As acquisition costs rise and data privacy limits expand, teams can’t rely on broad campaigns, they need targeted, trackable outreach that ties directly to revenue outcomes. Direct marketing meets that need when executed with disciplined data use, channel orchestration, and performance measurement across the funnel.
This guide outlines the fundamentals of effective direct marketing today, covering its benefits, key components, execution workflow, and evolving trends. It also explores how data integration, automation, and attribution modeling enable teams to scale personalization and quantify impact with greater accuracy.
Key Takeaways
- Direct Communication: Direct marketing eliminates intermediaries, speaking directly to a pre-selected target audience through channels like email, direct mail, social media, and telemarketing.
- Action-Oriented: Every direct marketing campaign includes a clear call to action (CTA) to prompt an immediate, measurable response from the potential customer.
- Highly Targeted & Personalized: Success relies on using customer data for precise segmentation, allowing for personalized messaging that boosts engagement and ROI.
- Measurable Results: Unlike mass advertising, direct marketing provides clear metrics like response rates and conversion rates, making it a cost-effective and data-driven marketing strategy.
- Key Channels: Common methods include email marketing, direct mail, SMS marketing, social media advertising, and telemarketing, each with unique advantages.
What Is Direct Marketing?
By leveraging customer data, marketers can create personalized and relevant marketing materials that speak directly to the needs and interests of potential customers, fostering a stronger connection and driving higher conversion rates.
Key Characteristics of an Effective Direct Marketing Campaign
A successful direct marketing strategy is built on several core pillars that distinguish it from other forms of advertising. These elements work together to create a powerful, results-oriented approach.
1. Targeted Audience Communication
The foundation of direct marketing is precision. It begins with identifying and segmenting a specific audience based on demographics, purchase history, online behavior, or other relevant customer data. This targeting ensures that marketing materials reach only the most likely potential customers, increasing efficiency and reducing wasted ad spend.
2. Personalized Messaging
Once the target audience is defined, the messaging can be tailored to their specific interests and needs. Personalization can range from using a consumer's name in an email to sending special offers based on past purchases. This one-on-one approach makes the recipient feel valued and understood, significantly boosting engagement.
