Effective dashboard design is a game-changer. It holds the key to unlocking valuable insights, driving informed decision-making, and staying ahead of the competition.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the ins and outs of dashboard design, from the importance of dashboard design to practical steps, best practices, and inspiring examples. This article aims to equip you with the knowledge and tools needed to create insightful and user-friendly dashboards that fuel data-driven success.
Why Dashboard Design Matters
Dashboard design is more than just aesthetics, it is a strategic asset for businesses. Well-designed dashboards enable marketers, analysts, and decision-makers to cut through the clutter of data overload and focus on the insights that matter most. By distilling complex information into visually digestible formats, dashboards promote efficient data comprehension, empowering stakeholders to make swift and informed decisions.
Additionally, intuitive dashboard design fosters collaboration, providing a centralized platform for teams to align efforts and gain a unified view of business performance. Team engagement and satisfaction are also enhanced, as intuitive dashboards encourage continuous exploration and discovery.
Key Concepts of Dashboard Design
Designing an effective dashboard is more than the visual display of data. The following key concepts play a pivotal role in creating a user-centric, insightful dashboard that assists in achieving strategic objectives.
Information Hierarchy
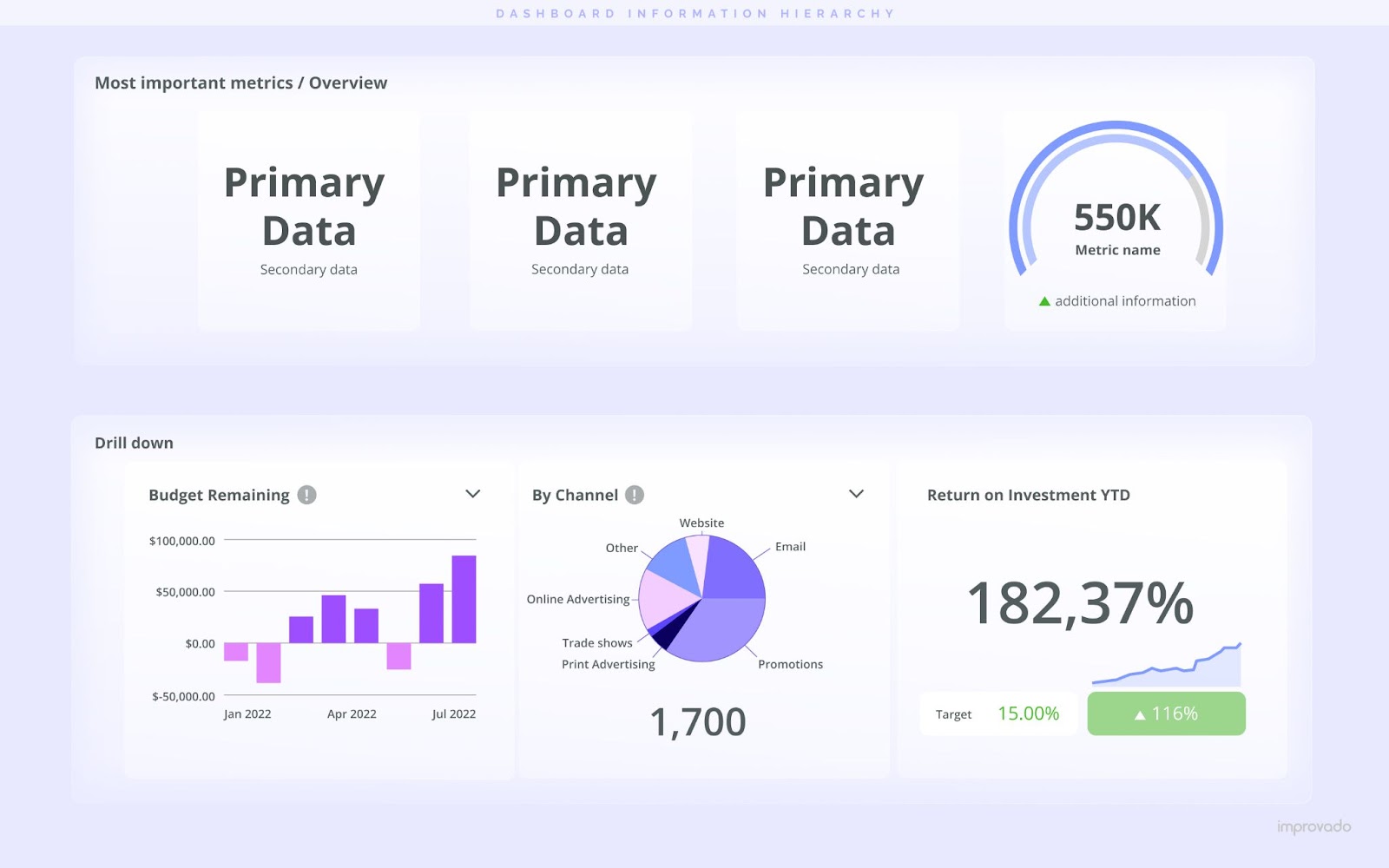
A successful dashboard follows a clear information hierarchy, highlighting critical data prominently while providing supplementary details as needed. This makes it easier for users to absorb key insights and make informed decisions.
