If you're a marketing leader, you know the pressure: proving the ROI of every campaign, optimizing spend, and making strategic decisions that drive growth. But what happens when the data you rely on is flawed?
Inaccurate, inconsistent, or incomplete data can lead to misguided strategies, wasted budgets, and a fundamental lack of trust in your analytics. It’s a challenge that undermines the very foundation of a data-driven organization.
Without a clear framework for ensuring your data is trustworthy from the moment it’s created, you’re operating with a significant handicap. How can you confidently report on performance, allocate resources, or justify your team’s impact to the C-suite? The answer lies in establishing and maintaining robust data integrity.
This article will break down the core concepts of data integrity, explore its different types, and provide a clear roadmap with actionable best practices to ensure your data is a reliable asset, not a liability.
Key Takeaways
- Data integrity is the overall accuracy, consistency, reliability, and completeness of data throughout its lifecycle, from creation to deletion.
- It is crucial for informed decision-making, regulatory compliance (like GDPR and HIPAA), data security, and maintaining customer trust.
- Data integrity is divided into Physical Integrity (protecting data from physical harm) and Logical Integrity (ensuring data makes sense in its context), which includes domain, entity, referential, and user-defined integrity.
- Key methods to ensure data integrity include data validation, implementing strict access controls, data encryption, regular backups, and maintaining audit trails.
- Common risks include human error, system failures, cyberattacks like malware and ransomware, and transfer errors.
What is Data Integrity?
Why Is Data Integrity Important?
Maintaining data integrity isn't just a technical task for IT departments; it's a strategic imperative that impacts every part of the business. When data integrity is compromised, the consequences can range from minor operational hiccups to catastrophic financial and reputational damage.
Enables Accurate, Data-Driven Decision-Making
Reliable data is the foundation of sound business strategy. When you can trust your data, you can confidently make critical business decisions about budget allocation, product development, and market expansion. High-integrity data provides accurate, data-driven insights, preventing the costly errors that arise from acting on flawed information.
Ensures Regulatory Compliance
In today's regulatory landscape, data integrity is non-negotiable. Regulations like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) mandate strict rules for how organizations handle sensitive data and personally identifiable information (PII). Maintaining data integrity is essential for meeting these requirements and avoiding severe penalties.
Strengthens Data Security
Data integrity and data security are closely linked. While data security focuses on protecting data from unauthorized access, data integrity ensures that the data itself is reliable and has not been tampered with. Strong integrity measures help protect against a data breach and other cyber threats by making it harder for malicious actors to alter or corrupt critical information without detection.
Builds Customer Trust and Protects Reputation
How you handle customer data directly impacts their confidence in your brand. A data integrity failure, such as sending a customer an invoice for something they didn't buy, can quickly erode trust. Consistently accurate and reliable data handling demonstrates professionalism and respect for customers, strengthening your brand's reputation.
Improves Operational Efficiency
Clean, consistent, and reliable data streamlines business processes. When your teams have access to high-integrity data, they spend less time validating numbers, troubleshooting errors, and reconciling conflicting reports. This frees them up to focus on strategic analysis and execution, boosting overall operational efficiency.
Data Integrity vs. Data Quality vs. Data Security
While these terms are often used together, they refer to distinct concepts. Understanding the difference is key to building a comprehensive data strategy.
- Data Integrity: This is the broadest concept, referring to the validity and trustworthiness of data throughout its lifecycle. It is the result of effective data quality and data security measures. It ensures data is whole, accurate, and consistent.
- Data Quality: This is a subset of data integrity that focuses on the condition or state of the data. It measures attributes like completeness, accuracy, timeliness, and relevance to its intended purpose. You can have high-quality data that is incorrectly formatted (a data integrity issue).
- Data Security: This focuses on protecting data from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, alteration, or destruction. Its goal is to maintain confidentiality and prevent external or internal threats. You can have perfectly secure data that is full of errors (a data quality issue).
