Marketing leaders are under mounting pressure to prove impact and optimize spend in an environment where data fragmentation, rising acquisition costs, and stricter privacy regulations complicate decision-making. Without a unified analytics strategy, teams risk inefficient budgets, misaligned targeting, and missed opportunities to drive sustainable growth.
This article examines advanced marketing analytics techniques that enable leaders to address these challenges head-on. We’ll explore how to centralize and govern marketing data, accurately measure ROI, and generate insights that power segmentation, targeting, and personalization at scale.
Why Marketing Analytics Matters in 2026
Marketing teams are operating in an era of unprecedented complexity, where the number of channels, tools, and customer touchpoints has grown exponentially. This creates a constant challenge: how to connect fragmented data into a cohesive view of performance and customer behavior.
The majority of consumer interactions are shaped by data-driven personalization, making analytics a critical driver of competitive advantage. Organizations that harness advanced analytics are positioned to deliver precise targeting, optimize spend, and adapt quickly to market changes.
Despite this potential, adoption remains uneven. Research shows that analytics influences only about 54% of marketing decisions, often due to siloed systems, inconsistent data governance, and a lack of visibility across teams.
This gap between what’s possible and what’s executed represents a major opportunity.
Marketing leaders who prioritize robust analytics strategies can close this gap, transforming disconnected data into actionable insights that directly drive growth, efficiency, and measurable ROI.
Establish a Unified Marketing Data Foundation
The foundation of all analytics is a unified data platform.
Without a unified view, teams face conflicting reports and spend time debating whose numbers are correct instead of optimizing campaigns. Gartner estimates poor data quality costs organizations $13 million annually, much of it tied to inconsistent metrics and misaligned reporting.
Automation is key to solving this problem.
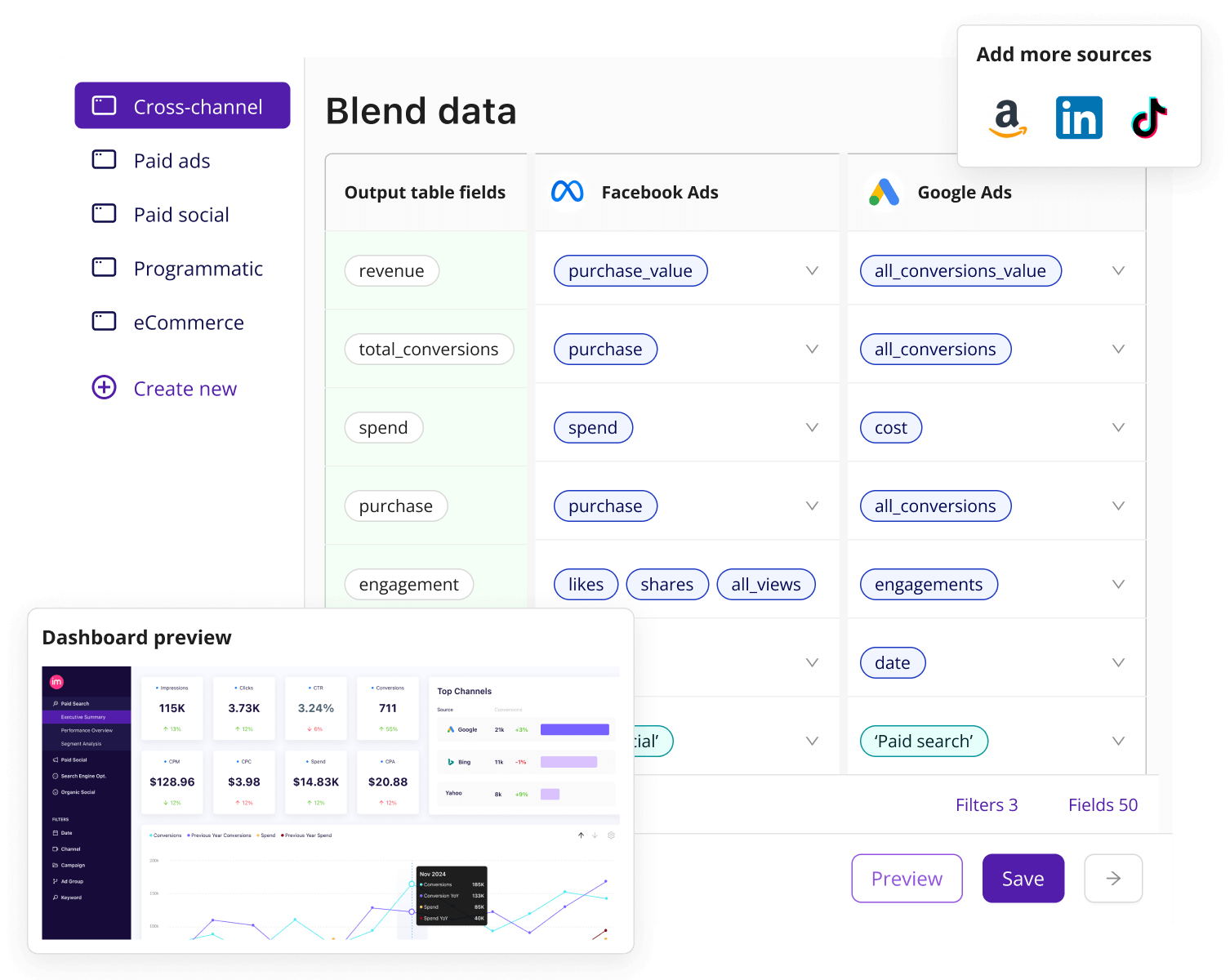
Analysts often spend 60–80% of their time cleaning data instead of analyzing it. Improvado helps eliminate this bottleneck by connecting to over 500 marketing and sales data sources and applying automated transformations to prepare data for analysis. Once harmonized, data can be fed directly into your data warehouse or BI tool of choice for advanced reporting and visualization.