Key elements to consider when building an information hierarchy:
- Prioritize Information: Identify the most critical data or metrics that the users need to see first or most often. Place this information prominently on the dashboard. This could mean positioning it at the top, in the center, or using design cues like size and color to draw attention.
- Logical Grouping: Group related information together to create logical sections or clusters. This approach, often termed 'chunking', can make the dashboard more organized and intuitive. Users can easily locate and analyze related data, which can enhance understanding and decision-making.
- Sequential Ordering: Arrange data in a sequence that reflects its priority. This could be from left to right, top to bottom, or in a Z or F pattern, which follows the natural reading paths of the human eye. This guides the users' attention in a specific flow, leading them to interpret the data in the intended order.
- Visual Weight: Employ visual weight to distinguish between primary, secondary, and tertiary data. This can be achieved through various design elements like color, size, contrast, or whitespace. For example, larger or darker elements are perceived as more important, and sufficient whitespace can help important elements stand out.
- Clear Labels and Annotations: Clearly label each section and data point to provide context and improve readability. Annotations can provide additional insights or draw attention to specific points within the data.
- Consistent Design Language: Consistent use of colors, fonts, and icons can serve as a guide through the hierarchy. This helps users intuitively understand the level of importance associated with each data point.
Data Visualization Techniques
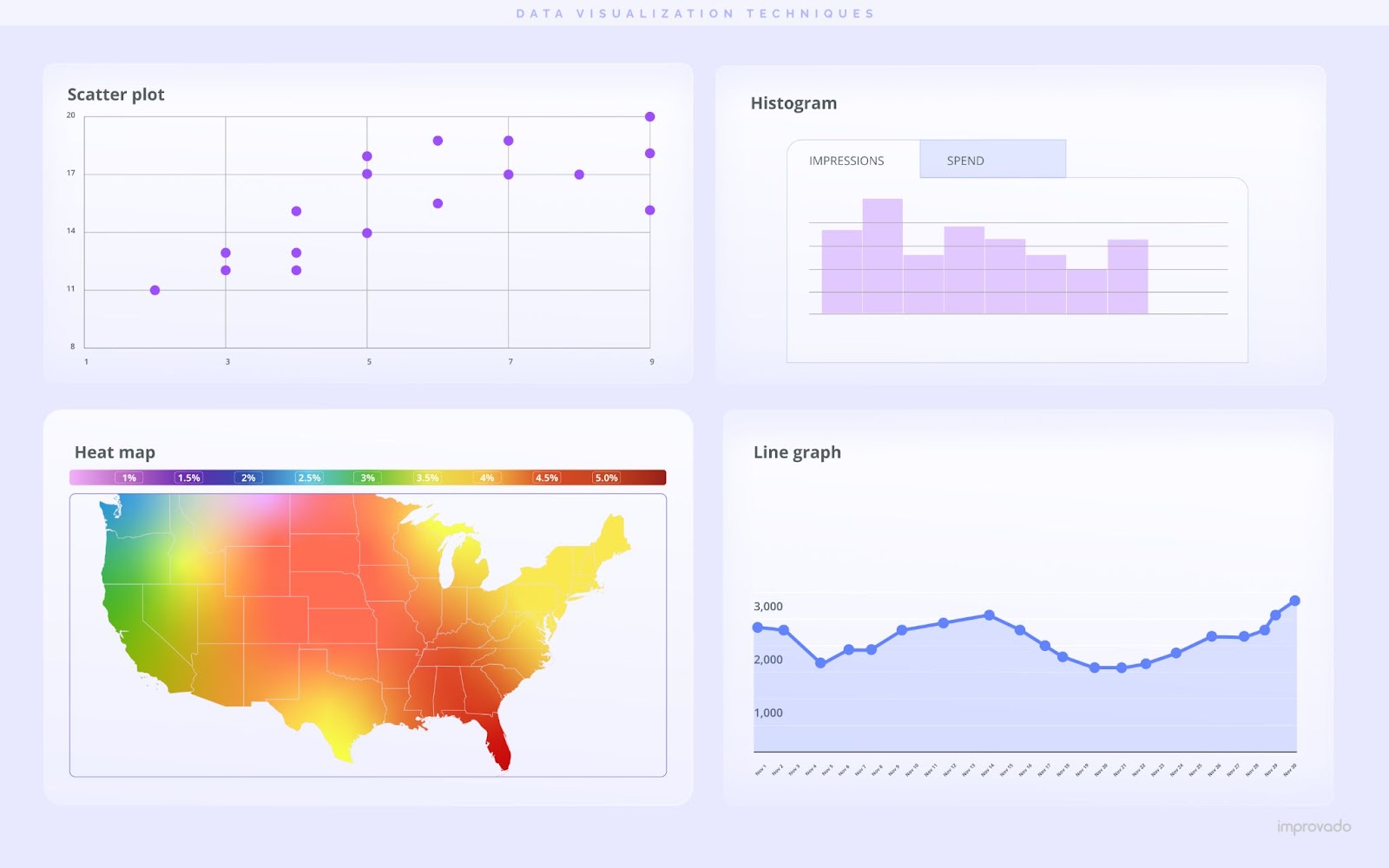
The core of any dashboard is its ability to visually represent data. Understanding and using various techniques such as bar graphs, line charts, pie charts, and heat maps is vital.
The selection should depend on the type of data being displayed and the insights intended to be gleaned:
- Bar and Column Charts: These are ideal for comparing discrete categories or groups. Bar charts are often used to represent categorical data. They work well for showing differences between categories or tracking changes over a period of time.
- Pie Charts: Pie charts are used to represent proportions or percentages of a whole, making them suitable for displaying nominal or ordinal categories. However, pie charts can become difficult to interpret with many categories, so it's best to use them with fewer data points.