Here’s a more detailed look at the difference between the three concepts.
| Aspect | Data Integrity | Data Quality | Data Security |
|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | Ensures data remains accurate, consistent, and unaltered throughout its lifecycle; reliability of data as it moves across systems. | Accuracy, completeness, timeliness, and consistency of data values; fitness for analysis and decision-making. | Protection from unauthorized access, breaches, or misuse via policies, encryption, and access controls. |
| Primary Goal | Maintain consistency and accuracy across sources, pipelines, and transformations. | Ensure data is correct, relevant, and usable for its intended purpose. | Safeguard confidentiality, integrity, and availability against threats. |
| Focus Area | Consistency and validation during collection, transfer, and storage. | Correctness, completeness, and freshness in analytics and reporting. | Protection, compliance, and governed access. |
| Common Practices | Referential integrity checks, schema enforcement, version control, audit trails. | Data profiling, deduplication, enrichment, error detection and correction. | Encryption (at rest/in transit), role-based access control, key management, SOC 2/GDPR controls. |
| Primary Risk if Neglected | System misalignment and corrupted datasets leading to unreliable analytics. | Poor decisions driven by inaccurate or incomplete insights. | Breaches, compliance violations, and reputational damage. |
| Measurement Metrics | Consistency rate, checksum validation, schema drift detection. | Accuracy score, completeness rate, timeliness ratio, error rate. | Security incident count, access compliance rate, encryption coverage. |
| Typical Ownership | Data engineering and governance teams. | Data operations and analytics teams. | IT security and compliance teams. |
| Relationship to Others | Builds on quality and security to ensure trustworthy data flow. | Depends on integrity for consistent inputs; enabled by security for safe access. | Foundational for preserving integrity and protecting high-quality data. |
Types of Data Integrity Explained
Data integrity can be broken down into two main categories — physical and logical — with logical integrity further subdivided into specific types of constraints within a database.
Physical Integrity
Physical integrity is concerned with protecting data from external factors that could compromise its storage and retrieval. This includes safeguarding the physical storage hardware from events like power outages, natural disasters, hardware failures, or even dust and corrosion.
Measures like uninterruptible power supplies (UPS), redundant hardware, and climate-controlled data centers are all part of maintaining physical integrity.
Logical Integrity
Logical integrity ensures that data remains accurate and consistent as it is used and modified within a relational database. It enforces rules to maintain the logical correctness of the data in a specific context. There are four primary types of logical integrity:
- Domain Integrity: Domain integrity ensures that all values within a column of a database table are valid and adhere to a specific format, type, and range. For example, a "Date" column should only contain valid dates, a "Phone Number" column should follow a defined numeric format, and a "Country" field might be restricted to a predefined list of countries. These integrity constraints prevent incorrect data entry.
- Entity Integrity: Entity integrity ensures that every row in a table is unique and identifiable. This is achieved by using a primary key – a unique identifier for each record (e.g., a Customer ID or Order Number). The entity integrity rule states that the primary key value cannot be null (empty), guaranteeing that every record can be uniquely referenced.
- Referential Integrity: Referential integrity is crucial for maintaining consistency between related data sets in a relational database. It uses a foreign key to ensure that a value in one table references an existing primary key in another table. For example, if an "Orders" table has a "CustomerID" column (a foreign key), referential integrity ensures that any CustomerID entered in that table must already exist in the "Customers" table. This prevents "orphan" records, such as an order with no associated customer.
- User-Defined Integrity: User-defined integrity involves custom rules and constraints set by an organization to meet specific business requirements not covered by the other types. These are business-specific rules that the database enforces. For example, a business might create a rule that a customer cannot place a new order if their account has an outstanding balance over $1,000.
10 Best Practices for Maintaining Data Integrity
Achieving and maintaining data integrity requires a proactive, multi-faceted approach. Here are ten actionable best practices your organization can implement.
1. Implement Data Validation and Verification
Ensure data is correct at the point of entry. Use data validation checks to confirm that new data conforms to predefined formats, ranges, and rules. Verification involves cross-checking data against a trusted source to confirm its accuracy.
2. Use Strict Access Controls
Implement role-based access control (RBAC) and the principle of least privilege to ensure users can only access and modify the data necessary for their roles. Using tools like multi-factor authentication (MFA) adds another layer of security to prevent unauthorized access.