For teams looking to move even faster, Improvado offers BI enablement features, ensuring datasets are clean, analysis-ready, and optimized for tools like Looker, Tableau, and Power BI.
In addition, its AI Agent allows teams to generate dashboards, reports, and insights using simple language prompts—no SQL or manual setup required—giving marketers faster access to actionable intelligence without relying on engineering resources.
With Improvado, marketing teams gain a trusted data foundation that scales as their stack grows. New channels can be onboarded quickly, reporting remains consistent, and governance stays intact—all while freeing analysts to focus on driving growth and improving campaign performance.
15 Key Marketing Analytics Techniques
Once you have a solid data foundation, you can apply specific techniques to solve business challenges. These methods fall into four categories: strategic modeling, market analysis, performance optimization, and data-centric methods.
Strategic Modeling Techniques
These techniques provide a macro-level view of how marketing contributes to revenue and long-term growth.
1. Marketing Mix Modeling (MMM)
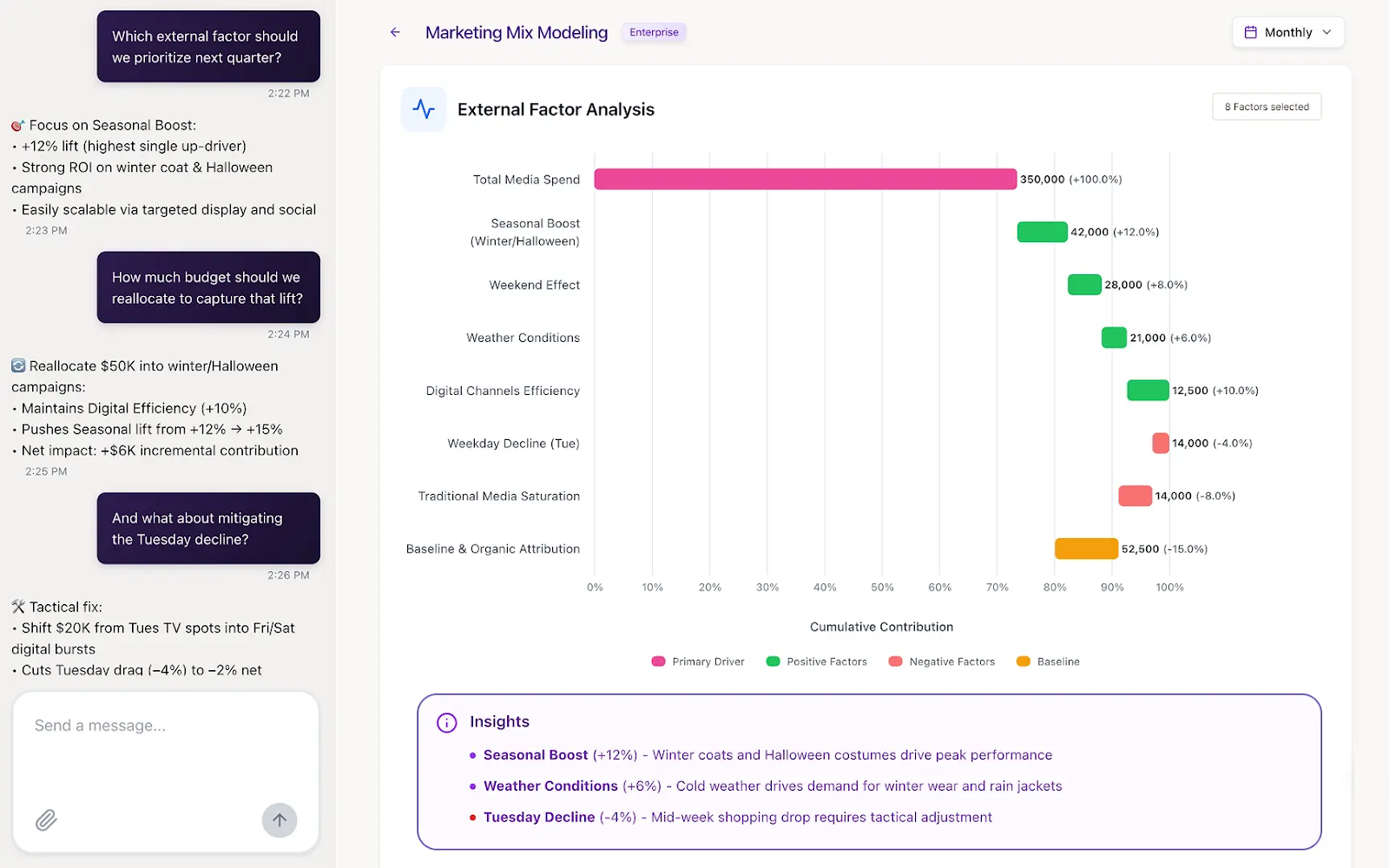
MMM uses statistical modeling to quantify the incremental impact of each marketing channel, both online and offline, on key business outcomes such as revenue, customer acquisition, or market share.