- Line Graphs: Line graphs excel at displaying trends over time (time-series data) or continuous data. They are particularly useful for demonstrating rise and fall patterns, making them ideal for tracking metrics like sales revenue over a year or website traffic.
- Scatter Plots: Scatter plots are useful for showing the relationship between two quantitative variables. They are often used for correlation analysis or for identifying trends, clusters, or outliers within the data.
- Heat Maps: Heat maps are great for visualizing large amounts of data by representing values as colors. They are often used for correlation matrices or to demonstrate user behavior on a website or app.
- Histograms: Histograms are used to represent the distribution of a single variable and are particularly helpful for identifying patterns like normal or skewed distributions.
- Box Plots: Box plots are a great way to visualize summary statistics (minimum, first quartile, median, third quartile, and maximum) of a dataset, including outliers. They are best suited for comparing distributions between different categories.
- Area Charts: Similar to line graphs, area charts are used to represent the development of quantitative values over an interval or time period. They are especially useful when comparing two or more categories.
Interactive Elements
Interactivity is a vital aspect of dashboard design, enabling users to delve deeper into specific data subsets, apply filters, and explore different scenarios. Interactive elements, including filters, drop-down menus, and drill-through functionality, empower users to customize their data exploration experience and make dashboards adaptable to individual needs.
Types of Dashboard Designs
The type of dashboard one opts for largely depends on the user's role, the intended use, and the nature of the data. Each dashboard type focuses on different aspects of data representation and caters to different user requirements. Here's a closer look at the primary types of dashboard designs.
Operational Dashboards
Operational dashboards provide real-time insights into daily operations, allowing users to monitor and respond swiftly to any issues or changes. These dashboards are best suited for roles that require constant vigilance over key performance indicators (KPIs), such as customer support or manufacturing.