3. Encrypt Data at Rest and in Transit
Encryption scrambles sensitive data, making it unreadable to anyone without the proper decryption key. Encrypting data both when it's stored (at rest) and when it's moving between systems (in transit) safeguards it from unauthorized modification or theft.
4. Create Regular Backup and Recovery Strategies
Data loss or corruption can happen unexpectedly. Implement automated, regular backups of all critical data, with copies stored both on-premises and off-site. Regularly test your recovery procedures to ensure you can quickly restore data in the event of a failure.
5. Maintain Detailed Audit Trails and Logs
Keep a detailed audit trail that logs all changes made to data, including who made the change, what was changed, and when. These logs are invaluable for tracking down the source of errors, identifying unauthorized activity, and satisfying compliance requirements.
6. Establish Robust Error Handling Procedures
Use automated tools like checksums and error-correcting algorithms to detect and flag inconsistencies or errors in your data. Having a clear procedure for handling these errors ensures they are addressed quickly and efficiently before they can impact business processes.
7. Educate the Workforce
Human error remains one of the biggest threats to data integrity. Conduct regular training for all employees on data entry best practices, the importance of data governance, and security awareness to minimize accidental data deletion or modification.
8. Remove Duplicate and Obsolete Data
Periodically cleanse your databases to remove duplicate records and obsolete information. This not only improves data accuracy but also enhances system performance and reduces storage costs.
9. Establish a Data Governance Policy
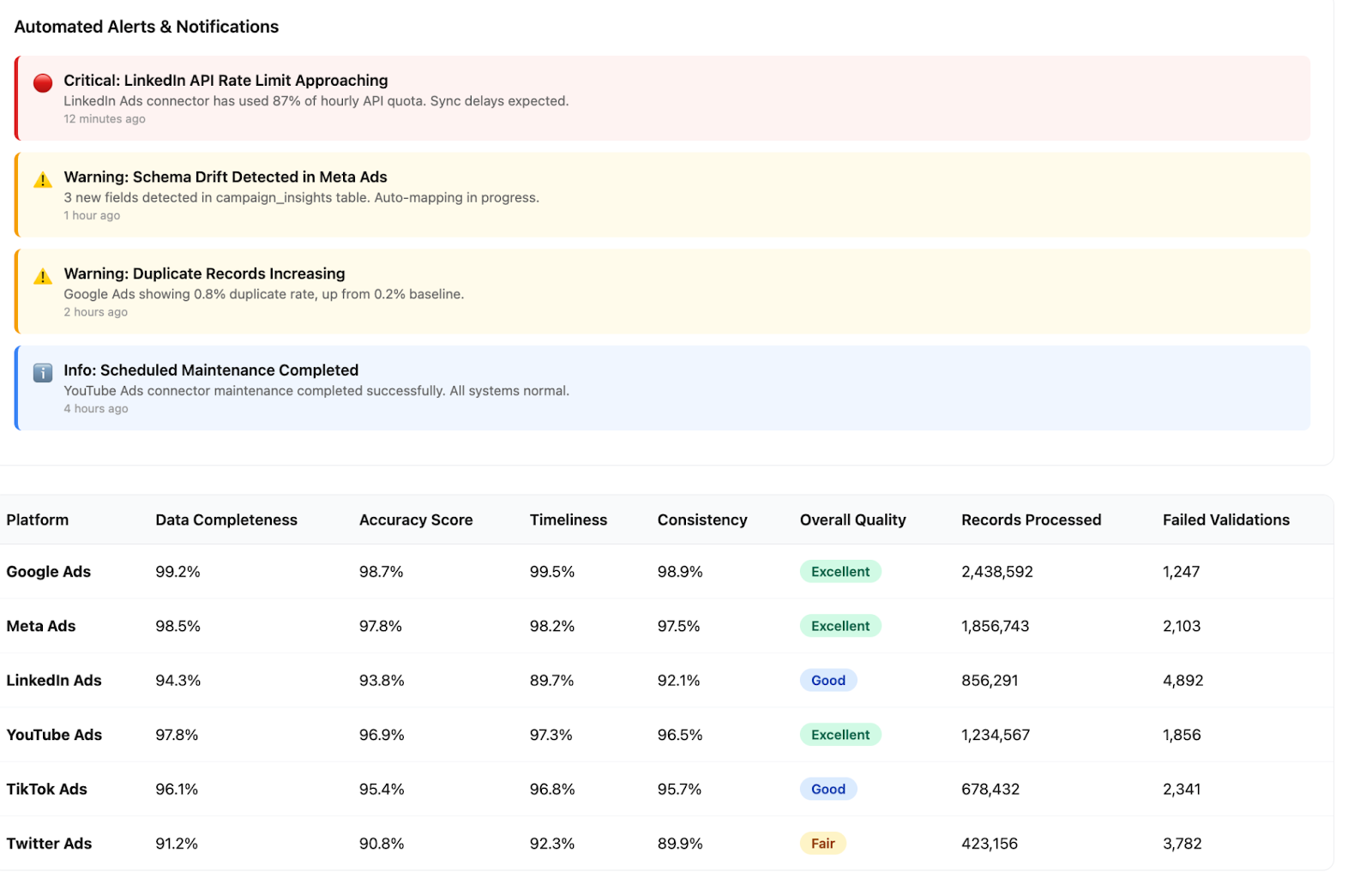
