Business databases are crammed full of data. This can make finding meaningful business insights to fuel strategy and operations very tricky. Proper data management solves this problem.
Key Takeaways
- Data management is the practice of effectively overseeing data throughout its lifecycle, from data creation to destruction.
- From a marketing perspective, data management fosters a data-driven culture and ensures that the data you collect and store is reliable and trustworthy.
- Techniques and solutions for creating sound data management strategies include data preparation, ETL pipelines, data governance, and more.
- Data management is not straightforward and comes with challenges. Follow best practices to create an effective strategy that everyone in the company can get behind.
What is Data Management?
Data management is the practice of effectively overseeing data throughout its lifecycle in a cost-effective and secure way. The main goal is to organize, store, and manage data in a way that allows easy access, retrieval, and use. This includes tasks like:
- Collecting data from various sources;
- Storing data in a secure and organized manner;
- Ensuring data is accurate and up to date;
- Protecting data from unauthorized access or tampering; and
- Analyzing and interpreting data to extract insights and enable decision-making.
In terms of marketing, well-established customer data management processes promote a data-driven culture within the department. It ensures that you store high-quality data to get an accurate and comprehensive view of your marketing efforts and customers at various touchpoints. This, in turn, helps you better understand your target audience, communicate values that match your audiences' pains, and identify the best-performing strategies that are more likely to increase return on marketing investment (ROMI).
Why Is Data Management Important?
Effective data management creates order within the large quantity of data that businesses collect.
It gives organizations a roadmap on how to properly collect and manipulate data to prevent it from becoming messy or unusable, allowing them to make decisions quickly and respond promptly to market needs.
It also frees up employees’ resources. For example, a poll by Vicky Boykis, senior machine learning engineer at Duo and a notable influencer in the niche, shows that the majority of data scientists spend 60% of their time cleaning and moving data:
Data management solutions can fully automate manual tasks and let analysts do their job instead of fixing raw data.
Data Management Solutions and Techniques
The good news is that petabytes of raw and poor data can be managed. With clear policies and the right tools, your business will thrive with a data-driven culture—and with employees who take full responsibility for the data they collect.
Data preparation
It's no secret that many businesses struggle with poor-quality data. Their data can be inconsistent and redundant or stored in different formats with no consistent taxonomy.
Data preparation is the process of aggregating, transforming, and structuring raw data to prepare it for further analysis. Data preparation tools bring data together in a unified format, eliminate inconsistencies, flag errors, and combine data automatically. All in all, this process ensures the insights your team derives during the analysis and the reports you look at are valid because the data they are based on are high quality.
Data pipeline
A data pipeline is an automated series of activities that starts with data ingestion and ends with a data sink, such as a data warehouse, a storage service, or another application. It streamlines data processing by eliminating manual data entry and manipulation, significantly speeding up the marketing analysis and reporting processes.
ETL pipeline
Extract, Transform, and Load (ETL) is a subset of a data pipeline.
The ETL process automates data extraction from one or multiple sources, transforms it into a standardized and usable format, and loads it to an endpoint, like a data warehouse or a BI software.
This endpoint becomes the organization's single source of truth (SSOT). The data stored here is already clean, formatted, and ready for analysis, visualization, or reporting.
For example, advanced marketing analytics tools like Improvado leverage ETL to pull data from 300+ marketing and sales data sources, like Shopify, Facebook Ads, Google Analytics, and more, transform data into analysis-ready format, and load it to the designated destination, i.e., a marketing data warehouse or a BI, visualization, or analytics tool.
Data warehouse
A data warehouse is the storage area for your business’s historical and real-time data. It usually stores structured data from multiple sources like various ad platforms, social media, and more.
In the very early stages of working with analytics, companies often use spreadsheets to store their data. Eventually, however, they reach the end of their spreadsheet. At this point, the datasets have become too large and queries grind to a halt. Technically advanced companies migrate to cloud data warehouses, such as Google Big Query, to enable analytics teams to query data more often and increase their overall productivity.