Unlike multi-touch attribution, MMM takes a holistic view by incorporating external variables like seasonality, pricing changes, promotions, and competitor activity, giving leaders a clearer picture of true channel performance.
- Use Case: A national consumer brand uses MMM to evaluate its full marketing portfolio and discovers that digital video delivers a significantly higher incremental ROI than in-store advertising. This insight allows the team to reallocate spend toward more effective channels while maintaining balance across the mix.
- Risk if Ignored: Without MMM, budgets remain tied to historical allocations and legacy channels, leading to inefficient spend and missed opportunities to invest in emerging, higher-performing tactics. Over time, this erodes ROI and slows growth.
2. Marketing Attribution Modeling
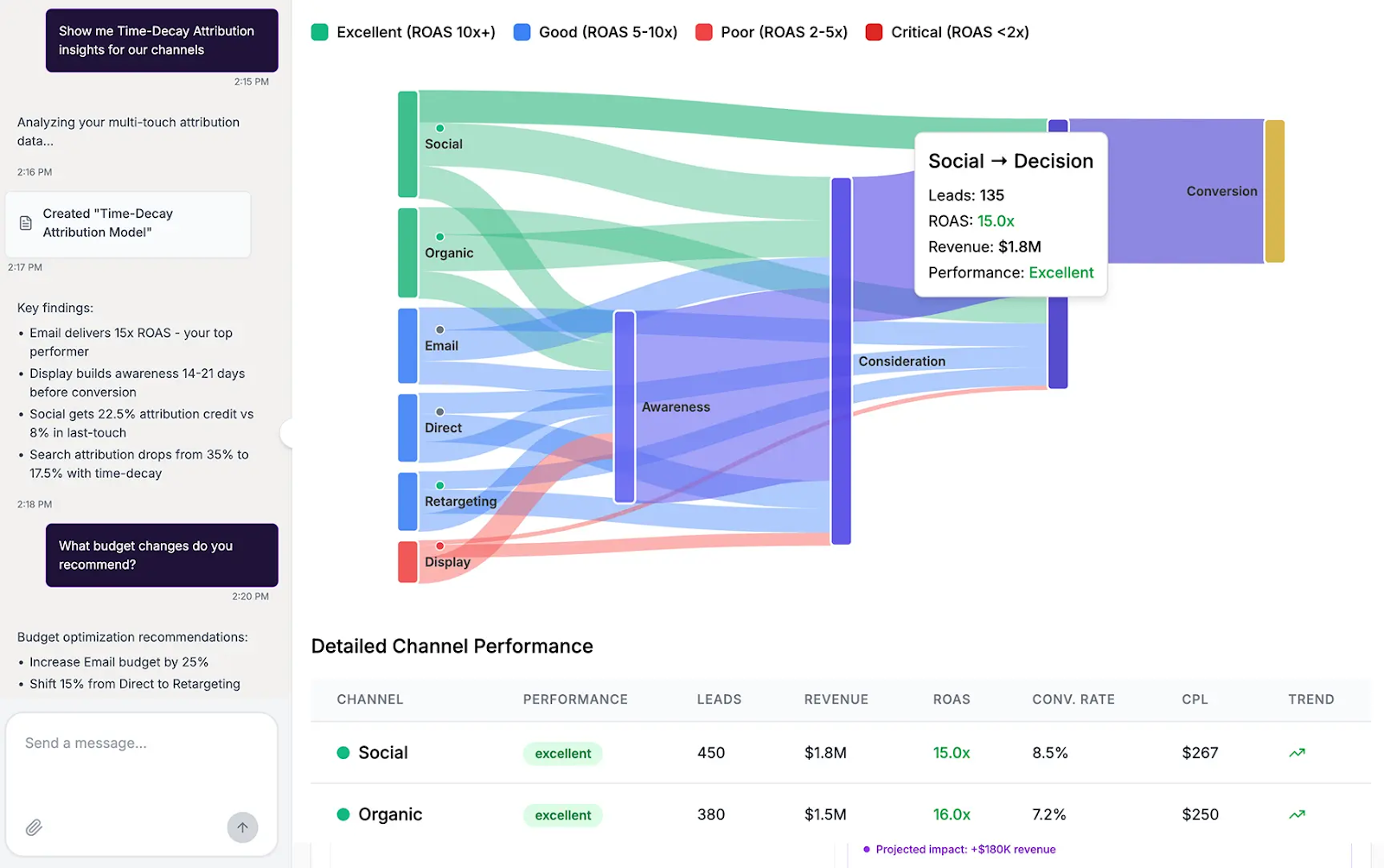
Multi-touch attribution (MTA) assigns proportional credit to all touchpoints a customer interacts with across their journey, rather than relying on a single click or conversion event.
This approach provides a more accurate view of how channels like display, search, email, and content marketing work together to influence conversions.
Unlike last-click models, MTA uncovers the combined impact of upper- and mid-funnel activities on outcomes.
