Organizations generate more data than ever, yet decision-making remains slow and fragmented. Teams operate across disconnected systems, inconsistent metrics, and delayed reporting cycles. Without a structured analytics framework, data becomes noise instead of insight. The challenge in 2026 is not collecting data. It is turning it into reliable, operational intelligence.
This guide breaks down business analytics in practical terms. It explains core concepts, architectures, tools, and use cases across reporting, diagnostics, forecasting, and AI-driven analysis. You’ll gain a clear framework for building analytics capabilities that support measurable, data-backed decisions.
Key Takeaways:
- Definition: BA is the process of using data, statistical methods, and technology to explore business performance, gain insights, and drive planning.
- Core types: Analytics falls into four categories–descriptive (what happened), diagnostic (why it happened), predictive (what will happen), and prescriptive (what to do).
- Process: Effective BA follows a clear, multi-step process from problem identification and data collection to insight generation and implementation.
- Importance: Mastering BA allows organizations to optimize operations, deepen customer understanding, and build a significant competitive advantage.
What Is Business Analytics?
Business analytics (BA) is a disciplined approach to making better decisions. At its core, BA is a field that combines data analysis, business intelligence, and computer programming to answer critical business questions.
Think of business analytics as a detective for your company. It sifts through clues (data) to uncover what happened, why it happened, and what is likely to happen next. It provides the evidence needed to make confident choices. Instead of guessing which marketing channel works best, business analytics shows you the data. Instead of hoping a new product will succeed, analytics helps you forecast demand.
The Core Components: Data, Statistics, and Business Acumen
Successful business analytics rests on three pillars:
- Data: This is the raw material. It can be structured (like sales figures in a spreadsheet) or unstructured (like customer reviews on social media). The quality and accessibility of data are paramount.
- Statistical methods: These are the techniques used to analyze the data. They range from simple averages to complex machine learning algorithms. These methods uncover patterns, correlations, and trends.
- Business acumen: This is the critical human element. It’s the ability to understand the business context, ask the right questions, and interpret the analytical results to create a strategic plan.
Why Business Analytics Is Crucial for Modern Success
In a competitive market, the companies that understand their data win. Business analytics provides the clarity needed to navigate uncertainty and seize opportunities.
Gaining a Sustainable Competitive Advantage
Companies like Amazon and Netflix don't just have better products; they have a better understanding of their customers. They use analytics to recommend products, personalize experiences, and optimize their supply chains.
This data-driven approach creates a moat around their business that is difficult for competitors to cross. BA enables you to find your own unique advantages in the market.
Driving Smarter, Data-Informed Decisions
Every major business decision involves risk. Should you enter a new market? Launch a new feature? Increase your marketing budget?
Business analytics reduces this risk by replacing guesswork with evidence. It allows you to model different scenarios, forecast potential outcomes, and allocate resources where they will have the greatest impact.
Enhancing Operational Efficiency and Reducing Costs
Inefficiencies often hide in plain sight. Business analytics can shine a light on them.
By analyzing operational data, a manufacturing company can identify bottlenecks in its production line. A retail company can optimize inventory levels to avoid stockouts and reduce storage costs. These small, data-driven improvements add up to significant bottom-line savings.
Deepening Customer Understanding and Personalization
Today’s customers expect personalized experiences. Business analytics allows you to move beyond generic marketing to one-on-one communication. By analyzing customer behavior, you can understand their needs, preferences, and pain points. This enables you to tailor product recommendations, marketing messages, and customer service for maximum impact.
The Four Types of Business Analytics Explained
Business analytics is not a single activity but a spectrum of analysis, ranging from simple reporting to sophisticated forecasting. These four types build on each other, providing progressively deeper levels of insight and value to the organization.
Descriptive Analytics: What Happened?
This is the most common form of analytics. It summarizes historical data to provide a clear picture of the past. Descriptive analytics answers the question, "What happened?"
Examples include sales reports, website traffic dashboards, and social media engagement summaries. It is the foundation upon which all other types of analytics are built.
Diagnostic Analytics: Why Did It Happen?
