Product and marketing teams expect real-time analytics without engineering bottlenecks. Finance demands cost transparency across multi-cloud environments. Security teams enforce stricter access controls and audit trails.
Meanwhile, many companies are still running layered, fragmented architectures built over years of tool adoption. This creates performance bottlenecks, compliance risk, and rising infrastructure costs.
This guide evaluates modern database software through a practical lens. It covers AI-ready architectures, operational vs analytical trade-offs, cloud and hybrid models, governance requirements, and cost optimization. You’ll get a clear framework to select database technology aligned with scale, compliance, and advanced analytics needs in 2026.
Key Takeaways:
- Database software (DBMS) is essential for storing, managing, and accessing data efficiently and securely.
- Key types include Relational (SQL), NoSQL, Cloud-Native, and In-Memory databases, each suited for different use cases.
- When choosing, evaluate your data type, scalability needs, team skills, and total cost of ownership (TCO).
- Top platforms for 2026 include PostgreSQL, Microsoft SQL Server, MongoDB, and cloud solutions like Amazon RDS and Snowflake.
- The future of database software lies in AI integration, serverless architecture, and enhanced data governance features.
What Is Database Software? And Why It Matters
Database software is a computer program designed to manage databases. It is often called a Database Management System (DBMS). This software acts as an interface between the database, the user, and other applications. It allows users to create, read, update, and delete data in an organized way.
Think of it as a digital librarian for your data. Instead of manually searching through files, the DBMS organizes everything. It provides tools to query information quickly. This system ensures data integrity, security, and concurrency control. Multiple users can access the data at the same time without conflicts.
Modern businesses run on data. A robust database app or program is not just a storage container. It is a strategic tool. It enables everything from real-time analytics to personalized customer experiences. Without effective db software, data becomes chaotic, insecure, and useless.
Core Benefits of Using Database Management Software
Implementing a proper DBMS provides significant advantages. It transforms raw data into a reliable and powerful business asset. Here are the primary benefits:
- Centralized data management: All your data resides in one place. This creates a single source of truth. It eliminates confusion from duplicate or conflicting datasets.
- Enhanced data security: A DBMS offers powerful security tools. This includes authentication, encryption, and access control. You can define who sees and modifies specific data, protecting sensitive information.
- Improved data integrity: The software enforces rules to ensure data is accurate and consistent. This prevents errors during data entry and updates.
- Reduced data redundancy: By centralizing data, you minimize unnecessary copies of information. This saves storage space and improves consistency.
- Efficient data access: Users can quickly retrieve information using query languages like SQL. This speeds up reporting and analysis, supporting faster decision-making.
- Scalability: Professional database software is built to grow with your business. It can handle increasing volumes of data and user traffic without a drop in performance.
- Backup and recovery: DBMS platforms include automated backup and recovery features. This protects your data from hardware failure, corruption, or human error.
Key Features to Look For in Modern Database Software
When evaluating different database programs, certain features are non-negotiable. These capabilities ensure your system is powerful, flexible, and future-proof.
- Performance and speed: The software must handle queries quickly, even with large datasets. Look for features like advanced indexing, query optimization, and in-memory caching.
- Scalability options: It should scale both vertically (more power on one server) and horizontally (distributing across multiple servers). Cloud-native platforms often provide the best elastic scaling.
- Security and compliance: Robust security is crucial. Features should include role-based access control, data encryption at rest and in transit, and detailed audit logs.