- Use Case: A SaaS company implements MTA and discovers that educational blog posts (first touch) and product demos (last touch) are the most influential drivers of conversions. With these insights, the team rebalances spend to support both awareness-building and conversion-focused activities.
- Risk if Ignored: Without MTA, budgets tend to favor last-click channels like branded search, while underfunding the earlier interactions that create demand. This leads to skewed reporting, inefficient spend, and a weakened acquisition pipeline over time.
3. Customer Lifetime Value (CLV) Analysis
CLV analysis estimates the total revenue a customer is expected to generate over the entire duration of their relationship with the company. It goes beyond one-time transactions to measure the long-term value of acquisition and retention efforts.
By factoring in purchase frequency, average order value, churn rates, and customer behavior patterns, CLV helps guide strategic decisions on marketing spend, segmentation, and retention tactics.
- Use Case: An e-commerce retailer analyzes CLV and finds that customers acquired through loyalty campaigns have a significantly higher lifetime value than those acquired via discount-driven ads. This insight leads the team to increase investment in retention and loyalty programs while reducing spend on low-value acquisition channels.
- Risk if Ignored: Without CLV analysis, marketing teams often optimize for short-term metrics like initial conversions or cost-per-acquisition (CPA). This can result in overspending on low-quality customers, underinvesting in retention, and ultimately reducing long-term profitability.
4. Demand Forecasting
Demand forecasting uses predictive analytics and historical data to anticipate future customer demand.
By understanding expected fluctuations, marketing teams can align budgets and campaigns with operational planning, ensuring that inventory, staffing, and supply chains are prepared to meet market needs.
This technique bridges marketing strategy with broader business operations to maximize efficiency and revenue impact.
- Use Case: A retailer leverages demand forecasting to predict a surge in seasonal apparel sales ahead of peak shopping periods. Armed with these insights, the marketing team proactively allocates budget to high-demand products, while operations scale inventory and staffing to match.
- Risk if Ignored: Without accurate forecasting, companies risk overspending during periods of low demand or facing stockouts during surges, leading to wasted marketing dollars, lost sales, and missed growth opportunities.
Market & Competitor Analysis Techniques
These techniques help organizations evaluate external forces shaping their performance. They uncover industry trends, benchmark competitors, and identify emerging risks or growth opportunities, enabling proactive strategy adjustments rather than reactive decisions.
5. Competitor Analytics
Competitor analytics involves tracking and analyzing competitor activities such as pricing, channel mix, campaign messaging, and share of voice. By benchmarking against competitors, marketing teams gain insights to adjust strategy, optimize spend, and identify emerging opportunities before they become mainstream.
This external perspective complements internal performance data to guide more informed decision-making.
- Use Case: A telecom provider monitors competitor ad spend and identifies a rapid increase in investment in a new digital channel. Acting early, the team reallocates budget to that channel, capturing market share before competitors fully establish their presence.
- Risk if Ignored: Without competitor analytics, companies risk falling behind in emerging markets or formats, reacting too late to shifts in customer behavior and losing share to faster-moving competitors.
6. Market Size Analytics
Market size analytics estimates the total addressable market (TAM) and quantifies potential revenue opportunities across products, regions, or customer segments.
This technique is critical for strategic planning, resource allocation, and market expansion decisions, helping teams prioritize investments where growth potential is highest.
- Use Case: A B2B SaaS company uses market size analytics to assess TAM in new geographic regions before launching localized campaigns. The analysis ensures marketing budgets align with realistic demand expectations and revenue potential.
- Risk if Ignored: Without market size analytics, organizations risk overestimating demand and over-committing resources, leading to costly missteps in new markets or underwhelming ROI on expansion efforts.
7. Brand Analytics
Brand analytics measures brand perception, awareness, recall, and share of voice across channels. It combines sentiment analysis, customer surveys, media tracking, and social listening to provide a comprehensive view of how audiences engage with and perceive the brand.
These insights guide messaging, positioning, and investment decisions to strengthen brand equity and protect reputation.
- Use Case: A global brand uses sentiment analysis to detect rising negative feedback in a specific region. By identifying the issue early, the team quickly adjusts messaging and campaigns to address concerns before they spread more broadly.
- Risk if Ignored: Without brand analytics, reputational issues can escalate undetected, only becoming visible once they begin to impact revenue and customer loyalty—making them more costly and difficult to resolve.
8. Unmet Needs Analytics
Unmet needs analytics identifies gaps in customer expectations and market offerings by analyzing qualitative data sources such as product reviews, support tickets, social media feedback, and community forums.
This technique helps marketing and product teams spot emerging trends, prioritize feature development, and align messaging with real customer pain points.
- Use Case: A software company analyzes customer feedback and discovers strong demand for a feature missing in competitors’ products. By addressing this need, the company gains a competitive advantage and strengthens customer loyalty.
- Risk if Ignored: Without unmet needs analytics, companies risk overlooking opportunities for innovation and retention, allowing competitors to capture dissatisfied customers and limiting long-term growth.
Pricing and Performance Techniques
Pricing and performance techniques focus on aligning spend with measurable outcomes. They evaluate how pricing models, budget allocation, and campaign efficiency impact profitability, ensuring every dollar invested delivers maximum return and sustainable growth.
9. Pricing Analytics
Pricing analytics evaluates price elasticity, customer behavior, and competitor positioning to determine the optimal pricing strategy. It combines historical sales data, multivariate testing, and market benchmarking to maximize revenue, margin, and competitiveness while adapting to changing market conditions.