Strategic Dashboards
Strategic dashboards offer a higher-level view of the organization's performance over time, tracking strategic objectives and goals. A marketing department, for instance, might use a strategic dashboard to monitor long-term trends like customer acquisition costs, conversion rates, and customer lifetime value. Such dashboards are most valuable to mid-level managers, project leaders, and team heads for long-term planning and tracking.
Analytical Dashboards
Analytical dashboards enable users to explore trends, correlations, and patterns in the data. A finance department could use an analytical dashboard to delve into revenue and expenditure data, evaluate trends across different quarters or analyze cost breakdowns. Roles that make the most use of analytical dashboards typically include data analysts, financial analysts, and market researchers.
Executive Dashboards
Executive dashboards provide a top-level view of the organization's performance, focusing on critical metrics that align with strategic objectives. For example, a CEO might use an executive dashboard to monitor key performance indicators like total revenue, net profit margin, market share, and customer satisfaction. These dashboards are primarily designed for top-level executives, including CEOs, CTOs, CFOs, and other C-suite roles.
How to Design a Dashboard
The design of a dashboard plays a significant role in how effectively it communicates information. Here are practical steps to create a user-friendly and insightful dashboard.
Define Your Objectives
Determine what the dashboard aims to achieve. This could range from monitoring real-time data, tracking progress toward goals, or analyzing trends. The objective will guide the selection of relevant data and appropriate visualizations.
Understand Your Audience
Know who will be using the dashboard. Different roles require different data. An executive might need high-level summary metrics, while an analyst might need detailed, granular data. Tailoring the dashboard to the needs of the audience enhances its utility and relevance.
Select Relevant Metrics
Choose the metrics that best align with the dashboard's purpose and the audience's needs. Avoid including every possible metric; focus on those that provide valuable insights and drive informed decision-making.
Choose Appropriate Visualizations
Match data with the right visualization techniques. Bar charts, line graphs, heat maps, and others each have their strengths, depending on the type of data and the insights to be communicated.
Organize Information Effectively
Apply principles of information hierarchy to arrange data and visualizations on the dashboard. Prioritize key information, group-related data, and use a logical sequence to enhance readability and understanding.
Incorporate Interactivity
If possible, add interactive elements such as filters, drop-down lists, or sliders. These allow users to explore data in more depth and customize the view to their specific needs.
Optimize for Clarity and Simplicity
Aim for a clean, clutter-free design. Use clear labels, maintain consistency in design elements, and ensure each visualization is simple to understand at a glance.
Test and Refine
Once the initial design is complete, test the dashboard with a group of users. Gather feedback on its functionality, ease of use, and relevance of the data presented. Use this feedback to refine and improve the design.
Keep it Updated
Ensure that the dashboard stays relevant by regularly updating it with new data. Also, review and update the dashboard design periodically to align with changing user needs and business goals.
Additional Dashboard Design Tips
Consider these tips to take your dashboard design to the next level:
- Use White Space Effectively: Utilize white space strategically to create a clean and uncluttered layout. Well-balanced white space guides users' attention to the most important elements and improves readability.
- Prioritize Mobile Responsiveness: Optimize your dashboard for mobile devices, ensuring a seamless user experience across different screen sizes. Mobile responsiveness enhances accessibility and allows users to access data on the go.
- Leverage Modern Design Trends: Stay abreast of modern dashboard design trends to create visually captivating dashboards. Incorporate sleek typography, subtle gradients, and minimalist aesthetics to give your dashboard a contemporary and polished look.
Dashboard Design Examples
To inspire your own dashboard designs, consider these real-world examples.
