Treating data as a product means viewing it as a valuable asset that can be curated, managed, and monetized just like a physical product.
Treating data as a product ensures it is accurate, consistent, and up-to-date, leading to better decisions and ultimately driving higher revenue and ROI. Reliable, well-managed data allows marketing teams to gain deeper insights into customer behavior.
This helps optimize targeting and segmentation, and personalize marketing efforts to enhance customer engagement and conversion rates. Accurate data enables more precise tracking of campaign performance, allowing marketers to allocate budgets more efficiently and focus on high-return strategies.
Now that you know the why, let’s dive into the fundamentals, how to implement it in your company, and key considerations.What Is Data-as-a-Product (DaaP)?
Key Takeaways:
- Definition: Data as a Product (DaaP) is a comprehensive approach to managing the entire data lifecycle. It focuses on delivering value to data consumers, not just storing data.
- Tangible outputs: A data product is a curated, reliable, and accessible dataset designed for a specific purpose, like a customer 360 view or a sales forecast model.
- Cultural shift: DaaP involves moving from centralized, ticket-based data teams to decentralized, domain-oriented teams who own their data products.
- Focus on self-service: Empowering business users (data consumers) to find, understand, and use data on their own is a core objective of DaaP. This accelerates decision-making.
- Business value: Successful implementation leads to faster innovation, lower operational costs, improved data governance, and higher ROI on data investments.
What Is Data as a Product (DaaP)?
Data as a Product, or DaaP, is an organizational and technical methodology. It treats data not as a raw exhaust from business operations but as a refined, valuable product. Just like a software product, a data product has a dedicated owner. It has a roadmap for future features. It also has a clear user base, known as data consumers.
This approach fundamentally changes how data is managed. The focus shifts from data storage and pipelines to user satisfaction and business value. Every dataset is designed to be easily discoverable, understandable, trustworthy, and accessible.
This ensures data is ready for consumption and analysis right out of the box.
The Product Mindset Explained
A product mindset means thinking about the "customer" first. In the world of data, the customers are analysts, data scientists, marketers, and executives. These are your internal data consumers.
Applying a product mindset involves asking critical questions:
- Who will use this data? (The target audience)
- What problem will they solve with it? (The use case)
- How can we make it easy for them to use? (The user experience)
- How will we ensure it is accurate and up-to-date? (Quality and reliability)
- How will we measure its success? (Key performance indicators)
This is a stark contrast to traditional IT-led data projects. Those projects often focus only on extracting and storing data. The product mindset ensures the final output is fit for purpose and genuinely valuable.
Core Characteristics of a Data Product
A dataset becomes a "data product" when it embodies specific qualities. These are often referred to as the "D-A-T-A" principles:
- Discoverable: Users can easily find the data product through a central catalog. Metadata is clear and searchable.
- Addressable: Each data product has a unique, permanent, and easy-to-use access point, like an API or a table in a data warehouse.
- Trustworthy: Data quality is paramount. Data products have clear ownership, lineage, and service-level objectives (SLOs) for freshness and accuracy.
- Accessible and self-describing: Users can understand and use the data without needing to consult the original creators. Documentation is built-in and comprehensive.
The Role of the Data Product Manager
A key role emerges in the DaaP model: the Data Product Manager. This person is responsible for the entire lifecycle of a data product.
They bridge the gap between the technical data producers and the business data consumers. Their job is to understand user needs, define the product vision, prioritize features, and ultimately ensure the data product delivers measurable business value.
Data Product vs. Data-as-a-Product: Understanding the Critical Difference
Diving deeper into the topic, we need to distinguish between two related but distinct concepts: data product and data-as-a-product. One is a tangible output; the other is the overarching strategy.
What Is a Data Product?
A data product is a specific, reusable data asset. It is built and maintained to be consumed by others. Think of it as a package. It contains not just the data, but also the code, metadata, and infrastructure needed to deliver it. A high-quality data product is reliable, well-documented, and easy to use.
Examples include:
- A cleaned and aggregated table of customer transactions.
- A machine learning model that predicts customer churn.