Data security
Data security is the practice of putting precautions in place to protect company data from corruption or unauthorized access throughout its lifecycle. It also ensures that the business complies with data privacy laws and regulations, like HIPAA, SOC-2, and GDPR.
Data governance
Data governance is the foundation of good quality data. It’s a process that details the governing policies and procedures for data collection, organization, storage, and analysis. Its purpose is to ensure accurate, complete, consistent, timely, valid, and unique data.
Data Management Frameworks
Teams work together with these solutions and techniques to achieve data quality and properly set up all processes to manage data. You can’t achieve the highest quality of data without implementing data governance, data security, information systems architecture, etc. all at once.
A data management framework is a set of rules and techniques required to implement data management in your company. Currently, there are two generally acknowledged frameworks.
DAMA-DMBOK 2
DAMA-DMBOK 2 stands for Data Management Association - Data Management Body of Knowledge version 2. It’s the second edition of the framework that was originally published in 2009.
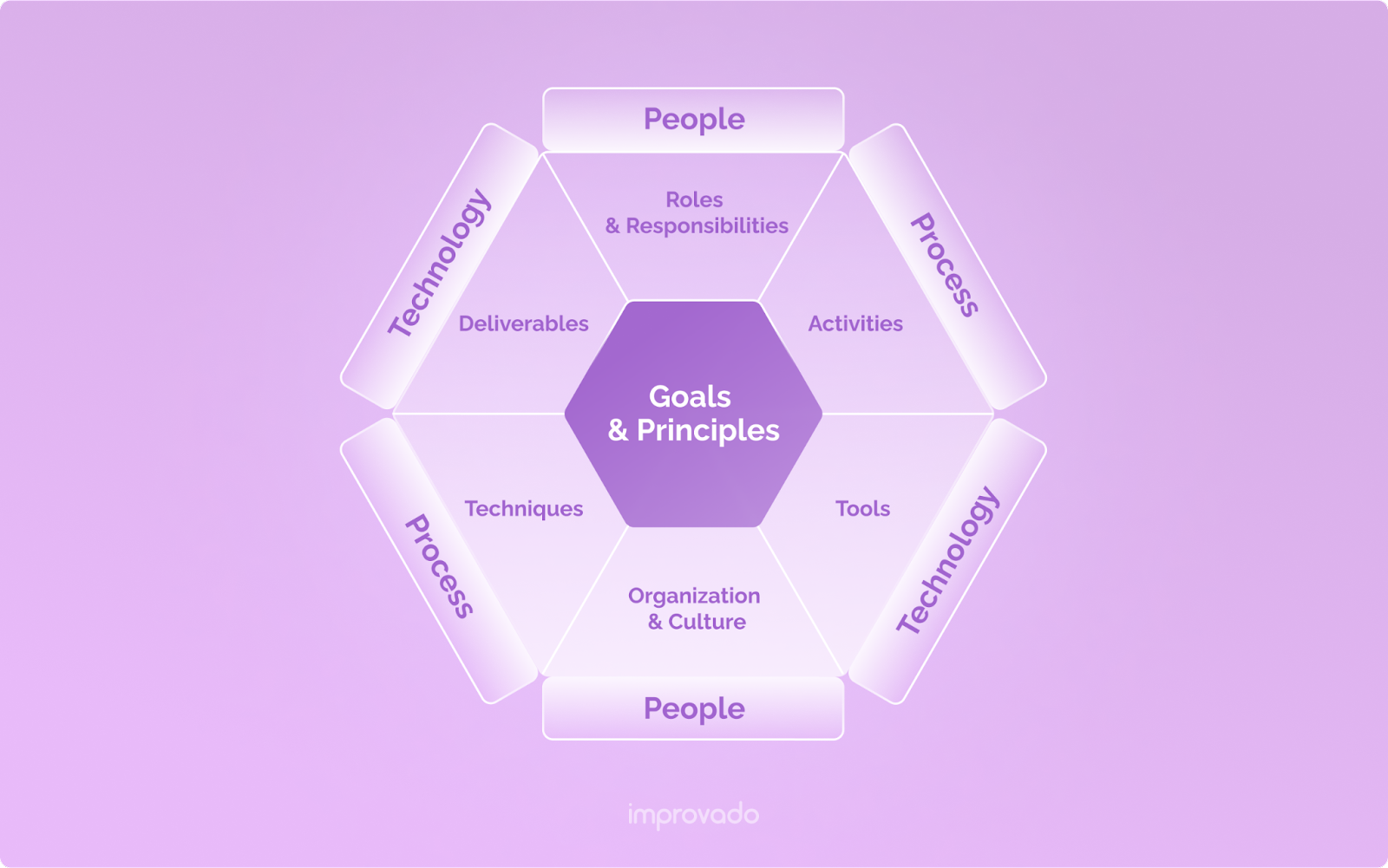
The framework identifies 11 interlinked knowledge areas that constitute data management. When following this framework, a company needs to take all areas into consideration.
