly complex workload requirements.
Best for: Large enterprises running high-concurrency, complex analytical workloads that require granular workload management, hybrid cloud support, and advanced performance optimization.
Pricing: Subscription-based and consumption-based models depending on deployment architecture and compute usage. Licensing structures vary across cloud and hybrid configurations.
Tradeoffs:
- Higher operational complexity and cost compared to fully managed cloud-native warehouses.
- Implementation and tuning often require specialized expertise.
- For simpler analytics use cases, the platform may be more extensive than necessary.
6. IBM Db2 Warehouse on Cloud
IBM Db2 Warehouse is a managed cloud data warehouse built on IBM’s Db2 engine. It emphasizes in-memory processing, high-performance SQL analytics, and tight integration with IBM Cloud and IBM’s AI services such as Watson. It supports both cloud and containerized deployments, enabling hybrid and private cloud scenarios.
Db2 Warehouse offers stronger alignment with IBM enterprise ecosystems and legacy Db2 environments than Snowflake. It is often selected where integration with IBM infrastructure and governance controls are priorities.
Best for: Organizations operating in regulated industries that require strict governance, auditability, and integration with IBM’s broader analytics and AI stack.
Pricing: Subscription-based with independent scaling of compute and storage.
Tradeoffs:
- Less cloud-native elasticity compared to hyperscaler-native warehouses.
- Ecosystem integration is strongest within IBM environments, which may limit flexibility for multi-cloud or heterogeneous stacks.
7. ClickHouse Cloud
ClickHouse Cloud is a managed service built on the open-source ClickHouse columnar database. It is optimized for high-performance OLAP queries, especially on large volumes of event, log, and time-series data. Its architecture is designed for low-latency aggregations and high concurrency.
ClickHouse prioritizes real-time query speed over full-service warehouse abstraction. Snowflake offers broader enterprise features, cross-cloud maturity, and deeper ecosystem integrations. ClickHouse is often chosen when ultra-fast analytical queries on streaming or event-driven data are the primary requirement.
Best for: Teams processing high-volume event data, application telemetry, ad logs, or behavioral analytics that require sub-second query performance and flexible cloud deployment options.
Pricing: Consumption-based.
Tradeoffs:
- Smaller ecosystem and fewer native integrations compared to hyperscaler-native warehouses.
- Advanced configuration and performance tuning may require deeper engineering expertise.
- It may not provide the same level of built-in governance and workload management found in enterprise-focused platforms.
Comparison Table: Snowflake vs. Competitors
Decision Framework: How to Choose the Right Snowflake Competitor in 2026
Choosing a cloud data platform depends on your organization’s priorities. Use this framework to guide your evaluation:
Identify primary use cases:
- SQL analytics with occasional ML: BigQuery or Redshift.
- Advanced ML and data science workflows: Databricks or Azure Synapse.
- Real-time or event-driven analytics: ClickHouse Cloud.
Assess cloud ecosystem compatibility:
- AWS-centric: Redshift or Snowflake for seamless integration.
- Google Cloud users: BigQuery offers tight coupling with native services.
- Azure users: Synapse and Teradata on Azure provide native support.
Evaluate performance needs:
- High concurrency workloads: Snowflake and Teradata.
- Ultra-low latency or streaming: Databricks and ClickHouse excel.
Consider cost structure:
- Pay-as-you-go suits variable workloads.
- Reserved capacity benefits predictable demand.
Watch for hidden costs like data egress or concurrency limits.
- Review Compliance and Security:
- Verify platform certifications (HIPAA, GDPR, SOC 2).
- Assess governance and auditing capabilities.
Factor vendor ecosystem and support:
- Compatibility with existing BI, ETL, and analytics tools.
- Vendor responsiveness and community engagement.
This approach helps prioritize factors aligned with your organizational context.
Scoring Rubric: Objective Criteria for Evaluating Snowflake Alternatives
To support transparent comparison, platforms can be scored on key criteria weighted by typical enterprise priorities.
Example Scoring Table (1 = Poor, 5 = Excellent)
Scores are indicative and based on publicly available information and typical enterprise use cases.
Methodology: What We Evaluated
This analysis draws from multiple authoritative sources to ensure balanced and current insights:
- Industry reports: Gartner Magic Quadrant for Cloud Data Warehouses and Forrester Wave Data Management Solutions provide vendor positioning and market trends.
- Vendor documentation: Official pricing, product details, and whitepapers supply feature and cost information.
- User reviews: Aggregated feedback from G2 and TrustRadius highlights real-world performance and support.
- Expert insights: Contributions from senior data engineers and independent analysts contextualize platform strengths and limitations.