- An API that provides real-time marketing campaign performance data.
- A set of certified KPI dashboards for executive reporting.
What is the Data-as-a-Product Approach?
Data-as-a-product (DaaP) is the strategic framework and cultural mindset.
It is the philosophy of treating data with the same discipline as software development. DaaP is the "how" – the set of principles, practices, and organizational structures you put in place to create and manage high-quality data products at scale.
Comparison Table: Data Product vs. DaaP Approach
| Aspect | Data Product | Data-as-a-Product (DaaP) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A tangible, reusable data asset (the "what"). | A strategic methodology and mindset (the "how"). |
| Scope | Specific and bounded. Solves a particular need. | Holistic and organizational. Covers the entire data lifecycle. |
| Goal | To provide a reliable, ready-to-use dataset or insight. | To create a scalable system for producing valuable data products. |
| Nature | An output, an asset. | A process, a strategy, a cultural shift. |
| Ownership | Owned by a data product manager or domain team. | Championed by leadership; adopted across the organization. |
| Example | "Q3 Customer Churn Prediction Model API" | "Our company-wide initiative to treat all key datasets as products." |
The Core Principles of the Data-as-a-Product Strategy
A successful DaaP strategy is built on a foundation of key principles. These principles ensure data products are not just created, but are valuable, trusted, and widely used across the organization. They form the pillars of a robust data culture.
Discoverability: Making Data Easy to Find
Data is useless if no one can find it.
Discoverability means data consumers can easily search for and locate relevant data products. This is typically achieved through a centralized data catalog. The catalog acts like a library card system for all data assets, with rich metadata, descriptions, and user ratings.
Addressability: Providing a Stable Access Point
Once found, data must be easily accessible.
Each data product should have a stable, unique, and programmatically accessible address. This could be a specific table name in a data warehouse, a well-defined API endpoint, or a stream topic. This prevents the chaos of users accessing inconsistent, ad-hoc data dumps.
Trustworthiness & Quality: Ensuring Reliable Data Assets
Trust is the currency of data. A data product must be reliable.
This involves clear service-level agreements (SLAs) for data freshness, uptime, and accuracy. Data lineage should be transparent, showing exactly where the data came from and how it was transformed.