Create and enforce a formal data governance policy that defines clear rules, roles, and responsibilities for managing data throughout its lifecycle. This policy should standardize how data is collected, stored, used, and protected across the organization. Automated platforms like Improvado are designed to handle these processes at scale, performing data validation and normalization during integration to ensure a clean, reliable dataset.
10. Conduct Regular Security Assessments
Proactively identify and address vulnerabilities in your systems by conducting regular security assessments, such as penetration testing and vulnerability scans. This helps you stay ahead of potential cyber threats that could compromise your data.
Common Threats to Data Integrity
Despite best efforts, several common threats can compromise data integrity. Awareness is the first step toward mitigation.
Key threats include:
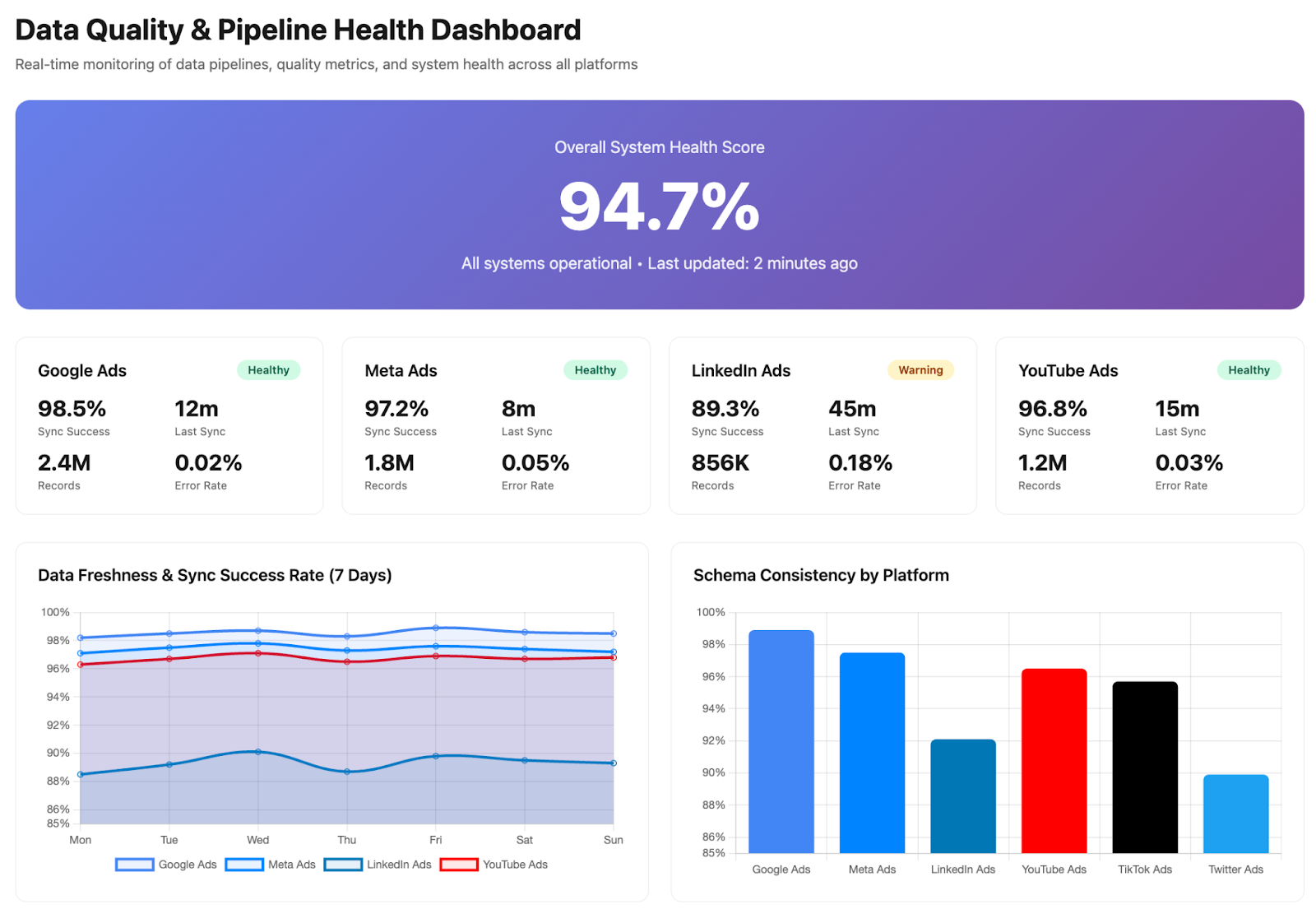
- Human error: Manual uploads, incorrect data mappings, or misconfigured transformations remain the leading causes of integrity loss. Even minor discrepancies in metric naming, date ranges, or schema definitions can cascade into large-scale reporting inconsistencies.
- System and hardware failures: Unplanned outages, software bugs, or failed API calls can interrupt data ingestion or transformation jobs. When writes or syncs fail mid-process, records may become incomplete or misaligned across platforms.
- Cyberattacks and unauthorized access: Ransomware, SQL injection, or credential misuse can alter, encrypt, or delete critical marketing data. Beyond direct manipulation, unauthorized edits and untracked changes create blind spots that undermine auditability.
- Transfer and synchronization errors: Data frequently travels between ad platforms, CRMs, data warehouses, and BI tools. Interruptions, format mismatches, or rate-limit issues during transfer can lead to duplication, truncation, or corrupted tables.
- Version drift and unmonitored transformations: As pipelines evolve, schema updates and transformation logic can fall out of sync between environments, leading to subtle but compounding inconsistencies in calculated metrics or attribution models.