3. Clear Call to Action (CTA)
Every piece of direct marketing material must include a clear and compelling call to action. Whether it's "Click Here to Buy Now," "Call Our Toll-Free Number," or "Scan this QR Code for 20% Off," the CTA tells the consumer exactly what to do next. This immediacy is crucial for generating a direct response.
4. Measurable Results and ROI
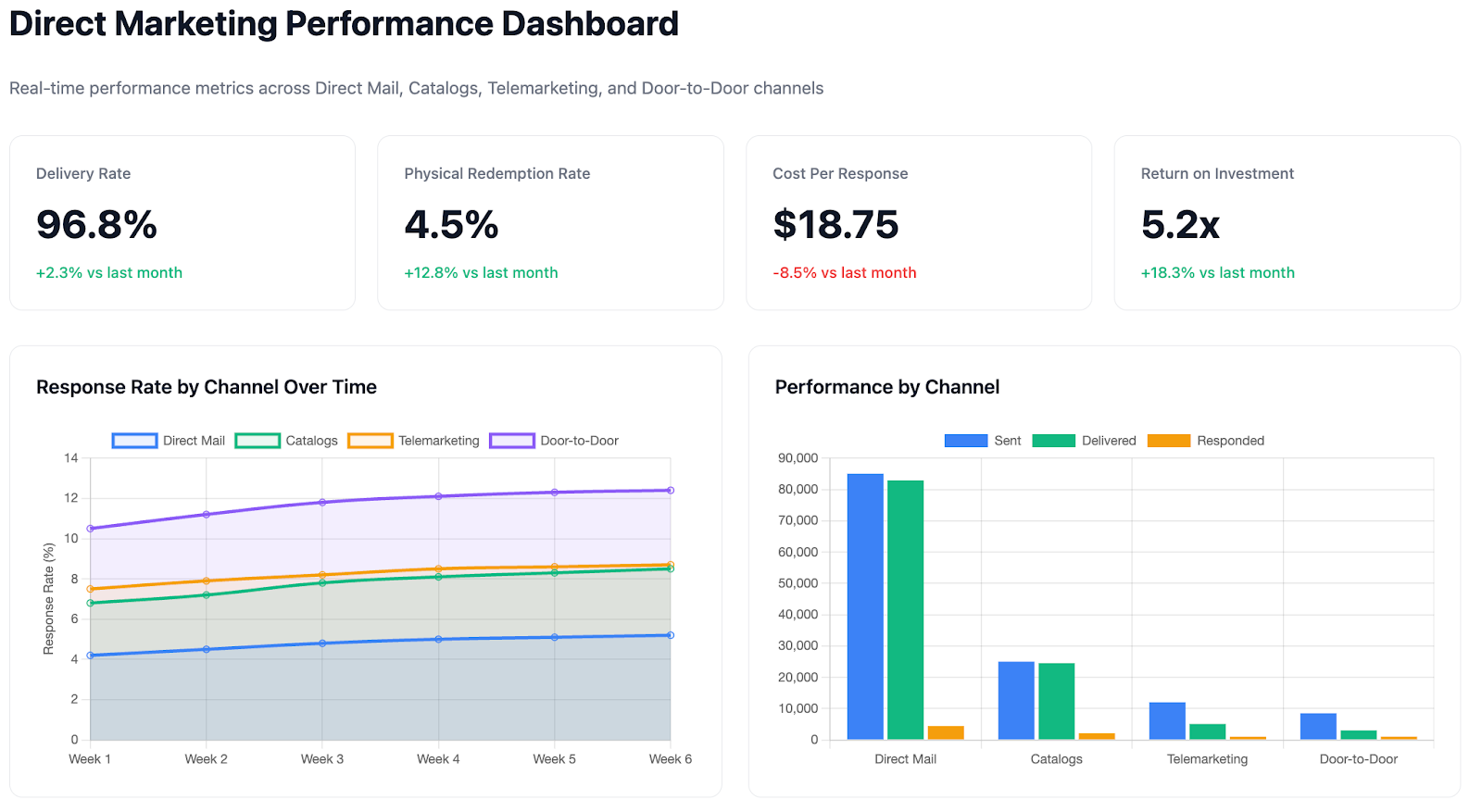
The true power of any direct marketing campaign lies in its measurability. Tracking response rates, conversions, and cost per acquisition is crucial. However, with multiple direct marketing channels running simultaneously, consolidating performance data becomes a major challenge for enterprise marketing teams.
Improvado solves this challenge by centralizing marketing performance data into a single, reliable environment. It automatically extracts and normalizes data from over 500 advertising, CRM, and automation platforms, aligning metrics and dimensions across campaigns and regions.
This unified dataset enables precise ROI measurement, cross-channel attribution, and revenue correlation, helping marketing and RevOps teams identify what drives conversion efficiency and optimize spend with complete transparency.
How Direct Marketing Works?
Direct marketing operates as a structured, data-driven feedback loop focused on precision targeting, personalization, and measurable performance.
The process starts with audience identification, aggregating customer and prospect data from CRM systems, purchase histories, and behavioral analytics. This dataset is then segmented using demographic, psychographic, or intent-based criteria to define high-probability conversion groups.
Next, marketers develop tailored messages and offers calibrated to each segment’s needs, preferences, and stage in the buying cycle. Campaigns are deployed through direct response channels, such as email, SMS, programmatic display, or personalized direct mail, where performance can be tracked at the individual or account level.
As responses and interactions are recorded, the data is analyzed to measure conversion efficiency, response velocity, and cost per acquisition. These metrics feed into ROI models that link engagement directly to revenue outcomes.
Insights from each cycle inform adjustments to audience selection, creative strategy, and channel mix, creating a continuous optimization loop that compounds effectiveness over time and strengthens attribution accuracy across the marketing ecosystem.