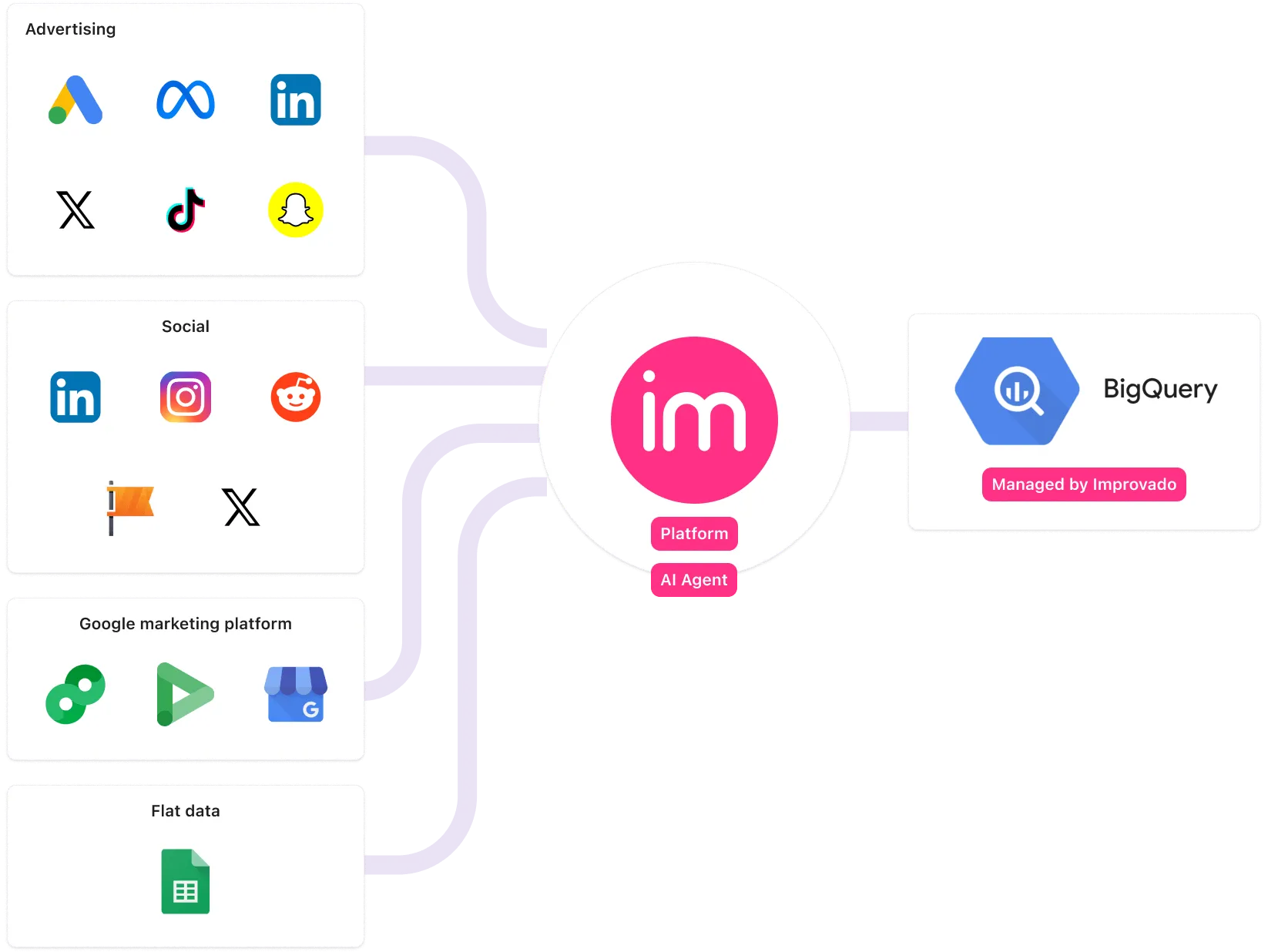
- Integration and connectivity: The DBMS must connect easily with your existing tech stack. This includes BI tools, application frameworks, and ETL tools. Connecting tools is not the same as standardizing data. Improvado extracts data from 500+ marketing and revenue platforms and eliminates broken joins and inconsistent naming at the source.
- Data modeling flexibility: The system should support your specific data types. This could be structured tables, semi-structured JSON documents, or key-value pairs.
- Reliability and availability: Look for features that guarantee high uptime. This includes replication, failover clustering, and automated backup mechanisms.
- Developer tools and ecosystem: A strong ecosystem makes development easier. This includes GUIs, command-line tools, and support from a large community or commercial vendor.
Types of Database Software Explained
Not all databases are created equal. They are built on different models to solve different problems. Understanding these types is the first step toward choosing the right solution.
1. Relational Databases (RDBMS)
Relational databases are the most traditional and widely used type. They organize data into tables with rows and columns. Each table has a rigid schema that defines its structure. Relationships between tables are created using keys.
The standard language for interacting with them is SQL (Structured Query Language). They are known for reliability and data consistency (ACID compliance).