DMBOK 2 also implies that it’s not only the data management professionals who take care of data management processes; all business professionals are involved in it. The DAMA Hexagon shows a direct relationship between people, processes, and technologies.
DMBOK 2 defines the main mission of data management in the following way: “To meet the data availability, quality, and security needs of all stakeholders”. It also outlines the tools, participants, metrics, and deliverables involved in the data management process.
However, this framework has one significant drawback. It doesn’t describe the relationship between different knowledge areas, leaving everything to be decided by you. Altogether, DMBOK 2 provides a lot of theoretical knowledge but not so many practical tips.
DCAM™
While DMBOK 2 is a publicly accessible framework, DCAM™ (the Data Management Capability Assessment Model) is closed for public access. Only Enterprise Data Management Council (EDC) members can access this framework.
The framework describes data management in terms of different capabilities with different maturity levels. Even though DCAM™ has a practical and operational focus, it doesn’t provide a clear viewpoint on the implementation of data management.
Companies use DCAM™ to evaluate their processes, educate stakeholders, and identify weaknesses in their data management programs. It also helps you mitigate risks of data privacy regulation violations, including GDPR.
Since the framework isn’t publically available, there’s not much information about its best practices and recommendations. However, the Enterprise Data Management Council has recently published a public version of their Cloud Data Management Capabilities Framework, which sheds some light on the approach the EDC uses to define its frameworks.
Both of these frameworks might serve as a good starting point in your data management journey. They outline crucial concepts, so you maintain total clarity when first implementing data management.
Data Management Challenges
You’ll come across many challenges in your efforts to manage your organization’s data. But when you are aware of these potential challenges, you’ll be better prepared to handle them.