Once you know what happened, the next logical question is why. Diagnostic analytics digs deeper to uncover the root causes of events. It involves techniques like data drill-downs, correlation analysis, and attribution.
For example, if sales dropped last quarter, diagnostic analytics could reveal it was due to a competitor's new campaign or a technical issue on your website.
Predictive Analytics: What Will Happen Next?
Predictive analytics uses historical data, statistical algorithms, and machine learning techniques to identify the likelihood of future outcomes. It moves from hindsight to foresight.
This type of analysis can be used to forecast sales, identify customers at risk of churning, or predict which marketing leads are most likely to convert.
Prescriptive Analytics: What Should We Do?
This is the most advanced form of analytics. Prescriptive analytics goes beyond predicting future outcomes to suggest actions to take advantage of those predictions. It answers the question, "What should we do about it?"
For example, a prescriptive model could recommend the optimal pricing for a product to maximize profit or suggest the next best offer for a specific customer.
The Business Analytics Process: A Step-by-Step Framework
Effective business analytics is not a random act of data exploration. It is a systematic process that ensures the insights generated are relevant, accurate, and aligned with business goals. Following a structured framework helps teams stay focused and deliver tangible value.
- Identify the business problem or opportunity: The process starts with a clear question. What decision do you need to make? What problem are you trying to solve? A well-defined objective prevents "analysis paralysis."
- Data collection and integration: Next, you gather the necessary data. This data often lives in different systems: your CRM, ad platforms, web analytics tools, and databases. The key challenge is integrating this data into a unified view.
- Data cleaning and preparation (ETL): Raw data is rarely perfect. This step involves cleaning the data to handle missing values, remove duplicates, and correct inconsistencies. This Extract, Transform, Load (ETL) process is critical for accurate analysis. A robust strategy using top ETL tools can save hundreds of hours.
- Data exploration and analysis: With clean data, the analysis begins. This is where you apply statistical techniques and algorithms to uncover patterns, trends, and correlations, using the four types of analytics described earlier.
- Data visualization and reporting: Insights are useless if they cannot be understood. Data visualization turns complex data into intuitive charts, graphs, and dashboards. This helps communicate findings to stakeholders clearly and effectively. Mastering data visualization techniques is a key skill.
- Insight generation and actionable recommendations: This step translates the analytical findings into business language. It's about telling a story with the data and providing clear, actionable recommendations based on the insights.
- Implementation and performance monitoring: The final step is to act on the recommendations and monitor the results. This creates a feedback loop, allowing you to measure the impact of your decisions and refine your analytics process over time.
Business Analytics vs. Business Intelligence vs. Data Science
The terms business analytics, business intelligence (BI), and data science are often used interchangeably, but they represent distinct disciplines with different goals and methodologies.
Understanding their differences is key to building a comprehensive data strategy.
Key Differences in Goals and Scope
- Broadly speaking, business intelligence focuses on the past and present (descriptive analytics), providing dashboards and reports on what has happened.
- Business analytics focuses on the future (predictive and prescriptive analytics), using data to forecast trends and recommend actions.
- Data science is a broader field that often involves building new algorithms and data products to solve complex, open-ended problems.
How They Complement Each Other in a Data Strategy
A mature organization doesn't choose one over the others; it integrates all three.
- BI provides the foundational reporting that everyone needs.
- BA builds on that foundation to provide forward-looking insights.
- Data Science tackles the most complex challenges that require advanced statistical modeling.
Together, they create a full-spectrum data capability. Many teams leverage business intelligence platforms as the hub for all three disciplines.
Essential Tools and Technologies in the BA Ecosystem
A structured business analytics program depends on a coordinated technology stack. Each layer serves a distinct function: data storage, ingestion, transformation, analysis, and modeling.
When these layers are disconnected, analytics becomes slow and inconsistent. When aligned, they create a controlled decision environment.
1. Data Warehousing and Storage
A data warehouse acts as the central analytical repository. It consolidates structured data from operational systems into one governed environment. It stores both historical and current datasets optimized for large-scale queries.
Modern cloud warehouses such as Snowflake, Google BigQuery, and Amazon Redshift separate storage and compute. This enables elastic scaling, workload isolation, and predictable performance. The warehouse becomes the backbone for reporting, forecasting, and AI workloads.