Best for: Financial transactions, CRM systems, ecommerce platforms, and any application requiring high data integrity.
2. NoSQL Databases
NoSQL ("Not Only SQL") databases were designed for the internet era. They handle large volumes of unstructured and semi-structured data. They offer flexible schemas and scale out horizontally.
There are several NoSQL sub-types:
- Document Stores (e.g., MongoDB): Store data in JSON-like documents. Great for content management and mobile apps.
- Key-Value Stores (e.g., Redis): Simplest model. Stores data as a collection of key-value pairs. Ideal for caching and session management.
- Column-Family Stores (e.g., Cassandra): Store data in columns instead of rows. Excellent for analytics on large datasets.
- Graph Databases (e.g., Neo4j): Focus on relationships between data points. Used for social networks and recommendation engines.
Best for: Big data applications, real-time web apps, IoT, and content management systems.
3. Cloud-Native Databases
These databases are built specifically for the cloud. They are offered as managed services (DBaaS – Database as a Service). This means the cloud provider handles all the infrastructure management, scaling, and backups. They often combine the benefits of relational and NoSQL models with unmatched scalability and global distribution.
Best for: Organizations that want to reduce operational overhead, achieve global scale, and build modern, resilient applications.
4. In-Memory Databases (IMDB)
In-memory databases store data primarily in the main memory (RAM) instead of on disk. This results in blazing-fast response times. They are perfect for applications that require real-time data processing and sub-millisecond latency. Many traditional databases also offer in-memory features.
Best for: Real-time analytics, ad bidding platforms, gaming leaderboards, and financial risk analysis.
5. NewSQL Databases
NewSQL databases are a modern class of relational databases. They aim to provide the scalability of NoSQL systems.
At the same time, they maintain the consistency guarantees of traditional RDBMS. They are designed for distributed environments and are often used for critical online transaction processing (OLTP) systems that need to scale.
Best for: Large-scale e-commerce, financial services, and global SaaS applications requiring both consistency and scale.
How to Choose the Right Database Software: A 7-Step Guide
Selecting a database is a long-term commitment. Follow this structured process to make an informed decision that aligns with your business goals.
- Define your primary use case: First, understand what the database will do. Is it for online transaction processing (OLTP) like an e-commerce store? Or is it for online analytical processing (OLAP) like a marketing data warehouse? The workload type is the biggest factor.
- Assess your data types and volume: Analyze the data you will store. Is it highly structured, like financial records? Or is it semi-structured, like user event logs? Estimate your data volume now and its projected growth over the next five years.
- Evaluate scalability and performance needs: Determine your performance requirements. Do you need sub-millisecond latency for real-time features? How will you handle traffic spikes? Choose a system that can scale to meet your peak demand without over-provisioning.
- Consider your team's technical skills: Evaluate your team's expertise. Do they have deep experience with SQL? Or are they more comfortable with NoSQL models? Choosing a familiar technology can reduce training time and speed up development.
- Analyze integration capabilities: Map out how the database will fit into your ecosystem. Ensure it has robust connectors for your programming languages, BI platforms, and other critical systems. Seamless data integration is key to a unified data strategy.
- Compare total cost of ownership (TCO): Look beyond the sticker price. Consider costs for licensing, hardware, maintenance, and skilled personnel. Open-source options may have no license fee but can require more management overhead. Cloud databases often have a predictable, pay-as-you-go model.
- Plan for security and compliance: Identify your security and regulatory requirements. Do you need to comply with GDPR, HIPAA, or other standards? Ensure the database provides the necessary features for access control, encryption, and auditing. Strong data governance tools are essential.
Top Database Software Platforms for 2026
Here is our curated list of the best and most popular database software. We've categorized them to help you find the right fit for your needs.
Best Relational Database Software (SQL)
These are the workhorses of the data world. They are known for their reliability, strict consistency, and powerful querying capabilities.
1. PostgreSQL
PostgreSQL is widely adopted in modern data architectures, including marketing data platforms and customer analytics systems. It supports structured campaign data, event tracking, and advanced indexing for performance optimization.
Its native JSON support allows teams to store semi-structured marketing data without losing relational integrity. Extensions and cloud-managed versions make it suitable for warehouse environments that power BI dashboards, attribution models, and marketing performance reporting.