- Use Case: An e-commerce company runs pricing experiments and finds that premium bundles generate higher revenue and retention than deep discount campaigns. The team adjusts its strategy to focus on value-driven offerings rather than aggressive discounting.
- Risk if Ignored: Without pricing analytics, businesses risk undervaluing products and eroding margins or losing market share to competitors with more strategic pricing models.
10. Trend Analysis
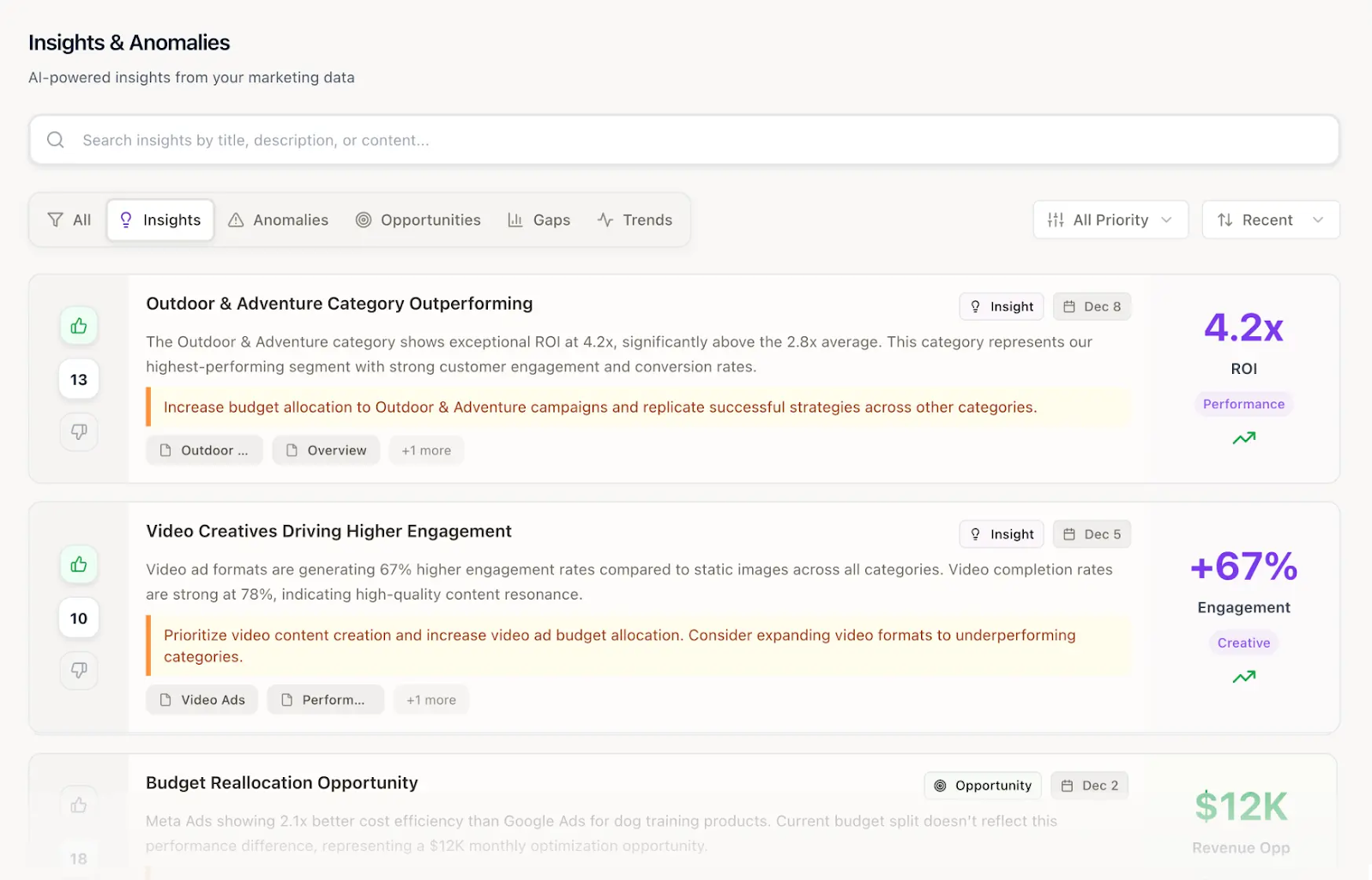
Trend analysis identifies patterns, seasonality, and emerging shifts in customer behavior by examining historical data across channels and time periods.
It enables marketing teams to anticipate demand changes, plan campaigns proactively, and align spend with market dynamics for maximum impact.
- Use Case: A travel brand uses trend analysis to spot early booking surges ahead of peak travel seasons. With this insight, the team reallocates budget and adjusts messaging to capture demand before competitors ramp up their efforts.
- Risk if Ignored: Without trend analysis, campaigns risk misalignment with market timing, leading to wasted budget, missed opportunities, and lower ROI.