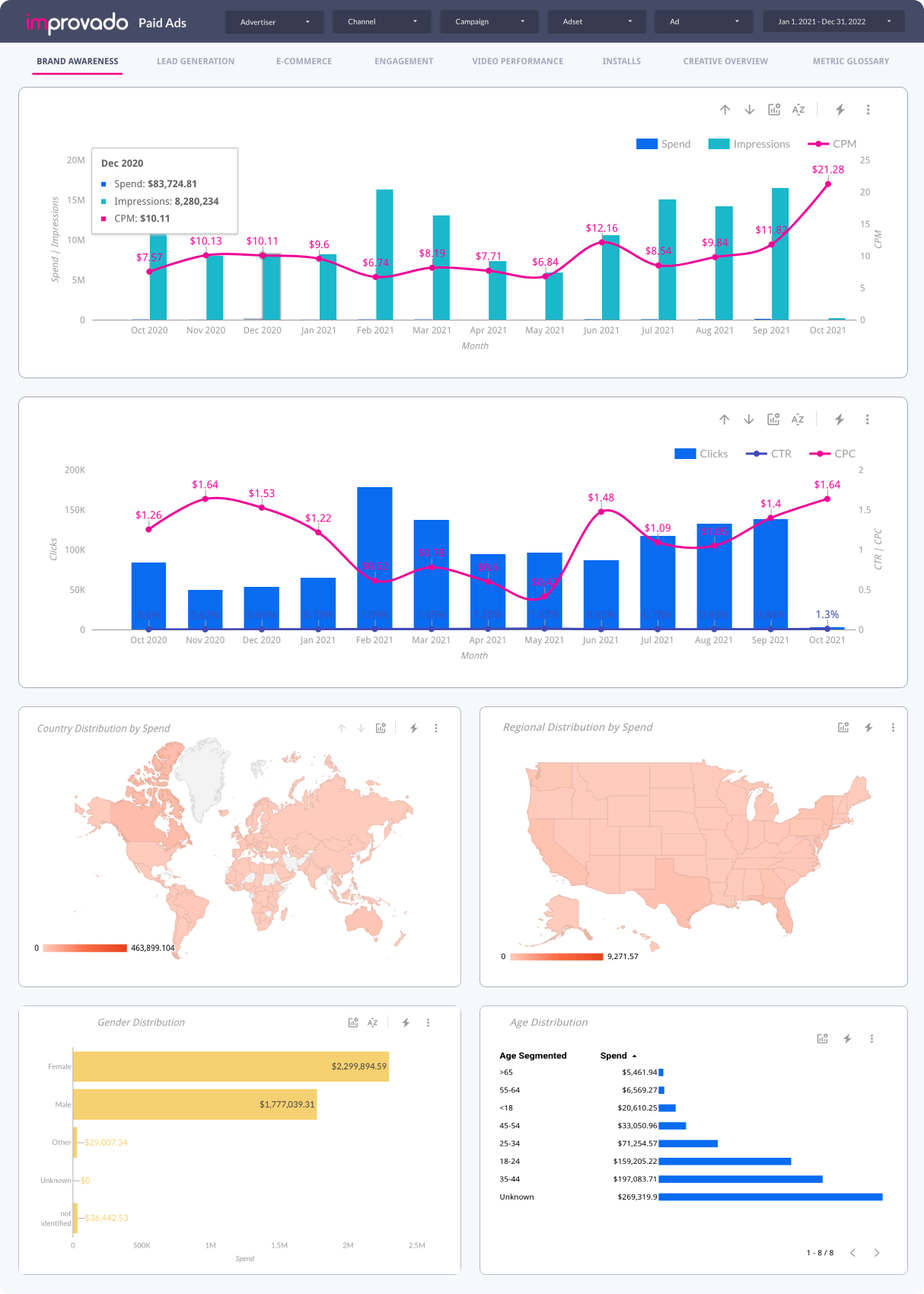
KPI Dashboard for Paid Ads Campaigns
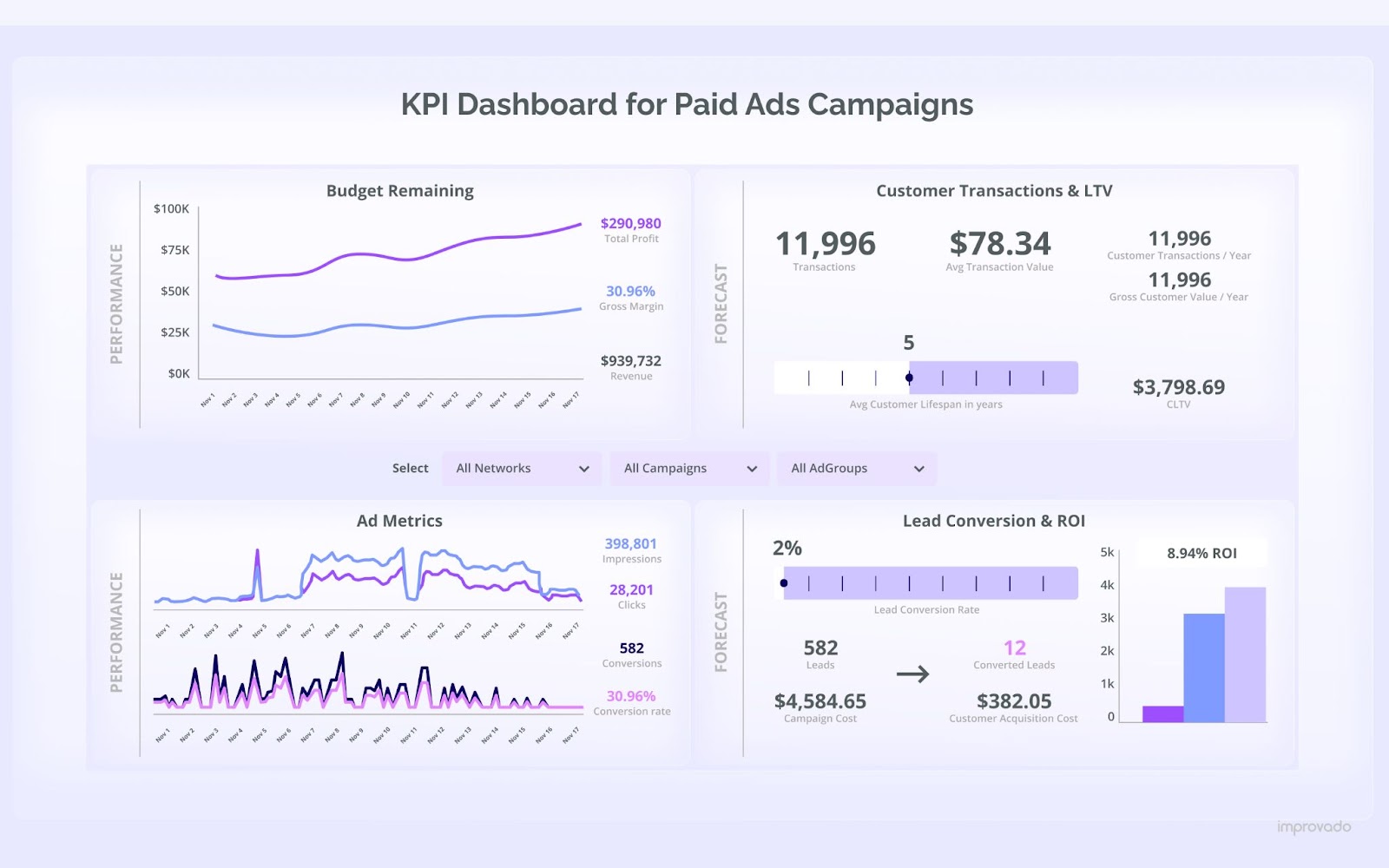
A KPI Dashboard for Paid Ads Campaigns consolidates key metrics like Cost per Click (CPC), Click Through Rate (CTR), Conversion Rate, and Return on Ad Spend (ROAS) from various ad platforms. Trend analysis charts reveal patterns over time, aiding in strategic planning. Interactive elements enable filtering by date, platform, or campaign type for detailed analysis. The dashboard serves digital marketers and executives, assisting them in optimizing their ad strategies for a higher return on investment.