2. Microsoft SQL Server
Microsoft SQL Server is common in enterprise organizations operating within the Microsoft ecosystem. Marketing teams often interact with it indirectly through CRM systems, ERP platforms, and BI tools such as Power BI.
It offers strong governance controls, access management, and integration with Azure-based data services. For marketing departments in regulated industries, its security model and audit capabilities are critical for handling customer and revenue data.
3. MySQL
MySQL frequently powers ecommerce backends, CMS platforms, and SaaS marketing applications. Many marketing automation tools and web platforms rely on MySQL-compatible infrastructure.
It is effective for transactional workloads such as order processing, lead capture, and customer profile storage. For growth teams managing high-traffic websites, MySQL’s performance and replication capabilities support scalable front-end operations.
4. Oracle Database
Oracle Database is typically embedded within large enterprise systems such as ERP, finance, and enterprise CRM platforms. Marketing data often intersects with these systems when calculating customer lifetime value, revenue attribution, or regional performance.
Its scalability and high-availability architecture make it suitable for global organizations with large customer datasets and complex reporting requirements. However, integration and operational complexity must be considered.
5. SQLite
SQLite is commonly used in lightweight marketing applications, mobile apps, and embedded analytics features. It supports local data storage and offline tracking scenarios.
While not appropriate for enterprise-scale campaign analytics, it plays a role in distributed marketing tools and edge data collection before synchronization with centralized systems.
Best NoSQL Database Software
NoSQL databases are increasingly relevant for marketing organizations managing high-volume behavioral data, event streams, personalization engines, and real-time campaign systems. They prioritize flexibility, horizontal scalability, and performance over rigid schemas.
6. MongoDB
MongoDB is a leading document-oriented database that stores data in flexible JSON-like documents. This structure aligns well with marketing event data, user attributes, and campaign metadata, which often evolve over time.
For marketing teams, MongoDB supports use cases such as customer profile stores, personalization engines, and content platforms. Its schema flexibility allows rapid iteration when tracking new engagement signals. Managed offerings like MongoDB Atlas reduce infrastructure overhead for teams integrating product and marketing data pipelines.
7. Redis
Redis is an in-memory data store optimized for speed. It is commonly used as a caching layer, session store, or real-time data engine.
In marketing contexts, Redis powers real-time personalization, recommendation systems, dynamic pricing, and campaign-trigger logic. Its low-latency performance makes it suitable for use cases where milliseconds matter, such as serving personalized content or updating bidding logic in real time. It is not designed for long-term analytical storage but plays a critical role in performance-sensitive applications.
8. Apache Cassandra
Apache Cassandra is a distributed, column-family database built for scale and availability. It is optimized for write-heavy workloads and large volumes of time-series or event data.
Marketing technology platforms use Cassandra for storing clickstream data, ad interaction logs, and telemetry at scale. Its architecture eliminates single points of failure, making it suitable for global applications that require high uptime. However, its complexity requires specialized engineering support, which may limit direct adoption by marketing departments without strong data teams.
Best Cloud Database Platforms
Cloud database platforms abstract infrastructure management and provide elasticity, security, and high availability. For enterprise marketing organizations, these services support scalable analytics, data warehousing, and AI-ready environments.
9. Amazon RDS
Amazon RDS is a managed relational database service that supports engines such as MySQL, PostgreSQL, Oracle, and SQL Server.
Marketing teams benefit from automated backups, patching, and scaling without managing infrastructure directly. RDS is commonly used to support ecommerce backends, marketing automation systems, and intermediate data layers feeding BI tools. It simplifies operational overhead but does not replace a full data warehouse for large-scale analytics.
10. Snowflake
Snowflake is a cloud-native data platform designed for analytics and data warehousing. Its architecture separates storage and compute, allowing independent scaling of workloads.
For marketing organizations, Snowflake supports centralized campaign reporting, multi-touch attribution modeling, customer lifetime value analysis, and AI-driven segmentation. It handles large volumes of cross-channel data and integrates with BI tools and machine learning environments. Its performance and scalability make it a common foundation for enterprise marketing intelligence stacks.
11. Google Cloud Spanner
Google Cloud Spanner is a globally distributed relational database that combines SQL consistency with horizontal scalability.