We focused on platforms with significant market presence, comparable technical capabilities, and active innovation in cloud data warehousing or lakehouse technologies. Given rapid cloud evolution and workload diversity, platform suitability may vary per use case.
Our scoring rubric and decision framework reflect common enterprise priorities but should be adapted to specific organizational contexts.
Migration Guide: Switching from Snowflake to Another Platform
Migrating from Snowflake requires detailed planning to minimize risks such as data loss, downtime, and performance degradation. Key steps include:
Pre-migration assessment:
- Inventory datasets, schemas, and workloads.
- Identify dependent ETL pipelines, BI tools, and integrations.
Data extraction and transformation:
- Securely extract data using bulk unloads or export tools.
- Transform data formats and schemas to suit the target platform’s requirements.
Testing and validation:
- Benchmark query performance on the new platform.
- Verify data integrity and completeness.
- Conduct user acceptance testing with stakeholders.
Rollback and contingency planning:
- Maintain parallel environments during cutover.
- Prepare rollback procedures in case of issues.
Post-migration optimization:
- Tune queries and workloads for the new platform.
- Adjust cost settings and resource allocations.
- Provide user training on new features and workflows.
Common challenges include underestimating schema conversion complexity, differences in SQL dialects, and insufficient testing. Engaging migration specialists or using dedicated migration tools can mitigate these risks.
How Third-Party Platforms Complement Snowflake and Competitors for Marketing Data Analytics
Snowflake and other cloud warehouses provide storage and compute. They do not extract, normalize, or standardize marketing data. That responsibility sits upstream.
Platforms like Improvado act as the controlled ingestion and transformation layer between marketing systems and the warehouse.
What Improvado does:
- Connects to 500+ marketing, CRM, ecommerce, and offline data sources
- Supports custom API integrations and flat file ingestion
- Automates incremental data extraction
- Standardizes cross-channel schemas and naming conventions
- Aligns metric definitions and attribution logic
- Resolves identifiers across campaigns, platforms, and accounts
- Applies governed transformations directly inside Snowflake, BigQuery, or Redshift
Instead of loading raw API dumps, it delivers structured, warehouse-native datasets ready for BI and AI workflows.
Improvado supports enterprise-grade compliance standards, including SOC 2 and GDPR. Data is delivered directly into your cloud warehouse, where you retain full ownership and control. Access permissions, role-based governance, and auditability remain within your existing security framework.
Conclusion and Next Steps
Selecting a Snowflake competitor in 2026 requires balancing performance, cost, cloud ecosystem fit, and compliance requirements. Using a structured decision framework and objective scoring rubric can clarify your options.
Careful migration planning minimizes risks when switching platforms. Third-party tools can further enhance marketing data workflows across these data clouds.
FAQ
How can I connect Tableau to Snowflake?
How do pricing models vary among Snowflake competitors?
Pricing models range from pay-per-query (BigQuery), node-based hourly rates (Redshift), reserved capacity (Snowflake), to compute consumption (Databricks). Understanding your workload patterns is key to estimating costs.
What are common pitfalls when switching from Snowflake?
Common issues include underestimating data migration complexity, incompatibility of SQL dialects, insufficient testing, and overlooking integration dependencies. Comprehensive planning and vendor support reduce these risks.
Can Snowflake competitors support multi-cloud deployments?
Snowflake supports AWS, Azure, and GCP. Databricks and Teradata also offer multi-cloud options. Redshift and BigQuery are limited to AWS and GCP respectively, while Azure Synapse operates solely on Azure.
Which Snowflake competitor is best for cost-sensitive businesses?
Google BigQuery’s pay-per-query pricing can be economical for variable workloads. Redshift and Teradata’s reserved pricing models fit predictable demand. ClickHouse Cloud offers consumption-based pricing with a focus on speed. Cost-effectiveness depends heavily on workload patterns and query complexity.
What are the main differences between Snowflake and its competitors?
Snowflake offers multi-cloud support, separation of compute and storage, and secure data sharing. Competitors like BigQuery emphasize serverless architecture and AI integration; Redshift is tightly integrated with AWS; Databricks focuses on unified data engineering and machine learning; and ClickHouse targets real-time analytics with an open-source core.
How difficult is it to migrate data from Snowflake to another platform?
Migration complexity depends on data volume, schema intricacy, and dependencies. Challenges include data format transformation, SQL dialect differences, and workload tuning. Detailed planning, testing, and rollback strategies are essential for success.
How does a platform like Improvado integrate with Snowflake and other data clouds?
Improvado connects to hundreds of marketing data sources and loads unified data into cloud warehouses such as Snowflake, BigQuery, and Redshift. It automates data pipelines, reducing manual effort and supporting compliance requirements.
.png)




.png)