Common Types of Direct Marketing Channels
Direct marketing employs a diverse set of channels to reach consumers. While some are traditional, others leverage modern digital platforms, often working in concert for a comprehensive marketing campaign.
Direct Mail (Postcards, Catalogs, Flyers)
A classic yet still effective channel, direct mail involves sending physical marketing materials directly to a consumer's mailbox. This can include postcards with special offers, detailed catalogs, flyers, or personalized letters. In a digitally saturated world, a tangible piece of mail can stand out and capture attention.
Email Marketing
Email marketing is a cornerstone of digital marketing. By sending targeted and timely emails, businesses can engage audiences with news, promotions, or educational content. Success hinges on a clean, opt-in email list and compelling, personalized messaging that encourages clicks and conversions.
Telemarketing (Including phone calls and SMS/text messages)
Telemarketing involves contacting potential customers directly via phone calls. A more modern iteration of this is SMS marketing, where businesses send promotional text messages to consumers who have opted in. Both methods offer an immediate and personal line of communication, ideal for time-sensitive offers or appointment setting.
Social Media Marketing (Targeted Ads and Direct Messaging)
Social media platforms offer powerful targeting capabilities, allowing marketers to place ads directly in the feeds of users based on their demographics, interests, and online behavior. Additionally, direct messaging features on platforms like Instagram and Facebook allow for one-on-one conversations with the customer base.
In-Person Selling (Face-to-face, door-to-door)
In-person selling is the most traditional form of direct marketing. This includes everything from face-to-face meetings with B2B clients to door-to-door sales. It offers the highest level of personalization and allows for immediate feedback and relationship building.
Direct Response Advertising (Infomercials, Digital Pop-ups)
This type of advertising is designed to elicit an immediate response. Classic examples include television infomercials urging viewers to "call now." In the digital world, this takes the form of pop-ups on a website, online ads with a direct purchase CTA, or other forms of direct-response advertising that prompt immediate action.
| Direct Marketing Type | Best For |
|---|---|
| Email Marketing | Nurturing existing leads, promoting new products, and delivering personalized offers at scale with measurable engagement metrics. |
| SMS Marketing | Time-sensitive promotions, reminders, and transactional updates requiring high open rates and immediate visibility. |
| Direct Mail | High-value or localized campaigns that benefit from tangible, personalized outreach to improve recall and brand perception. |
| Telemarketing | High-touch engagement for B2B or complex sales cycles where conversation and qualification drive conversions. |
| Social Media Direct Ads | Targeted audience acquisition and retargeting using behavioral and demographic data for personalized ad delivery. |
| Messenger and Chat Marketing | Real-time engagement, customer support, and personalized product recommendations through conversational automation. |
| Direct Response TV (DRTV) or Video Ads | Generating immediate viewer action (e.g., sign-ups or purchases) via measurable, trackable calls-to-action in broadcast or streaming formats. |
| Catalog and Print Marketing | Showcasing a wide product range or seasonal offerings to niche audiences with strong brand affinity and purchase intent. |
| Push Notifications | Re-engaging app users with personalized updates, reminders, or limited-time offers that drive quick, trackable responses. |
| Direct B2B Outreach (Email or LinkedIn) | Account-based marketing efforts focused on specific decision-makers, personalized outreach, and pipeline acceleration. |
Advantages and Disadvantages of Direct Marketing
Like any marketing strategy, direct marketing has distinct benefits and drawbacks that organizations must weigh before launching a campaign.
Advantages
- Targeted Messaging: Direct marketing allows businesses to reach specific segments of their audience, ensuring the message is relevant and more likely to resonate.
- High ROI Potential: By focusing marketing efforts on individuals most likely to convert, companies can achieve a higher return on investment compared to broad, untargeted advertising.
- Building Personal Connections: Personalized communication helps foster a direct relationship with customers, which can lead to increased loyalty and word-of-mouth marketing.
- Cost-Effective: Digital channels like email and social media can be highly cost-effective, while even direct mail can be efficient when properly targeted, avoiding the high costs of mass media.