It is designed for mission-critical, globally distributed applications. For marketing technology providers or large enterprises operating across regions, Spanner supports real-time transactional systems at global scale. Its strong consistency model makes it suitable for applications requiring reliable customer or transaction records across geographies.
12. Microsoft Azure SQL Database
Azure SQL Database is a fully managed relational database service integrated into the Microsoft cloud ecosystem.
Enterprise marketing teams operating within Azure environments use it to support CRM systems, marketing automation platforms, and operational reporting layers. It includes built-in performance tuning, security monitoring, and compliance features. Integration with Azure Synapse and Power BI enables structured analytics workflows across marketing and finance teams.
Specialized & Niche Database Tools
These tools serve specific roles within modern enterprise architectures. Some extend database functionality. Others address operational or application-layer needs that traditional databases do not solve directly.
13. Improvado
Improvado is not a database engine. It is a marketing data foundation platform that sits upstream of databases and warehouses.
Enterprise marketing teams use Improvado to centralize data from hundreds of marketing, CRM, ecommerce, and revenue systems. It automates API ingestion, schema normalization, metric standardization, and governance before data reaches Snowflake, BigQuery, Redshift, or other warehouses.
This layer eliminates manual exports, inconsistent naming conventions, and broken attribution logic. It ensures that the database receives clean, analysis-ready data. For marketing organizations, this reduces reporting latency, improves metric consistency, and enables AI-ready datasets without engineering bottlenecks.
14. Microsoft Access
Microsoft Access is a desktop-based database tool designed for small-scale applications and departmental use.
It allows non-technical users to create basic relational databases, forms, and reports. In enterprise marketing contexts, Access is occasionally used for localized tracking projects or temporary data workflows. It is not suitable for large-scale, multi-user, or real-time analytics environments.
15. Claris FileMaker
Claris FileMaker is a low-code development platform with an embedded relational database.
It enables teams to build custom internal tools, workflow applications, and lightweight data systems without full-scale engineering resources. In marketing departments, it may support internal project tracking, asset management, or operational workflows. It is best suited for controlled environments with moderate data complexity.
16. CockroachDB
CockroachDB is a distributed SQL database built for cloud-native resilience.
It combines relational consistency with horizontal scalability and automatic failover. It is designed to maintain uptime across server or region failures without manual intervention.
For marketing technology providers or global ecommerce platforms, CockroachDB supports always-on transactional systems. It is particularly relevant where customer data, order processing, or real-time personalization must remain available across regions.
The Role of Database Software in Marketing Analytics
Database software is the execution layer behind attribution models, segmentation, forecasting, and ROI analysis. Advertising platforms, CRM systems, ecommerce engines, and analytics tools generate large volumes of data in different formats. A database management system stores, structures, and makes that data queryable at scale.
Without a strong DBMS, data remains fragmented. Queries become slow. Metrics become inconsistent. Cross-channel analysis becomes unreliable. A centralized database or warehouse enables structured joins across campaigns, customers, transactions, and costs. This is the foundation for lifetime value modeling, margin analysis, and multi-touch attribution.
However, a DBMS does not solve data ingestion or normalization. Raw marketing data arrives with inconsistent schemas, naming conventions, currencies, and timezones. API limits, refresh schedules, and schema changes create additional complexity.
This is where Improvado connects directly to the database layer.
Improvado automates data extraction from hundreds of marketing and revenue platforms. It standardizes schemas, aligns metric definitions, resolves identifiers, and applies transformations before or inside the warehouse.
The result is structured, analysis-ready data stored directly in systems such as Snowflake, BigQuery, or other DBMS environments.
Conclusion
Database software decisions now directly impact analytics speed, governance control, and AI readiness. A DBMS must support scalable querying, reliable performance, and structured data modeling under growing workload pressure. Without disciplined ingestion and standardization, even a high-performance database becomes fragmented and difficult to trust.
That is where the connection becomes critical. The database delivers storage and computational scale. Improvado ensures that the data flowing into it is standardized, governed, and transformation-ready. Together, they create a controlled analytics backbone that supports attribution, performance modeling, and AI-driven workflows without manual pipeline maintenance.
Request a demo to see how Improvado strengthens your database architecture for measurable impact.
.png)




.png)