11. Conversion Prediction
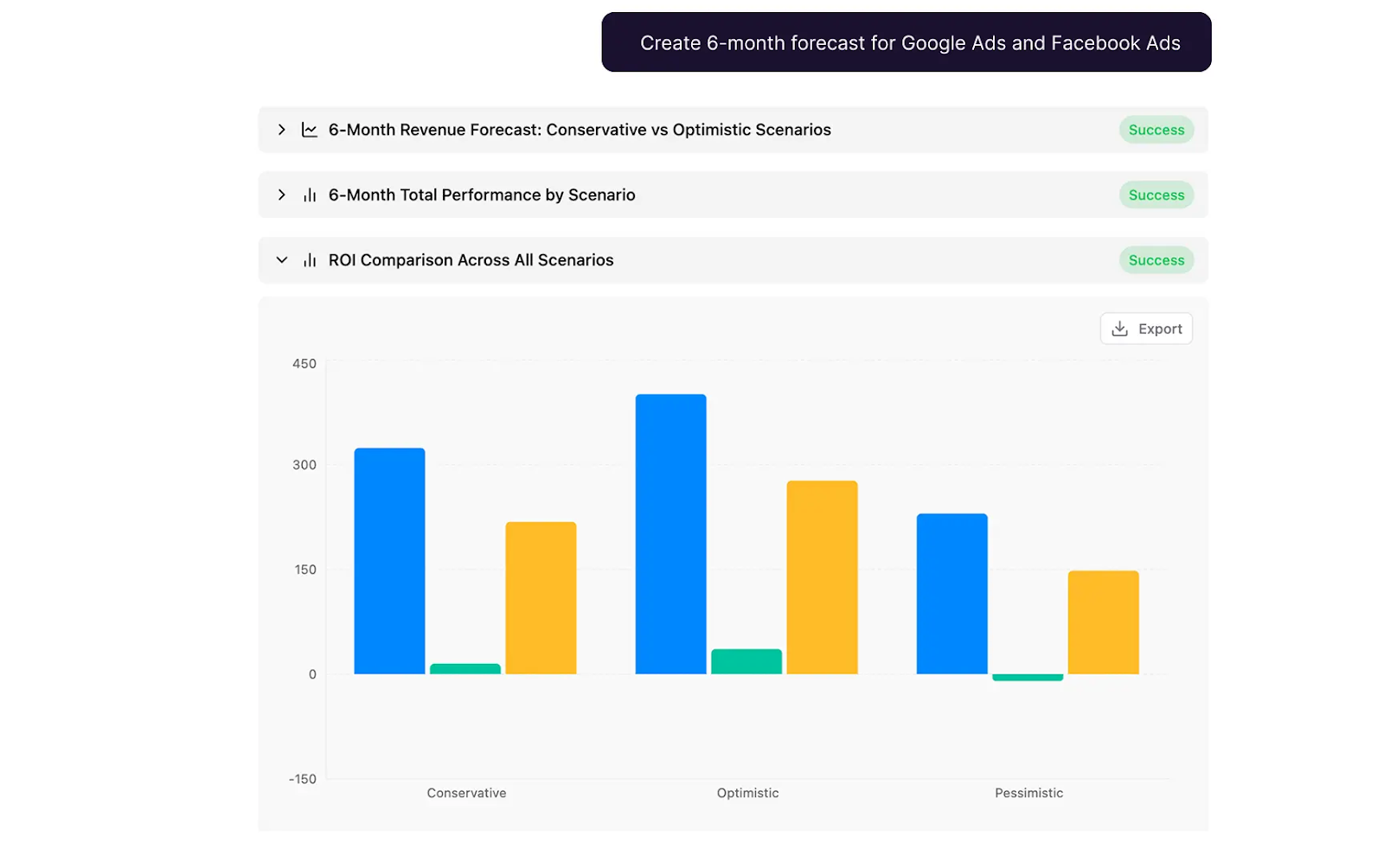
Conversion prediction uses machine learning models to assess the likelihood that a lead or user will complete a desired action, such as making a purchase, signing up, or requesting a demo.
By scoring prospects based on behavior, demographics, and engagement signals, marketing and sales teams can prioritize high-propensity opportunities and allocate resources more efficiently.
- Use Case: A financial services company applies conversion prediction models to rank incoming leads by likelihood to convert. Sales teams focus their outreach on the top tier of prospects, improving close rates and shortening the sales cycle.
- Risk if Ignored: Without conversion prediction, teams risk spending time and budget on low-intent prospects, reducing efficiency and missing opportunities to engage with the leads most likely to generate revenue.