However, the warehouse does not solve ingestion or data consistency. It processes what it receives.
2. Data Integration and ELT Platforms
Data originates in advertising platforms, CRM systems, product databases, finance tools, and more. Each source has its own schema and API constraints. Manual extraction introduces errors and latency.
Automated ELT platforms move data from source systems into the warehouse on scheduled refresh cycles. Improvado specializes in marketing and revenue data integration. It connects to hundreds of platforms, standardizes schemas, aligns metric definitions, and applies transformations directly inside the warehouse.
This ensures the warehouse contains clean, analysis-ready datasets. Without this layer, analytics teams spend time fixing pipelines instead of generating insight.
3. Business Intelligence and Visualization
BI tools translate structured warehouse data into decision-ready dashboards. Platforms such as Tableau, Power BI, and Looker enable interactive reporting, KPI monitoring, and executive summaries.
These tools rely on consistent upstream data modeling. When paired with Improvado and a governed warehouse, BI layers operate on standardized metrics and validated transformations. This reduces reporting disputes and improves cross-team alignment.
4. Statistical and Advanced Analytics Tools
Advanced analytics extends beyond descriptive dashboards. Predictive and prescriptive models require statistical and machine learning frameworks.
Python and R remain dominant for modeling, with libraries for regression, classification, forecasting, and clustering. These tools operate directly on warehouse datasets. Clean ingestion and standardized schemas are prerequisites for reliable modeling.
A mature analytics ecosystem integrates all layers: warehouse for storage and scale, Improvado for structured ingestion and governance, BI for visualization, and statistical tools for advanced modeling. Each layer strengthens the next.
Practical Applications of Business Analytics Across Departments
The true power of business analytics is realized when it is applied to solve real-world problems across the entire organization. From marketing to finance, data-driven insights can revolutionize how departments operate.
Marketing: Optimizing Campaigns and Customer Segmentation
Marketing is one of the most data-rich departments. Business analytics helps marketers move beyond simple metrics. It enables them to perform deep marketing analytics to understand customer behavior, segment audiences for personalization, optimize ad spend across channels, and attribute revenue to specific campaigns.
Advanced analysis of the customer journey analytics helps create more effective touchpoints.
Finance: Financial Modeling and Risk Assessment
The finance department uses BA for everything from budgeting and forecasting to risk management. Predictive models can forecast revenue with greater accuracy.
Analytics can identify drivers of profitability and detect fraudulent transactions. By analyzing historical market data, financial analysts can better assess investment risks and opportunities.
Operations: Supply Chain Optimization and Process Improvement
For businesses that deal with physical goods, BA is essential for operational efficiency. It can optimize inventory levels to balance supply and demand, identify the most efficient delivery routes to reduce fuel costs, and predict when machinery might need maintenance to prevent downtime.
This leads to a more resilient and cost-effective supply chain.
Human Resources: Talent Acquisition and Employee Performance
HR departments are increasingly using "people analytics." BA can help identify the characteristics of top-performing employees to improve hiring decisions. It can analyze employee engagement data to reduce turnover. And it can help ensure fair and equitable compensation practices by analyzing salary data against performance and market benchmarks.
Building a Data-Driven Culture with Business Analytics
Technology does not create a data-driven organization. Behavior does. A data-driven culture is built through accountability, access, and trust in the data.
Executive Sponsorship and Accountability
Data initiatives fail when they are treated as technical projects. They succeed when leadership ties analytics to measurable outcomes such as revenue growth, cost control, and operational efficiency.
Executive sponsorship sets priorities. It defines KPIs. It aligns budget allocation with analytics maturity. When leadership reviews dashboards built on governed data, it signals that decisions must be supported by consistent metrics.