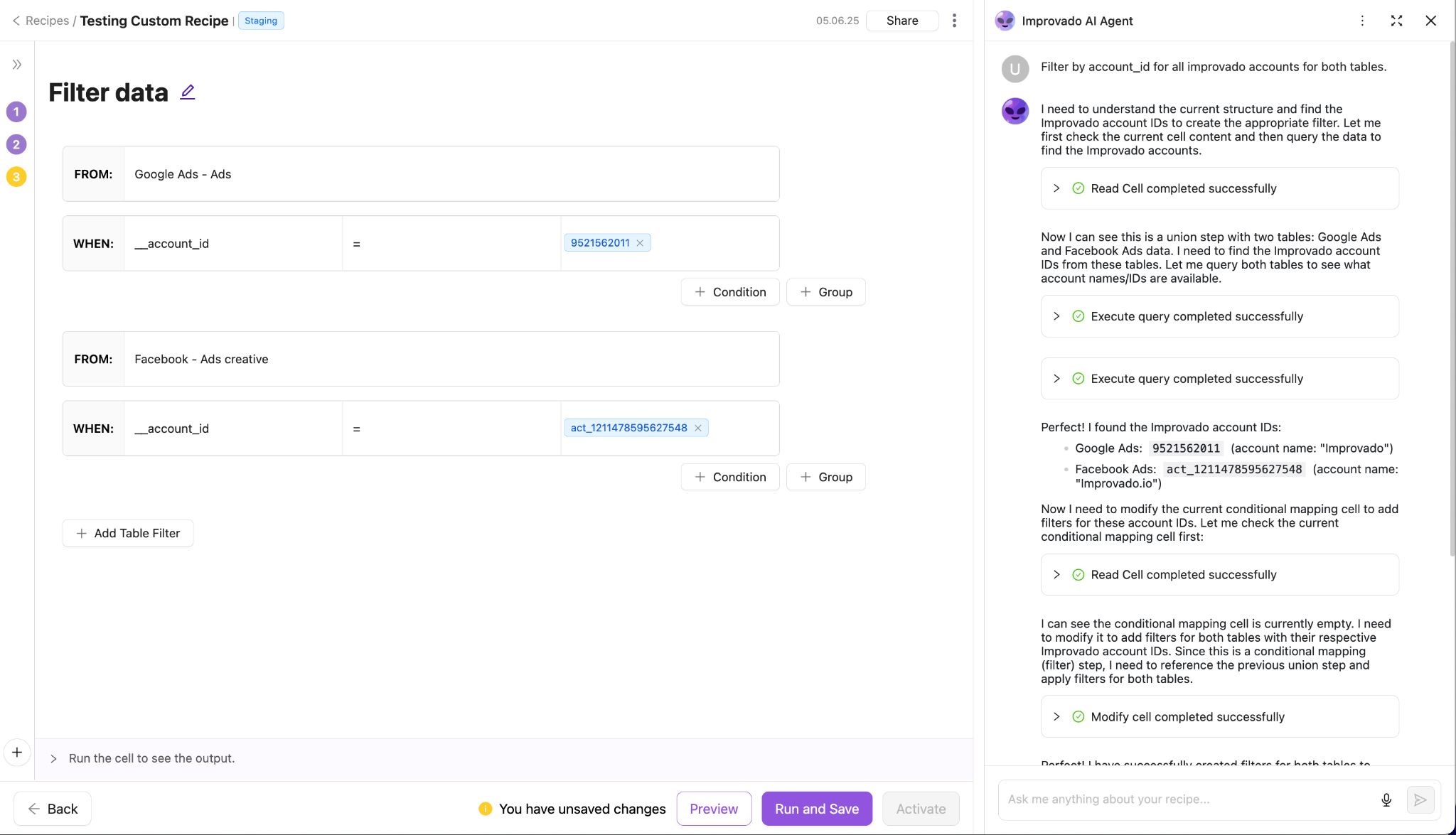
One way to ensure this consistency at scale is to use platforms like Improvado, which automate the entire data management cycle and enforce quality checks at every stage — from extraction to transformation to delivery.
Improvado centralizes all marketing and revenue data into a governed, fully standardized dataset, eliminating manual errors and inconsistencies. By automating validation and normalization across hundreds of sources, it provides a predictable, trustworthy foundation for every downstream data product.
Self-Service Accessibility: Empowering Data Consumers
The goal is to eliminate data bottlenecks. Data consumers should be able to access and use data products on their own. This requires intuitive tools that make insights available without relying on technical teams.

Improvado’s AI Agent is a strong example of this principle in action — giving business and even non-technical users instant access to governed data through natural-language questions. Instead of writing SQL or navigating complex dashboards, teams can simply ask and receive clear, analysis-ready answers in seconds, accelerating decision-making across the organization.
Interoperability: Standardizing for Seamless Integration
Data products do not exist in a vacuum. They need to work together. Interoperability ensures that data products use standardized formats, data types, and naming conventions. This makes it easy for data consumers to join and analyze data from multiple products, creating a more holistic view of the business.
Platforms like Improvado make this standardisation practical at scale. It automates the alignment of data from 500+ sources, applies consistent taxonomies and business logic, and enforces audit trails and lineage tracking.
Through its AI-powered transformation workflows, teams can merge and reconcile disparate datasets into a unified, analytics-ready structure, enabling seamless cross-platform integration without manual glue code.
Security & Governance: Protecting Your Data Assets
With great accessibility comes great responsibility. Data products must adhere to strict security and governance policies. This includes robust access control mechanisms to ensure only authorized users can view or modify data. It also means complying with regulations like GDPR and CCPA, with privacy features built directly into the product design.
Why Adopt DaaP? Key Business Benefits and Outcomes
Adopting data as a product model is a strategic business decision that delivers tangible returns. By shifting from a cost-center view of data to a value-creation engine, companies unlock significant competitive advantages.