Securing business data
There are many internal and external threats to data security and integrity. And data breaches can happen at any time. This puts your customers’ private and personal data at risk.
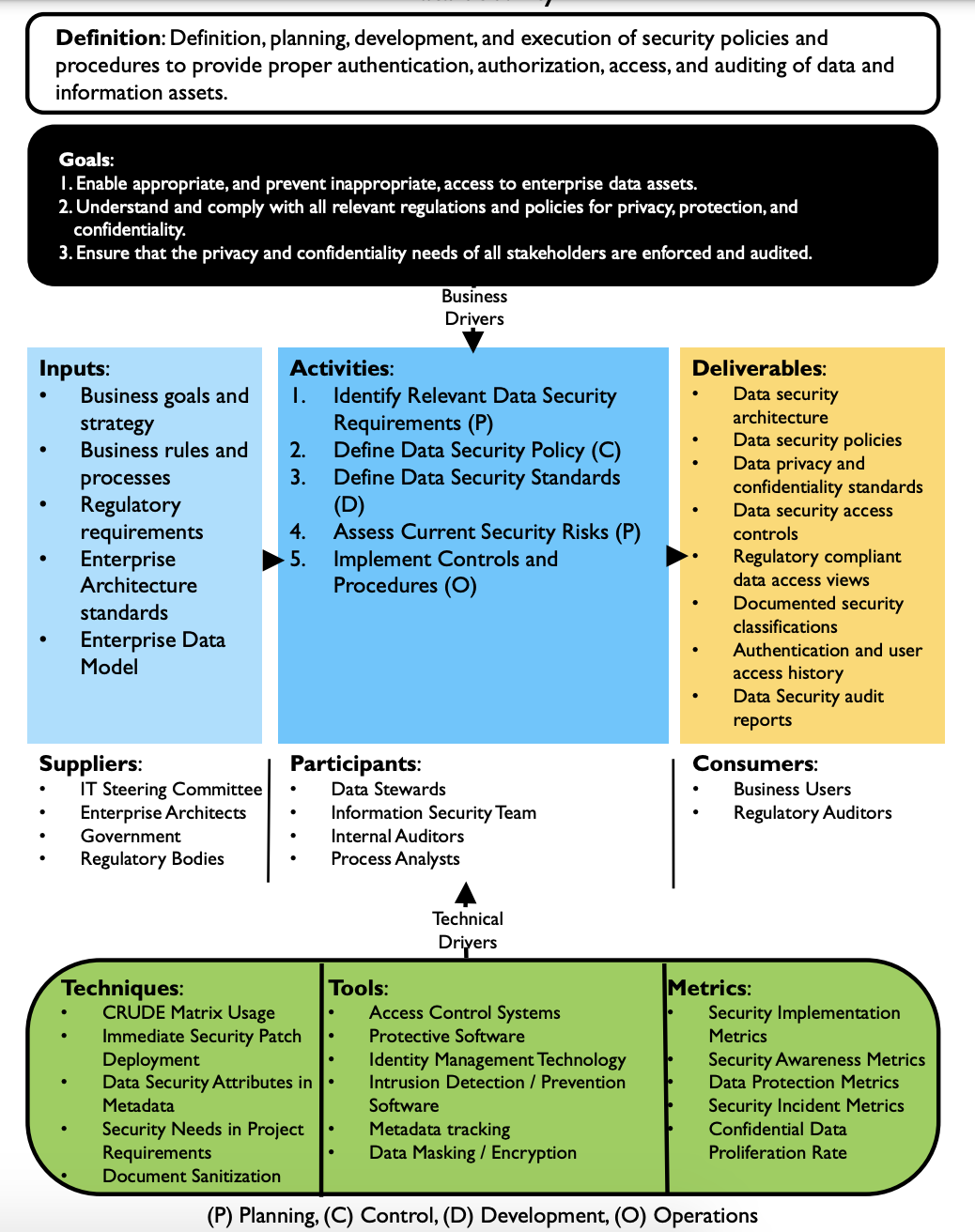
Here’s how DMBOK-2 defines data security process:
It’s always best to address security risks with coordinated efforts, instead of individual attempts. The process involves too many tasks for a single employee to take care of. On a grander scale, data security revolves around four main activities:
- Identify and classify sensitive data assets;
- Locate sensitive data within the company;
- Determine how each asset needs to be protected; and
- Understand how this information interacts with business processes.
Then, you also need to assess external threats, such as the ignorance or inattentiveness of your employees. Data access management and compliance with policies reduces the risk of sensitive data exposure and increases the security level of your business infrastructure.
Dealing with too much data
Up to 73% of data is unused because many businesses struggle to keep up with the huge amount of data coming in from different sources. Organizations that do not have data management guidelines for omnichannel analytics get overwhelmed, so they make things up or do not use the data available.
However, don’t try to manage all data at once. Companies produce large datasets, a large portion of which is never used. That’s why the data management lifecycle recommends focusing on the most critical data and minimizing data ROT (data that is Redundant, Obsolete, or Trivial).
Combining data from different sources
Think of the dozens of tools your business uses. Even within the marketing department, you probably utilize multiple data collection and analytics tools.
This can create data silos, which happen because data is stored in isolated storage solutions that don’t communicate with each other. As a result, each department sits on their data making cross-departmental collaboration more difficult.