Distributed Analytics Skills and Access
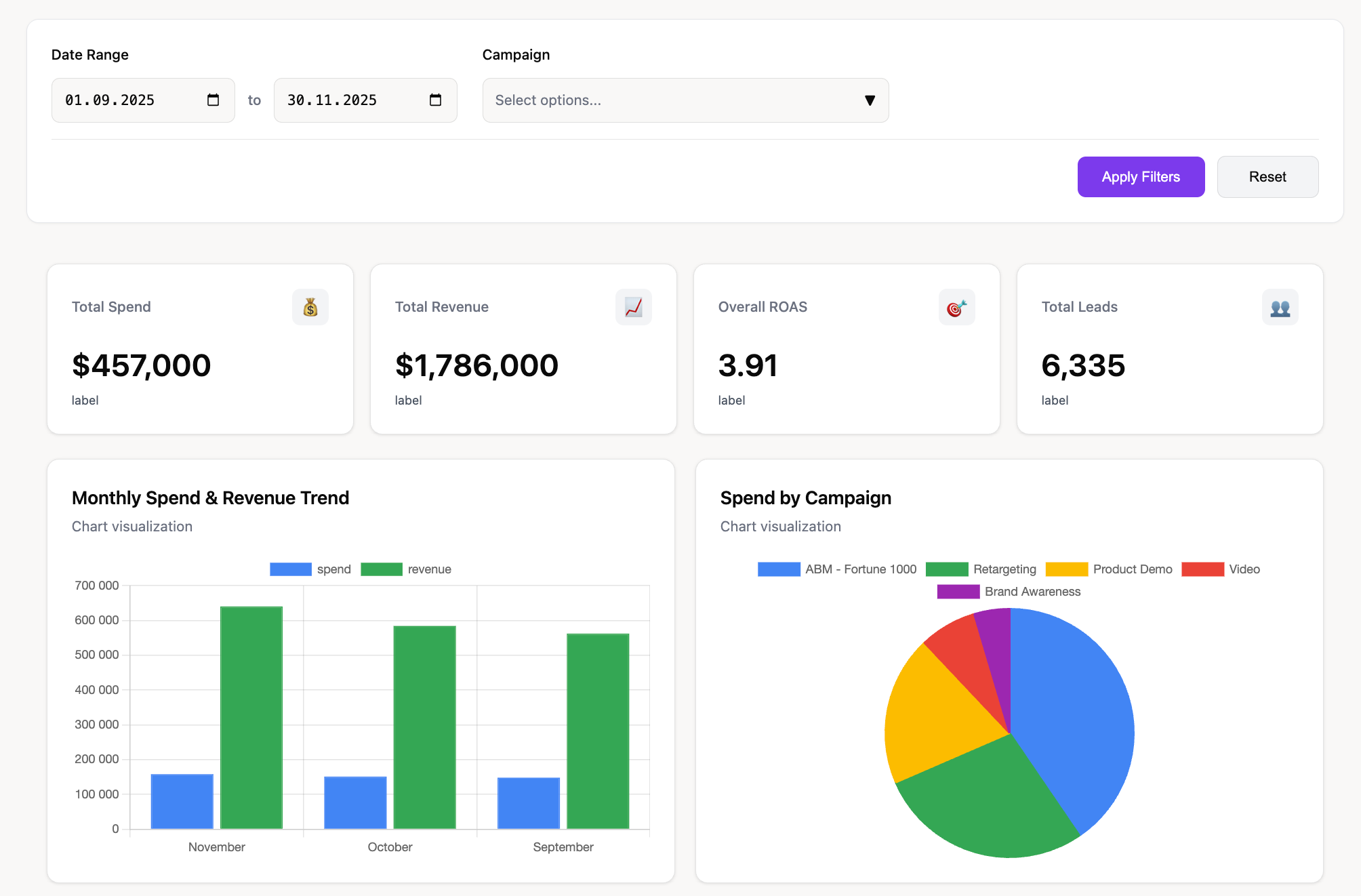
Data literacy must extend beyond analytics specialists. Operational teams need direct access to validated datasets and trusted KPIs. Decision cycles slow down when every question requires a ticket to the data team.
This requires:
- Self-service BI tools connected to governed warehouse data
- Clear documentation of metric definitions
- Structured access controls
- Consistent transformation logic across teams
Improvado’s AI Agent expands this access layer. It allows stakeholders to query unified, governed data in plain English. Users can generate dashboards, summaries, and performance analyses without writing SQL or relying on analysts. This reduces bottlenecks while preserving metric consistency.