Accelerate Innovation and Time-to-Market
When high-quality data is readily available, teams can build and experiment faster. Data scientists spend less time on data wrangling and more time on model building. Product teams can quickly analyze user behavior to inform new features. The speed of insight directly translates to the speed of innovation.
Improve Data-Driven Decision Making
Trustworthy and accessible data leads to better, faster decisions at all levels of the organization. From executive strategy to marketing campaign optimization, decisions are based on reliable evidence, not guesswork. This improves outcomes and reduces risk.
Reduce Operational Costs and Complexity
DaaP reduces redundant work. Instead of multiple teams cleaning the same raw data sources for their own projects, one domain team creates a single, certified data product for everyone to use. This eliminates duplicate data pipelines and storage, saving significant time and money.
Enhance Data Governance and Compliance
By design, DaaP embeds governance directly into data products. Ownership is clear. Access controls are granular. Data lineage is tracked automatically. This makes it far easier to manage compliance with privacy regulations and internal security policies. It moves governance from a reactive checklist to a proactive, automated process.
Foster a True Data-Driven Culture
Perhaps the most significant benefit is cultural. When business users are empowered with self-service data tools they trust, they begin to see data as an integral part of their job.
DaaP breaks down the walls between "data people" and "business people," creating a unified organization that speaks the language of data and is committed to improving their marketing ROI and other key metrics.
Real-World Data Product Examples Across Industries
The concept of a data product can seem abstract. Let's make it concrete with examples from different business functions. These show how raw data is transformed into a valuable, reusable asset.
Marketing: Unified Customer 360 View
- Raw data: CRM contacts, website clicks, email opens, ad platform impressions, support tickets.
- Data product: A single, unified table named `dim_customer_360`. Each row represents a unique customer. It includes attributes like lifetime value, last engagement date, preferred marketing channel, and recent support interactions.
- Consumers: Marketing teams use it for audience segmentation. Personalization engines use it to tailor website content. Support teams use it to understand customer history.
Sales: Lead Scoring and Propensity Models
- Raw data: Website form submissions, product trial usage data, company firmographic data from third-party sources.
- Data product: An API endpoint `api/lead_score`. Given a new lead's information, it returns a score from 1-100 indicating their likelihood to purchase.
- Consumers: The CRM system calls this API to prioritize leads for the sales team. Marketing automation tools use it to enroll high-scoring leads into targeted nurture campaigns.
Finance: Real-Time Fraud Detection Feeds
- Raw data: Transaction streams from payment processors, user login events, device information.
- Data product: A real-time data stream named `transactions_with_fraud_risk`. It enriches each incoming transaction with a risk score and flags suspicious patterns.
- Consumers: A fraud detection application subscribes to this stream to block high-risk transactions automatically. Analysts use a dashboard connected to the stream to investigate flagged events.
Operations: Supply Chain Optimization Datasets
- Raw data: Inventory levels from warehouses, shipping logs from carriers, supplier delivery times, sales forecasts.
- Data product: A set of curated tables in a data warehouse, including `fct_daily_inventory` and `dim_supplier_performance`. These tables are refreshed daily.
- Consumers: Supply chain analysts query these tables to optimize inventory levels and reduce shipping costs. A demand planning tool ingests this data to improve the accuracy of its forecasts.
How to Implement Data as a Product: A Step-by-Step Framework
Transitioning to a DaaP model is a journey. It requires careful planning, executive support, and an iterative approach. Rushing the process can lead to confusion and resistance.
Follow these steps to build a solid foundation for success.
Step 1: Secure Executive Buy-In and Define Business Goals
DaaP is a strategic change, not just a tech project. You need sponsorship from senior leadership.
Frame the initiative in business terms. Explain how it will solve key pain points, like slow reporting or inconsistent metrics. Align the initial goals with a major company objective, such as "improving customer retention by 10%."
Step 2: Identify High-Value Use Cases and Data Consumers
Don't try to boil the ocean. Start small. Work with business stakeholders to identify one or two critical business problems that can be solved with a better data product. Find a "customer" group that is enthusiastic and willing to partner with you.