- Third-party dependency failures: Reliance on multiple APIs and external connectors increases exposure to rate limits, schema updates, or deprecations that silently break pipelines and distort results downstream.
The strongest defense against these integrity threats is automation and observability. Improvado enforces data integrity across every stage—automating extraction, standardization, and validation while continuously monitoring for schema drift, API changes, and sync failures. By minimizing manual intervention and establishing audit-ready lineage across marketing and sales data, Improvado ensures analytics teams can trust the accuracy and consistency of every dataset they use for decision-making.
Understanding the Principles of Data Integrity (ALCOA+)
In regulated industries, data integrity is often measured against the ALCOA+ framework. These principles provide a useful checklist for ensuring data is robust and trustworthy.
- Attributable: Data should be traceable to the person or system that generated it.
- Legible: Data must be readable and understandable throughout its lifecycle.
- Contemporaneous: Data should be recorded at the time the work is performed.
- Original: The data should be the first-hand source or a certified true copy.
- Accurate: The data must be correct, truthful, and reflect the actual event.
- Complete: All necessary data is present, with nothing missing.
- Consistent: Data is presented in a consistent format and sequence.
- Enduring: Data is stored on durable media that will last throughout its required retention period.
- Available: Data can be accessed for review whenever needed.
How Improvado Ensures Data Integrity for Marketing Analytics
For marketing organizations drowning in data from hundreds of platforms, maintaining data integrity is a massive challenge. Manually collecting, cleaning, and consolidating this data is not only time-consuming but also prone to human error and transfer errors.