Poor quality data
Organizations spend almost a quarter of their revenue on resolving data quality issues.
Poor quality data results from errors during data entry, data corruption when transporting data from one tool to another, or a lack of standardized practices.
Here’s a comprehensive overview of data quality management by DMBOK-2:
Data management lifecycle, data governance, and a focus on critical data are some of the most important factors to consider when trying to increase the quality of your data.
Keep in mind that “data quality” is a collective term that includes 12 characteristics that a trustworthy dataset should have.
Shortage of qualified data analysts
Despite all the talk about the importance of data to digital and modern businesses, expert data analysts are hard to come by. Hiring a qualified analyst takes time, and training new hires can be expensive and time-consuming.
Lack of data governance
Many businesses create data governance standards as an afterthought when their data has already become messy. Without data governance, organizations get swamped with poor-quality data. As a result, analysts spend too much time in the weeds cleaning it up, and end users spend too much time trying to make sense of it.
Data Management Best Practices
Data management is a big task involving a lot of moving parts. But there are data management best practices that can start you off on the right foot.
Prioritize data protection and security
Data security breaches are million-dollar problems that can be prevented with good data management principles.
Some data protection measures include having proper user permissions, having a centralized system that handles and manages the data, and using only software that adheres to data privacy laws.
Integrate all your data and build one source of truth
Organizations have a lot of data that may be stored away in data silos. This means it's difficult to get a full view of the business landscape. For marketing professionals, this prevents them from seeing different customer touchpoints.
When you integrate all data into one centralized storage area using an ETL pipeline, for example, it becomes easier to get revenue data insights.
Use quality data management software
Manual data manipulation doesn't cut it anymore with the volumes of data that businesses deal with.
Fortunately, there are many new technologies and automation software solutions that make data collection and analysis easier and quicker. Use good-quality software that integrates well with other applications.
Build a glossary of your organization's metadata
Have a standardized definition of all the data you collect (also called “metadata”). Include specific details such as data attributes, creation date, creator’s name, and storage area.
This ensures transparency and alignment across the whole organization.
Make everyone responsible for data quality
Data quality is a shared responsibility. It’s only by making everyone in the organization accountable and responsible for it that common data issues can be reduced.
What is the marketer’s role in this? Marketers are partially responsible for the primary data collection—they know UTM tags taxonomy, the markup on advertising campaigns, and the accounts they need to track. Meanwhile, data engineers and analysts are responsible for data quality at other stages of the data flow.
First Steps to Establishing Data Management Practices
The road to becoming a data-driven organization starts with proper data management practices. Support this transformation by following practices that successful data-driven businesses adhere to.
1. Get the C-suite invested in creating a data management plan
Data management is challenging when the C-suite is not invested in the whole undertaking. They have to see the value of a properly executed data management strategy so that they become proactive in implementing it.
2. Audit current data
Most likely, your company is already gathering a lot of data. Audit what you already have. Observe the lay of the land and make a data management plan based on the data you already have, considering your organization's goals and resources.
3. Use automation tools as much as possible
Human error is a common cause of poor data quality. Data management becomes quicker and easier if you choose the right automation tools. You will also significantly reduce human error during data collection, manipulation, and analysis.
4. Plan for growth
The data your company collects will only grow. Make your data management strategy flexible so that it grows with your company and drives scaling effortlessly.
5. Find a reliable technological partner
Building a tech stack and finding the right partners are vital for establishing reliable data management processes, especially when the security of customer data is at stake. Improvado is an advanced marketing analytics solution that fits into the existing analytics environment and fosters data culture in the organization. The solution is automated marketing data management and reporting, which ensures your team relies only on high-quality and up-to-date data to drive business performance.
Your Turn
Following the data management best practices outlined in this guide will help clean up your data and usher your organization into a more data-driven mindset. It's not going to be an easy process. It's a journey. But it's well worth doing it to get high-quality data that everyone in your company can trust and rely on for actionable business insights.
.png)







.png)