A great first project often involves unifying data for a crucial business function, like marketing performance analysis across various marketing analytics platforms.
Step 3: Establish Your First Data Product Team
Assemble a cross-functional team to build your first data product. This team should be "domain-oriented," meaning they have deep expertise in the business area (e.g., marketing, finance). The team typically includes:
- Data Product Manager: The owner who defines the vision and roadmap.
- Data Engineers: They build the pipelines and infrastructure.
- Analytics Engineer / Analyst: They transform the raw data and model it for usability.
- Subject Matter Expert: A representative from the business who provides context.
Step 4: Design and Build Your Minimum Viable Product (MVP)
Apply agile principles. Focus on delivering a small, valuable piece of the data product quickly. This is your Minimum Viable (Data) Product. For a Customer 360 product, the MVP might just combine data from the CRM and website. The goal is to get feedback from your initial data consumers early and often.
Step 5: Develop the Underlying Technical Infrastructure
Your team will need the right tools. This includes a modern data stack. You'll need platforms for data ingestion, storage (like a cloud data warehouse), transformation, and discovery.
Focus on self-service and automation to enable teams to work independently. This often involves creating a robust marketing data pipeline to handle the flow of information.
Step 6: Iterate, Measure, and Scale
Once your MVP is live, gather usage metrics and feedback. What do users like? What is confusing? Use this input to iterate on the data product, adding new data sources and features.
At the same time, showcase the success of your first product to the rest of the organization. This builds momentum and encourages other domains to adopt the DaaP model.
DaaP and the Data Mesh: A Symbiotic Relationship
You cannot discuss Data as a Product without mentioning the Data Mesh. The two concepts are deeply intertwined. Data Mesh is an architectural paradigm, and DaaP is one of its core, foundational principles. Understanding how they fit together is key to scaling your data strategy.
What Is a Data Mesh? A Quick Overview
A data mesh is a type of data architecture. It challenges the traditional, centralized data warehouse or data lake model. Instead of one monolithic data platform managed by a central team, a Data Mesh advocates for a decentralized approach. It proposes distributing data ownership to the business domains that know the data best.
How DaaP is a Cornerstone of the Data Mesh Architecture
For a decentralized Data Mesh to work, you need a way to ensure quality and interoperability. This is where Data as a Product comes in.
Data Mesh architecture is built on four key principles:
- Domain-oriented ownership: Business domains (e.g., Marketing, Sales) own their data end-to-end.
- Data as a product: Domains must serve their data as high-quality products to the rest of the organization.
- Self-serve data platform: A central platform team provides the tools for domains to build and share their data products easily.
- Federated computational governance: A set of global rules and standards ensures all data products work together securely and effectively.
As you can see, DaaP is not just related to Data Mesh; it is the principle that makes the whole architecture possible. Without it, decentralization would simply lead to more data silos and chaos.
Common Challenges in DaaP Implementation and How to Overcome Them
The path to implementing DaaP is filled with potential obstacles. Being aware of these common challenges can help you plan ahead and navigate them effectively. Success requires addressing both cultural and technical hurdles.
Challenge: Shifting Organizational Culture
The biggest challenge is often cultural. Moving from a centralized, service-oriented data team to a decentralized, product-oriented model is a major change. People may resist new responsibilities or ways of working.
Solution: Start with strong executive sponsorship. Communicate the "why" behind the change relentlessly. Showcase early wins from the first data product team to build excitement and prove the value of the new model.
Challenge: Lack of Technical Skills and Roles
The DaaP model requires new roles like the Data Product Manager and skills in data modeling and software engineering within business domains. These can be hard to find or develop internally.
Solution: Invest in training and upskilling your existing teams. Create clear career paths for these new data roles. For the initial teams, embed experts from a central team to help bootstrap their capabilities and establish best practices.
Challenge: Integrating Disparate Data Sources
Creating a valuable data product often means combining data from dozens of different systems. This technical complexity can be overwhelming, especially for new domain teams. The use of powerful data integration tools becomes critical here.