Web Analytics Dashboard
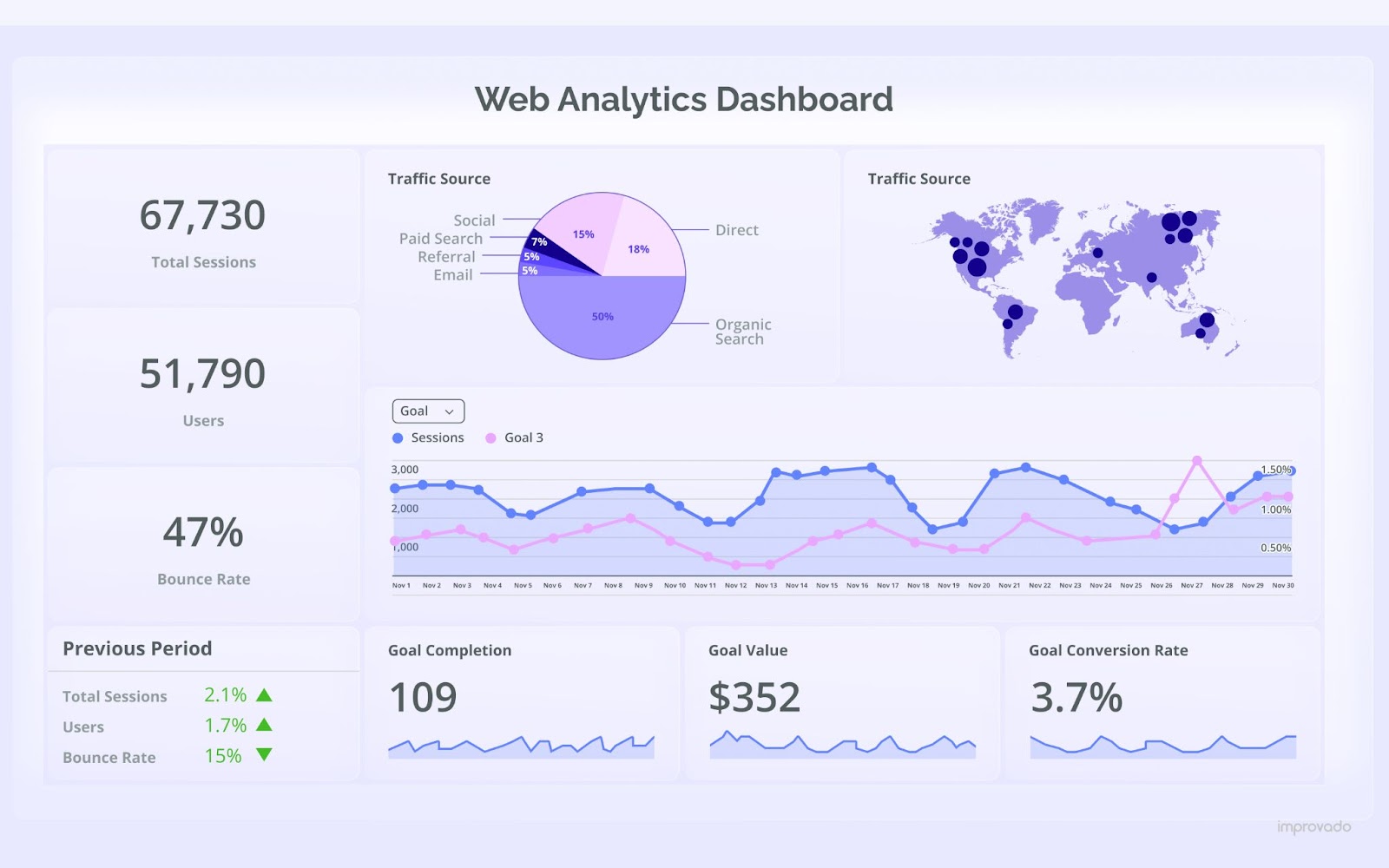
A Web Analytics Dashboard offers a centralized overview of website performance metrics, providing valuable insights for marketers, SEO specialists, and website managers. Key metrics like page views, bounce rate, session duration, traffic sources, and conversion rates are prominently displayed. The integration of interactive elements allows for customization, offering more granular insights by time period, user demographics, or specific pages. This tool aids in refining website strategy, enhancing user experience, and improving overall website performance.
Empower Your Marketing Team with Custom-Tailored Dashboards
Custom dashboard design is critical as it ensures alignment with the specific needs and goals of the user. Rather than adopting a one-size-fits-all approach, custom dashboards are tailored to display the most relevant data, in the most useful formats, for the intended audience. This enhances data interpretation, fosters informed decision-making, and ultimately increases efficiency and productivity.
Improvado is an automated reporting tool and marketing analytics platform. This end-to-end solution assists at every stage of the marketing reporting cycle, from data collection to report customization. The platform comes with over 500 data sources and integrates with Power BI, Redash, Tableau, and many other data visualization and business intelligence (BI) tools.
.png)





.png)