Disadvantages
- Potential Intrusiveness: Unsolicited emails, phone calls, or mail can be perceived as annoying by consumers, potentially damaging brand reputation if not executed carefully (e.g., providing an easy opt-out).
- Lower Response Rates: With consumers being bombarded by advertising, response rates for direct marketing can sometimes be low. Success often requires highly compelling offers and creative execution to break through the noise.
- Data Privacy Concerns: The use of customer data is central to direct marketing, raising privacy concerns. Marketers must be compliant with regulations like HIPAA and CCPA to build trust and avoid legal issues.
- Environmental Impact: Traditional direct mail campaigns contribute to paper waste, which can be a concern for environmentally conscious consumers and brands.
Real-World Direct Marketing Examples
To see the power of direct marketing in action, let's look at a few innovative campaigns that generated significant buzz and results.
B2C Example: Nike's Stadium Shoebox
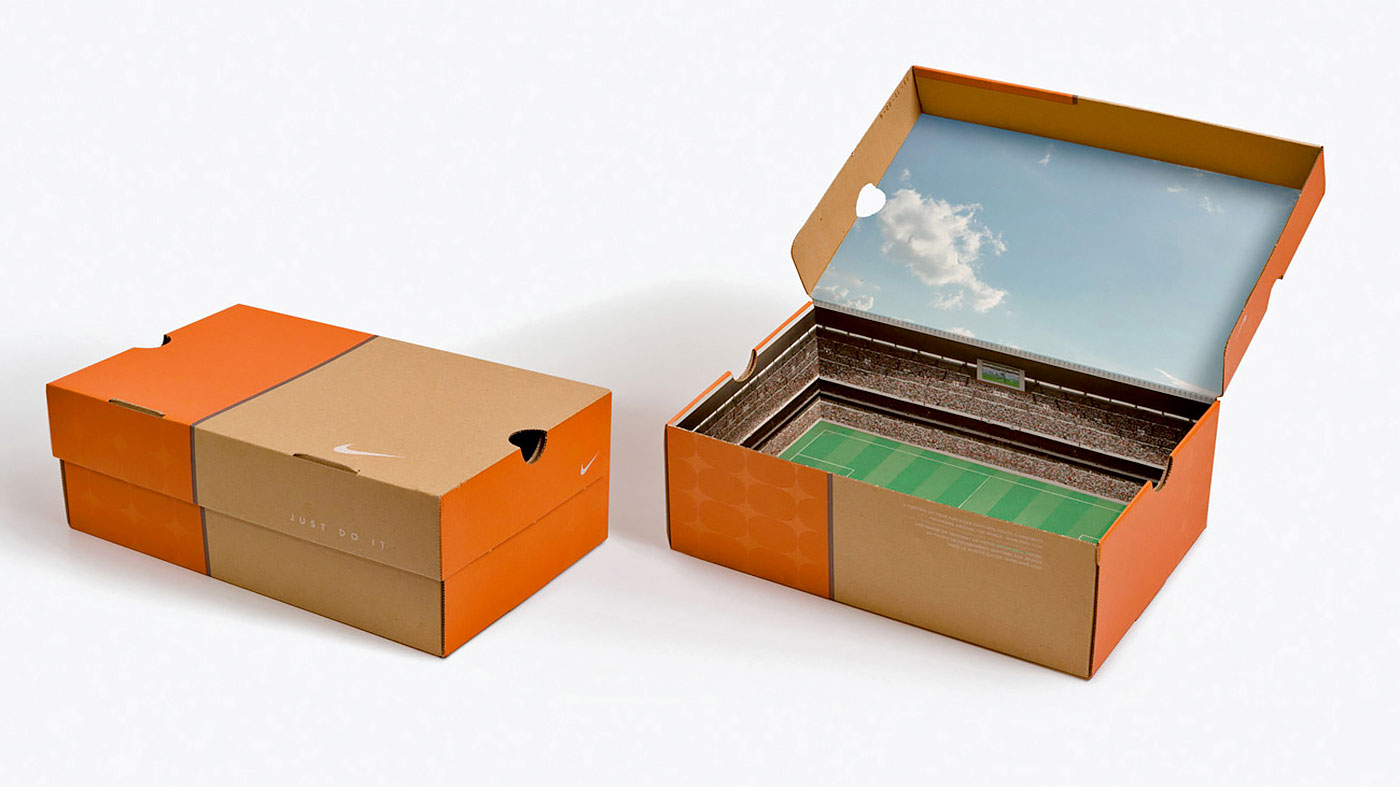

Nike launched a limited-edition Air Max sneaker through a creative direct mail campaign. They sent select customers a shoebox designed to look like a concrete stadium, complete with stadium sounds that played when opened.