12. Anomaly Detection
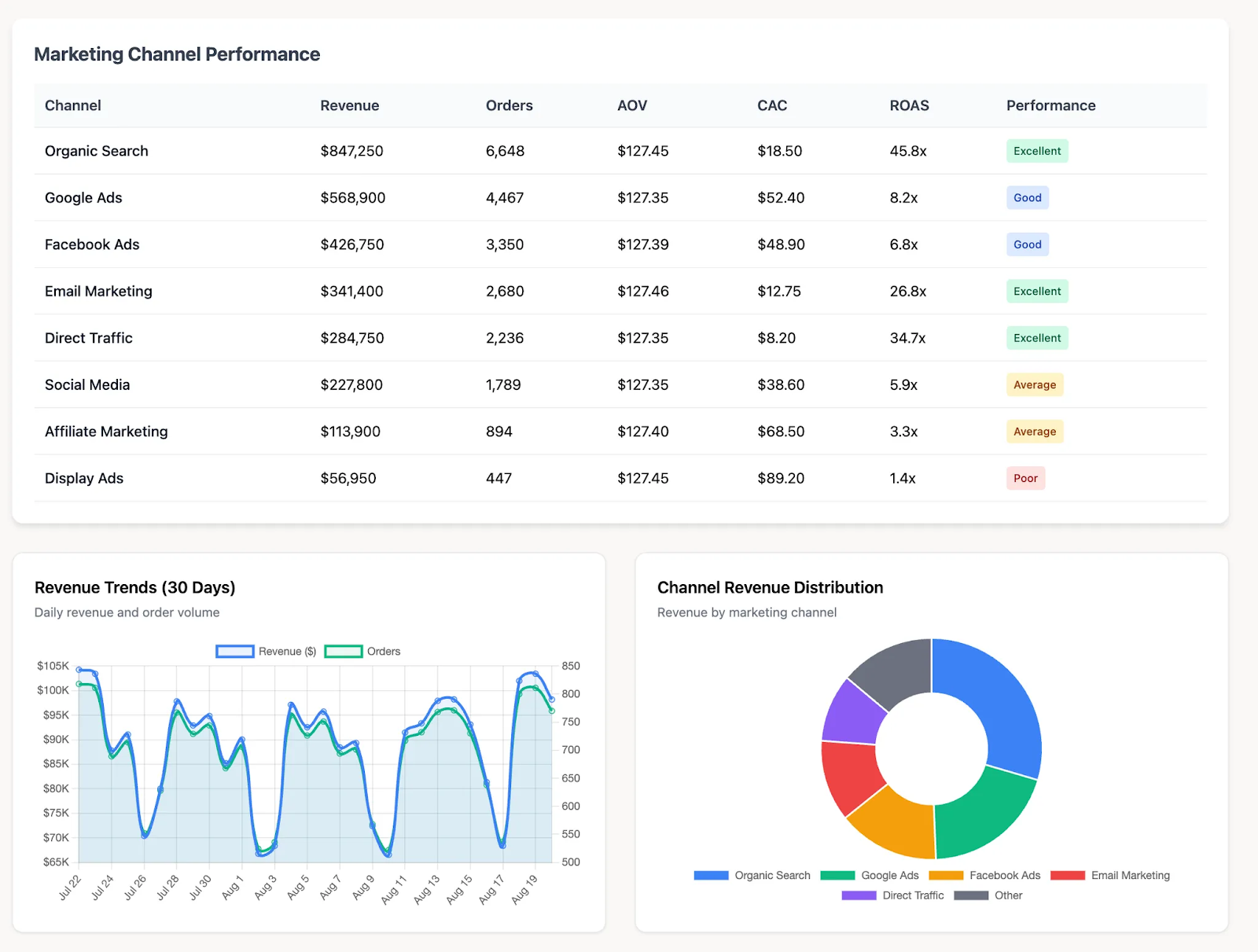
Anomaly detection uses statistical models and machine learning to identify outliers and unexpected changes in marketing performance data.
It helps teams quickly detect issues such as sudden cost spikes, drops in conversions, broken tracking pixels, or unusual traffic patterns, enabling rapid investigation and resolution before they escalate.
- Use Case: A retailer’s anomaly detection system flags a sudden drop in conversions caused by a broken tracking pixel. The alert allows the team to fix the issue immediately, preventing days of lost data and inaccurate reporting.
- Risk if Ignored: Without anomaly detection, critical issues can remain hidden for weeks, only surfacing during routine reporting cycles, leading to wasted spend, missed opportunities, and flawed performance insights.
Data-Centric Analytical Methods
Data-centric analytical methods provide the statistical backbone for advanced marketing models.
They focus on organizing, validating, and interpreting raw data to uncover patterns, correlations, and causality, forming the basis for predictive modeling, attribution, and optimization techniques.
13. Regression Analysis
Regression analysis quantifies the relationships between dependent and independent variables, making it a foundational technique for advanced marketing analytics and the core of Marketing Mix Modeling (MMM).
It enables teams to understand how changes in key inputs, such as ad spend, pricing, or promotions, affect outcomes like sales, revenue, or customer acquisition, providing statistical evidence to guide budget allocation and strategic planning.
- Use Case: An analyst builds a regression model to evaluate how shifts in ad spend across search, social, and TV impact overall sales performance. The results help marketing leaders optimize channel mix and forecast the effects of future budget decisions.
- Risk if Ignored: Without regression analysis, teams rely on assumptions rather than evidence, leading to inaccurate conclusions about cause-and-effect and potentially misallocating resources across campaigns and channels.
14. Customer Segmentation
Customer segmentation divides a customer base into distinct, meaningful groups based on shared characteristics such as demographics, behaviors, interests, or purchase history.
This technique allows marketers to tailor messaging, offers, and campaigns to each segment, improving engagement, conversion rates, and overall customer experience.
- Use Case: A streaming service segments its audience by viewing habits and engagement levels, then creates personalized campaigns for high-engagement segments, boosting retention and upsell opportunities.
- Risk if Ignored: Without customer segmentation, marketing efforts rely on generic, one-size-fits-all messaging, which reduces relevance, lowers conversion rates, and weakens long-term customer loyalty.
15. Content Analysis
Content analysis examines qualitative data sources such as customer reviews, support tickets, chat transcripts, and survey responses to identify themes, trends, and sentiment.