The goal is controlled autonomy. Stakeholders can explore data independently, but within a governed framework.
Governance as a Cultural Foundation
Increased access without governance creates confusion. Multiple versions of the same KPI erode trust. Inconsistent attribution logic leads to conflicting conclusions.
A strong governance framework defines:
- Standard metric definitions
- Approved data sources
- Transformation rules
- Access permissions
- Data validation processes
Trust in analytics is not built through visualization. It is built through consistency.
A data-driven culture emerges when leadership demands evidence, teams access governed data easily, and systems enforce consistency by design.
Key Metrics and KPIs for Measuring Analytics Success
Analytics initiatives must be evaluated like any other business investment. Success is not defined by dashboards built or data pipelines deployed. It is defined by measurable impact on revenue, cost structure, operational speed, and decision quality.
Effective measurement connects analytics outputs to commercial outcomes.
Linking Analytics to Core Business Objectives
Every analytics initiative should begin with a defined business objective. This may include revenue growth, margin improvement, customer retention, risk reduction, or cost optimization.
KPIs must be mapped directly to these objectives. Examples include:
- Revenue growth rate influenced by pricing models
- Margin improvement after campaign optimization
- Reduction in customer acquisition cost
- Improvement in retention or churn rate
- Reduction in reporting cycle time
When analytics projects are tied to clearly defined financial or operational goals, impact becomes measurable and accountable.
Tracking ROI and Operational Gains
Analytics ROI is measured through quantifiable performance shifts.
Common indicators include:
- Revenue lift from campaign reallocation
- Cost savings from automation or process redesign
- Faster decision cycles due to real-time dashboards
- Reduction in manual reporting hours
- Increase in forecast accuracy
These metrics demonstrate that analytics is improving execution, not just reporting visibility.
Marketing-specific KPIs often include:
- Marketing ROI
- Customer acquisition cost vs lifetime value ratio
- Conversion rate improvement
- Incremental revenue from attribution-driven budget shifts
Analytics must be evaluated on how it changes business performance, not how it visualizes data.
Using Attribution and Causal Measurement
Attribution models are essential when outcomes are influenced by multiple touchpoints. Simple last-click metrics rarely reflect true impact.
More advanced approaches include:
- Multi-touch attribution
- Time-decay or position-based models
- Incrementality testing
- Controlled experiments and lift studies
These methods quantify contribution across channels and reduce budget misallocation.
Reliable attribution requires standardized, cross-channel datasets. Without unified data models, attribution logic becomes inconsistent and results lose credibility.
Analytics success is proven when decisions improve measurable business outcomes and when those improvements can be traced back to structured, governed data analysis.
Overcoming Common Challenges in Business Analytics
The path to becoming a data-driven organization is not without its obstacles. Being aware of these common challenges can help you proactively address them and keep your analytics program on track.
Dealing with Poor Data Quality and Silos
Poor data quality is the most persistent barrier. Inconsistent schemas, duplicated records, missing fields, and manual exports distort analysis.
Siloed systems compound the issue. Marketing, finance, CRM, and product platforms operate independently. Without centralized ingestion and normalization, metrics diverge across dashboards.
Mitigation requires:
- Automated data integration
- Standardized metric definitions
- Consistent naming conventions
- Validation and anomaly detection
- Controlled transformation logic
Improvado addresses this at the ingestion layer. It centralizes data from hundreds of systems, standardizes schemas, aligns identifiers, and applies governance rules before data reaches the warehouse. This reduces metric drift and improves trust in reporting outputs.
Data quality must be enforced upstream, not corrected in dashboards.
Analyst-to-Decision Alignment
Insights create value only when they influence decisions. A common failure point is the disconnect between analytical output and operational action.
Challenges include:
- Overly technical reporting
- Inconsistent KPI definitions
- Long turnaround times for analysis requests
- Limited stakeholder access to validated data
Clear metric governance and shared data models reduce friction. Improvado’s AI Agent allows stakeholders to query governed datasets directly in plain language. This shortens the gap between question and answer while maintaining metric consistency.