This highly targeted, tactile experience created a sense of exclusivity and excitement, generating massive social media buzz and selling out the product instantly.
B2B Example: Zoominfo's Personalized Video Cards
To engage high-value enterprise accounts, Zoominfo sent key decision-makers physical cards that contained a small video screen. When opened, the card played a personalized video message addressing the recipient by name and highlighting how Zoominfo could solve their specific business challenges.
This hyper-personalized, high-tech approach cut through the digital noise and secured meetings with hard-to-reach executives.
Current Trends in Direct Marketing
Direct marketing continues to evolve with technology and changing consumer expectations. Several key trends are shaping its future.
Personalization at Scale with AI
Artificial intelligence is enabling marketers to deliver hyper-personalized experiences to millions of consumers simultaneously. AI algorithms analyze vast amounts of customer data to predict behavior, recommend products, and customize messaging in real-time across various digital channels.
Automation and Omnichannel Integration
Modern consumers interact with brands across numerous touchpoints. An effective marketing strategy requires an omnichannel approach, integrating channels like email, social media, and direct mail.
To manage this complexity, marketing operations leaders rely on automated data pipeline solutions. Improvado helps enterprise organizations automate the extraction and transformation of data from all marketing channels, freeing up teams from manual reporting to focus on strategic insights and campaign optimization.
Data Privacy and Ethical Marketing
With the rise of regulations like GDPR, consumers are more aware of how their data is used. The future of direct marketing lies in ethical, permission-based practices. Successful marketers are focusing on transparency, giving consumers control over their data, and building trust by providing genuine value in exchange for information.
Steps to a Great Direct Marketing Plan
Executing a successful direct marketing campaign requires a structured approach. Following these steps can help ensure your efforts are strategic, targeted, and effective.
1. Understanding the Market
Before launching any campaign, it is essential to understand your audience. Develop detailed customer personas based on data, identifying their needs, pain points, and preferred communication channels. A deep understanding of who you're talking to is the first step toward crafting a message that resonates.
2. Looking at Others
Analyze the direct marketing strategies of your competitors. What channels are they using? What kind of offers are they making? Observing others in your industry can provide valuable insights into what works and reveal opportunities to differentiate your approach.
3. Choosing the Best Way to Talk
Select the most appropriate direct marketing channels based on your target audience and campaign goals. An older demographic might respond better to direct mail, while a younger audience may be more receptive to social media ads or SMS marketing. An integrated, multi-channel approach is often the most effective.
4. Crafting the Perfect Message
The content of your message is the heart of the campaign. It should be clear, concise, and compelling. Highlight the value proposition, address a specific customer need, and include a strong, unambiguous call to action that prompts an immediate response.
5. Learning and Growing
After a campaign concludes, the work isn't over. It's crucial to gather feedback and meticulously analyze the results. Track key metrics like response rates, conversion rates, and cost per acquisition. This data-driven approach allows you to refine your strategies, making each subsequent campaign more effective than the last.
Conclusion
Direct marketing remains a potent strategy for businesses aiming to cut through the noise and connect with consumers on a personal level. By leveraging precise targeting, personalized messaging, and a clear call to action, it creates a direct path to measurable results.
Whether through traditional direct mail or sophisticated digital channels powered by AI, the core principles of understanding and communicating directly with the customer are more relevant than ever. As technology evolves, the ability to execute and measure these campaigns with data-driven precision will continue to define the most successful marketing efforts.
.png)



.png)