This technique helps marketing and product teams understand customer perceptions, uncover pain points, and guide improvements in messaging, user experience, and service delivery.
- Use Case: A brand analyzes support logs and customer reviews to identify recurring complaints about a complex onboarding process. Armed with this insight, the team simplifies UX flows and updates messaging to reduce friction and improve customer satisfaction.
- Risk if Ignored: Without content analysis, negative feedback can go unnoticed, leading to unresolved issues that hurt retention, damage brand perception, and ultimately impact revenue.
How to Implement a Marketing Analytics Strategy
Marketing analytics only delivers value when applied systematically. This five-step framework aligns analytics initiatives with business outcomes, ensuring every insight leads to measurable impact.
Step 1: Define Goals and KPIs
Defining precise goals and KPIs sets the foundation for a marketing analytics strategy that drives measurable results. Instead of starting with raw data, begin by clarifying business outcomes.
From there, translate these outcomes into measurable KPIs.
- For instance, revenue growth could tie to marketing-qualified leads (MQLs), return on investment (ROI), or customer acquisition cost (CAC).
- A focus on retention may require tracking lifetime value (LTV) or cohort retention rates.
These KPIs provide a tangible way to evaluate performance and link marketing activities directly to business impact.
Finally, establish benchmarks and thresholds.
Use historical data or industry standards to set realistic performance targets. This creates alignment across teams, ensuring everyone measures success using the same definitions.
Step 2: Centralize Marketing Data
Data silos prevent accurate, cross-channel analysis – consolidate all marketing, sales, and revenue data into a single source of truth.
- Unify all data sources: Consolidate marketing, sales, and revenue data into a single repository to eliminate silos and inconsistent reporting.
- Standardize and normalize metrics: Apply consistent naming conventions, taxonomies, and metric definitions across all platforms for accurate cross-channel analysis.
- Automate data integration: Use platforms like Improvado to connect 500+ marketing and advertising sources, automate ingestion, and manage API complexities at scale.
- Enable advanced analytics: A unified, clean dataset becomes the foundation for attribution modeling, predictive analytics, AI-driven insights, and real-time reporting.
Step 3: Choose the Right Analytical Techniques
Map the right analytical technique to each business question:
- Marketing Mix Modeling (MMM): Optimize budget allocation across channels and campaigns.
- Customer Lifetime Value (CLV): Identify high-value segments and guide retention strategies.
- Attribution Modeling: Assign credit to touchpoints across the customer journey.
- Descriptive Analytics: Review historical performance to establish trends and patterns.
Step 4: Select Tools for Execution
Use a layered tech stack that supports both data preparation and insight delivery:
- Platform-native tools: Google Analytics, Meta Business Suite, Salesforce Marketing Cloud.
- BI and visualization tools: Tableau, Power BI, Looker Studio for reporting and exploration.
- Unified analytics platforms: Improvado provides end-to-end functionality, from data integration and transformation to AI-powered insights and cross-channel reporting.
Step 5: Analyze, Report, and Act
At this stage, marketing analytics must move beyond observation. The goal is to convert raw data into decisions that drive measurable business outcomes.
This requires delivering insights in a format that stakeholders can understand and act on immediately, supported by continuous monitoring and optimization.
- Turn insights into action: Provide clear, context-driven recommendations rather than static reports or raw datasets.
- Leverage real-time visibility: Use live dashboards to monitor KPIs, identify anomalies, and detect emerging trends as they occur.
- Integrate AI-driven alerts: Deploy AI systems to automatically flag performance issues or growth opportunities, reducing the lag between detection and response.
- Close the feedback loop: Track the impact of decisions, measure results against defined KPIs, and refine strategies to continuously improve outcomes.
This approach ensures analytics is not just descriptive but becomes a core driver of operational excellence and revenue growth.
Overcoming Common Challenges
Even the most carefully designed marketing analytics strategy will encounter operational and technical hurdles.
These challenges can slow down decision-making, dilute data quality, and prevent analytics from driving real business value. Below are the most common barriers and expert solutions to address them effectively.
Challenge 1: Fragmented Data
Enterprise marketing teams often rely on dozens of platforms—ad networks, CRMs, analytics tools, and offline systems. When data is spread across these silos, it's nearly impossible to measure ROI accurately or maintain consistent reporting.
Challenge 2: Lack of Technical Resources
Advanced analytics techniques, such as marketing mix modeling, multi-touch attribution, and predictive modeling, traditionally required specialized data scientists and engineers.
Most marketing teams lack the bandwidth or budget to support these roles in-house.
Challenge 3: From Insights to Action
Generating insights is only half the battle. Many organizations struggle to translate analytics into tangible outcomes, leading to missed opportunities and wasted resources.
Data Foundation for Your Marketing Analytics
High-quality data is the cornerstone of advanced marketing analytics. Without a trusted data foundation, even the most sophisticated models, dashboards, and AI-driven insights will produce unreliable results.
Improvado unifies data from 500+ marketing and sales sources, applies standardized naming conventions, and ensures accuracy through automated governance and anomaly detection. This creates a single source of truth for reliable attribution, forecasting, and performance measurement.
Book a demo today to see how Improvado can power your marketing analytics with clean, consistent, and analysis-ready data.
.png)
.jpeg)



.png)