Solution: Use a no-code data pipeline like Improvado that automates the entire ingestion and transformation workflow. Improvado provides 500+ pre-built data connectors, no-code transformation capabilities, and pre-built data models that standardize metrics across platforms.
Its AI Agent can even support transformation tasks through natural-language instructions, eliminating the need for SQL or engineering resources. With everything from extraction to modeling handled in a unified, no-code environment, teams can focus on business logic rather than pipeline plumbing.
Challenge: Measuring the ROI of Data Products
It can be difficult to draw a direct line from a data product to a revenue number. This can make it hard to justify continued investment in the DaaP strategy.
Solution: Define success metrics from the beginning. These can include operational metrics (for example, reduction in ad-hoc data requests) and adoption metrics (for example, number of users of the data product). Work with data consumers to document how the product helped them achieve a business outcome, such as launching a campaign 50% faster.
Measuring Success: KPIs for Your Data Products
"If you can't measure it, you can't improve it." This is especially true for data products. To justify investment and guide your roadmap, you must track Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) that reflect the health, adoption, and impact of your products.
Adoption and Engagement Metrics
These metrics tell you if people are actually using your data product. They are the first signal of value.
- Number of unique users: How many individuals or services have queried the data product in the last month?
- Query volume: How many queries are being run against the product?
- Top consumers: Which departments or downstream systems are your power users?
- User growth rate: Is adoption increasing over time?
Quality and Reliability Metrics
These KPIs measure the trustworthiness of your data product. Low scores here will destroy user adoption, no matter how useful the data is.
- Data freshness / latency: How up-to-date is the data? Measure the time between an event happening and it appearing in the data product.
- Data uptime: What percentage of the time is the data product available and meeting its SLAs?
- Data quality score: What percentage of records are complete, valid, and accurate, based on automated data tests?
Business Impact Metrics
This is the ultimate measure of success. These metrics connect the data product to tangible business outcomes. They can be harder to measure but are the most powerful.
- Time saved: How many hours of manual reporting or data preparation has the product eliminated? This directly relates to the value of reporting automation.
- Decisions influenced: Survey your users. Ask them to list specific business decisions that were made using the data product.
- Contribution to business KPIs: Can you correlate the use of a data product with improvements in a core business metric, like customer conversion rates or operational efficiency?
The Future of Data: How DaaP is Shaping Business Intelligence
The Data as a Product movement is not just a trend; it's a fundamental shift that is redefining the future of data analytics and business intelligence. As this approach matures, it will unlock even more powerful capabilities for organizations.
The Rise of AI and ML-Powered Data Products
As organizations build a strong foundation of trustworthy data products, the next frontier is embedding intelligence directly into them. Instead of just providing historical data, future data products will include predictive forecasts, anomaly detection flags, and prescriptive recommendations as new columns in the dataset. This makes advanced analytics accessible to a much broader audience.
Monetizing Data as an External Product
Once a company masters creating internal data products, it can look outwards. Many companies have unique datasets that could be valuable to partners, suppliers, or even new customers.
The DaaP model provides the perfect framework for packaging, securing, and monetizing these data assets, creating entirely new revenue streams.
The Evolution of Self-Service Analytics
DaaP is the engine for the next generation of self-service BI. When business users have a catalog of reliable data products to choose from, they can build their own reports and analyses with confidence. This leads to a future where data exploration is as common as using a spreadsheet, truly fulfilling the promise of a data-driven organization.
Conclusion
The journey from data chaos to a thriving ecosystem of data products is transformative. Data as a product is more than a new architecture or a set of tools. It is a strategic commitment to treating data as a first-class corporate asset. It demands a new culture of ownership, collaboration, and relentless focus on the consumer.
By adopting the principles of discoverability, trustworthiness, and self-service, you can break down data silos and eliminate bottlenecks. By empowering domain teams to own and build their own data products, you can scale your data capabilities and accelerate innovation.
The benefits are clear: faster decisions, lower costs, stronger governance, and a significant competitive edge in an increasingly data-driven world. The time to start building your first data product is now.
.png)







.png)