When access is structured and definitions are enforced, insights become actionable.
Security and Compliance Controls
Analytics programs operate within strict regulatory environments. GDPR, CCPA, and regional privacy frameworks require controlled access and documented data handling.
Risk areas include:
- Unauthorized access to customer-level data
- Uncontrolled data exports
- Inconsistent anonymization practices
- Lack of audit trails
A compliant analytics stack requires role-based access controls, data lineage tracking, and enforced transformation rules.
Analytics scalability depends on security, governance, and trust. These controls must be embedded into the data architecture, not added later.
The Future of Business Analytics: Trends to Watch
Business analytics is shifting from retrospective reporting to operational intelligence. The focus is no longer on describing what happened. It is on predicting outcomes, automating decisions, and embedding analytics into workflows. Organizations that adapt their architecture and governance early gain structural advantage.
Several trends are reshaping how analytics is designed and deployed.
AI and Machine Learning Embedded in Analytics
AI and machine learning are moving from experimental projects to embedded capabilities inside analytics platforms. Models now support forecasting, churn prediction, demand planning, fraud detection, and dynamic resource allocation.
Modern systems apply machine learning to:
- Detect anomalies in performance metrics
- Identify outliers in financial or operational data
- Recommend budget reallocation
- Predict customer lifetime value
- Forecast revenue under different scenarios
Generative AI is also influencing analytics workflows. Systems can generate narrative summaries, propose follow-up questions, and recommend visualizations. The focus is shifting from building dashboards to automating interpretation.
The challenge is governance. As AI becomes embedded in analytics, model transparency, bias detection, and explainability become mandatory.
Self-Service and Augmented Analytics at Scale
Analytics consumption is expanding beyond analysts and data scientists. Business users expect direct access to trusted data without long request cycles.
Self-service analytics enables:
- Direct querying of centralized datasets
- On-demand dashboard customization
- Rapid scenario testing
Augmented analytics enhances this by providing automated insights, suggested correlations, and intelligent alerts. The goal is faster time-to-insight without sacrificing governance.
However, self-service only works when underlying data models are standardized. Without centralized definitions and validation rules, distributed analytics increases metric inconsistency.
Real-Time and Streaming Intelligence
Batch reporting is increasingly insufficient. Competitive environments require decisions based on current data, not yesterday’s aggregates.
Real-time analytics enables:
- Dynamic pricing adjustments
- Campaign budget pacing optimization
- Fraud detection and risk monitoring
- Inventory and supply chain responsiveness
- Immediate user behavior personalization
This shift requires streaming ingestion frameworks, incremental data processing, and low-latency query engines. Architectures are evolving toward event-driven models rather than daily refresh cycles.
Data Governance as a Strategic Layer
As analytics becomes embedded in operational systems, governance becomes more critical. Privacy regulations, regional data restrictions, and audit requirements are increasing.
Future-ready analytics frameworks emphasize:
- Role-based access control
- Column-level security
- Data lineage tracking
- Version-controlled datasets
- Policy-driven transformations
Governance is no longer a compliance checkbox. It is foundational to trust in analytics outputs.
Analytics as Operational Infrastructure
The long-term shift is clear. Analytics is moving from reporting support to embedded decision infrastructure. Models trigger actions. Dashboards guide operations. Data pipelines feed automated systems.
Organizations that invest in scalable architecture, governed data models, and AI-ready infrastructure will move faster than those relying on static reporting workflows.
The future of business analytics is intelligent, automated, real-time, and governed by design.
Conclusion
Understanding business analytics is a journey, not a destination. It begins with a fundamental appreciation for how data can illuminate the path forward. By embracing the four types of analytics, following a structured process, and building a supportive culture, any organization can transform itself into a data-driven powerhouse.
The journey from raw data to actionable insight requires the right foundation. It demands a commitment to breaking down data silos and creating a single, reliable source of truth. This is the bedrock upon which all successful analytics programs are built.
By investing in a unified data strategy, you empower your teams to stop debating the numbers and start making the intelligent decisions that will define your future success.
.png)






.png)