This is where Improvado provides a powerful, automated solution.
Automated Data Integration and a Single Source of Truth
Improvado’s automated data pipelines connect directly to over 500 marketing sources, eliminating the manual data handling that leads to human error and transfer errors.
By aggregating all your data into a single, unified repository, Improvado creates a single source of truth, ensuring everyone in the organization is working from the same reliable, up-to-date dataset.
Built-in Data Validation and Normalization
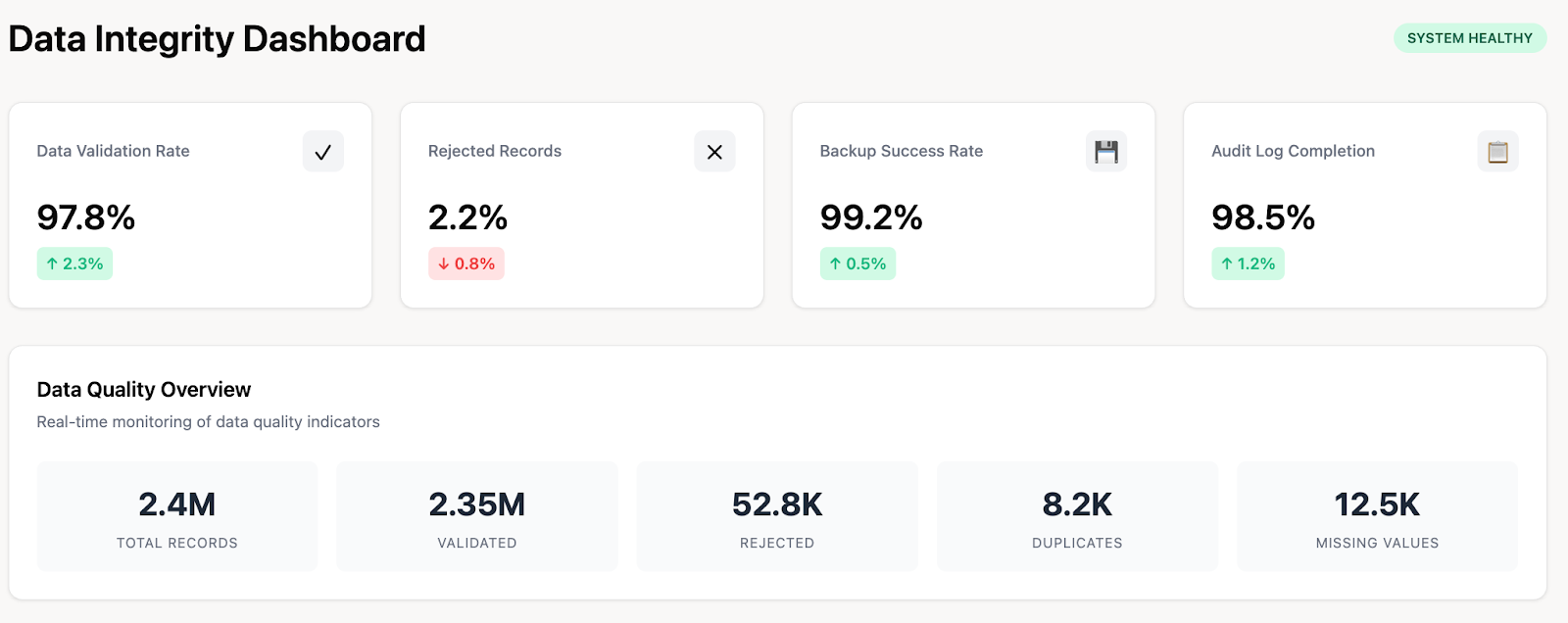
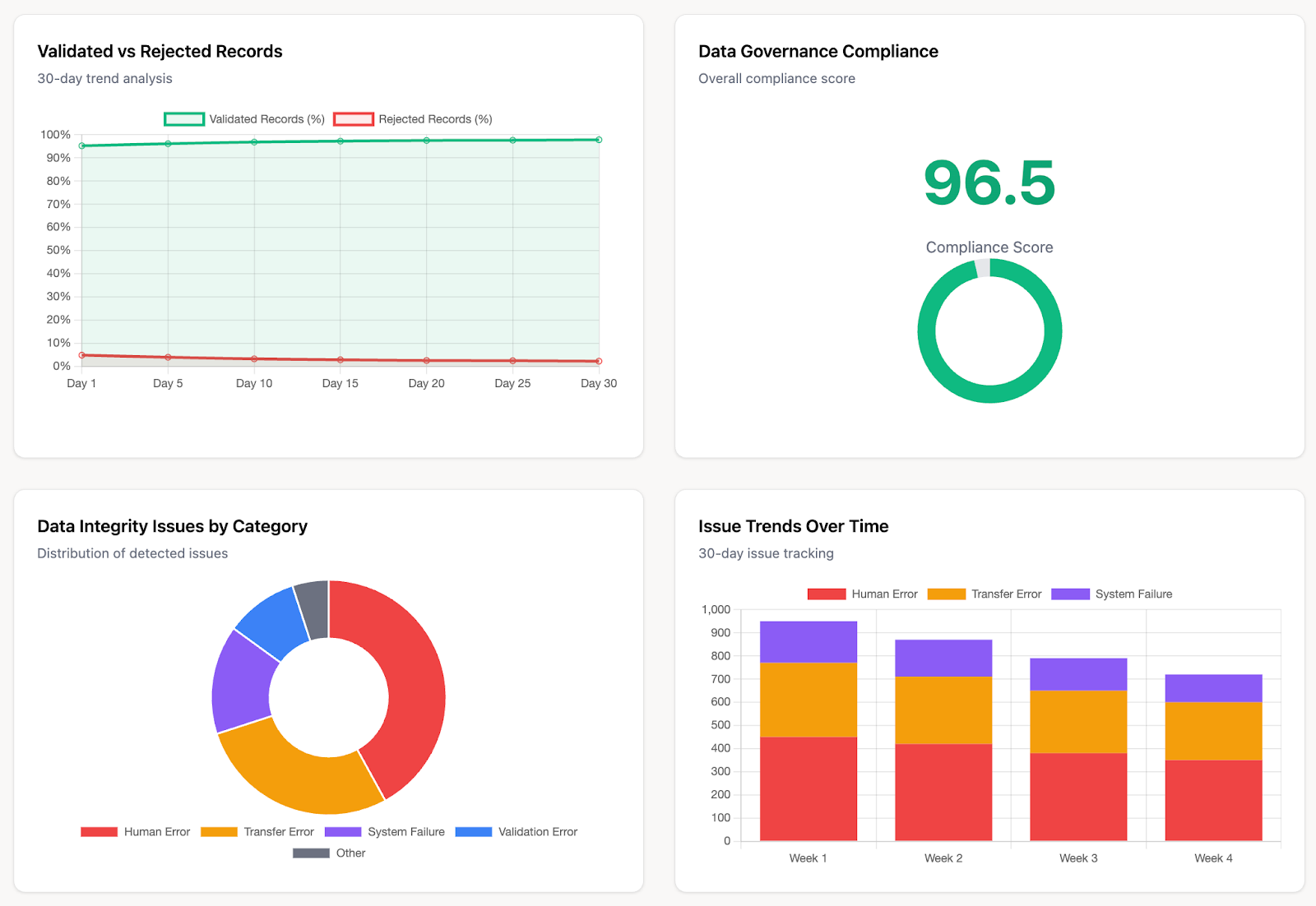
The platform automatically cleanses, maps, and standardizes data as it's integrated. This built-in data validation and normalization process resolves inconsistencies in naming conventions, currency, and formatting across different platforms, guaranteeing superior data quality and consistency for accurate analytics.
Enterprise-Grade Security and Governance
Improvado is compliant with SOC 2, HIPAA, and GDPR, providing enterprise-grade security and governance features. This aligns directly with the data security and regulatory compliance principles discussed earlier, ensuring your sensitive marketing and customer data is protected according to the highest industry standards.
.png)





.png)
