Retail is undergoing rapid transformation. Customer behavior changes in real time, digital and in-store journeys are tightly interconnected, and competition is driven by data rather than intuition. In this environment, retailers need precise measurement to understand performance, identify risks, and uncover growth opportunities. Retail KPIs provide that foundation.
These metrics translate complex retail operations, sales, inventory, customer loyalty, and operational efficiency, into objective, actionable insights. This guide outlines the most critical KPIs for modern retail organizations, explaining how to select, track, and operationalize them to improve decisions, strengthen profitability, and support long-term growth.
Key Takeaways:
- Retail KPIs are quantifiable metrics that measure performance against strategic goals in areas like sales, inventory, and customer satisfaction.
- Tracking the right KPIs provides data-driven insights to optimize operations, improve customer experiences, and increase profitability.
- KPIs should be categorized into Sales, Customer, Inventory, Marketing, and Financial groups for a holistic view of the business.
- Choosing effective KPIs requires aligning them with specific business objectives using frameworks like SMART (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, Time-bound).
- Automated data platforms are crucial for overcoming challenges like data silos and providing the real-time insights needed for effective decision-making.
Why Retail KPIs Are the Cornerstone of Modern Retail Success
Retailers in 2026 are operating under unprecedented pressure. Foot traffic is declining for many specialty stores, digital ad costs continue to rise, supply chain volatility disrupts campaigns, and consumer expectations shift faster than many teams can adapt.
In this environment, retail KPIs have become a stabilizing force that helps retailers navigate uncertainty, prioritize investments, and operate with precision. KPIs transform fragmented retail data into a unified decision system that leaders rely on to steer their organizations through volatility.
From Instinct to Evidence-Based Growth in a High-Pressure Market
Relying on intuition is especially dangerous when marketing spend is rising and competition for consumer attention is intensifying.
KPIs replace guesswork with empirical clarity. Metrics like sell-through rate, demand forecasting accuracy, ROAS, and inventory turnover reveal patterns that would otherwise be obscured by disruption, from delayed product availability to shifting consumer preferences driven by inflation.
As promotions are harder to plan and product cycles become unpredictable, data-driven validation becomes the only reliable compass for growth.
Creating Advantage Amid Market Fragmentation and Rising Costs
Retailers face structural challenges: fragmented loyalty programs, inconsistent messaging across wholesale channels, geographic pricing scrutiny, and weakened brand differentiation. KPIs illuminate these gaps.
Benchmarking customer retention, segmentation performance, unit economics, and omnichannel contribution exposes where retailers are overinvesting, underperforming, or failing to meet emerging expectations.
These insights enable teams to refine pricing, strengthen loyalty engagement, and ensure the brand shows up consistently across every touchpoint, even when operational realities lag behind marketing ambition.
Operational Efficiency as a Strategic Imperative
With inflation squeezing margins and store closures reducing physical presence, operational discipline is a frontline strategy.
KPIs such as stockout rate, shrinkage, labor productivity, customer support response time, and fulfillment accuracy directly influence marketing credibility and customer trust. When marketing promises do not align with product availability or support capacity, churn accelerates and loyalty erodes.
KPI-driven operational improvement keeps retailers aligned, efficient, and capable of delivering on the expectations their campaigns create.
Understanding the Core Categories of Retail KPIs
To get a complete picture of your business, you need to track KPIs across several key areas.
Grouping metrics into categories helps organize your analysis and ensures no aspect of your operation is overlooked. A balanced approach provides a 360-degree view of performance.
| KPI Category | Primary Goal | Example Metrics | Business Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sales Performance | Measure revenue generation and sales efficiency. | Conversion Rate, Average Transaction Value (ATV) | Directly impacts top-line revenue and growth. |
| Customer Experience | Gauge customer loyalty and satisfaction. | Customer Lifetime Value (CLV), Net Promoter Score (NPS) | Drives repeat business and long-term profitability. |
| Inventory Management | Optimize stock levels and cash flow. | Inventory Turnover, Sell-Through Rate | Reduces holding costs and prevents stockouts. |
| Store and Operations | Evaluate physical store and staff efficiency. | Sales Per Square Foot, Foot Traffic | Maximizes the productivity of physical assets. |
| Marketing and eCommerce | Assess the effectiveness of marketing efforts. | Return on Ad Spend (ROAS), Cart Abandonment Rate | Optimizes marketing spend and digital sales funnels. |
| Financial Health | Monitor overall profitability and stability. | Gross Margin, Net Profit Margin | Ensures long-term business sustainability. |
Top Sales Performance KPIs Every Retailer Must Track
Sales KPIs are the lifeblood of any retail analysis. They provide a direct measure of your ability to convert products into revenue. These metrics should be monitored closely and frequently to react quickly to changing market conditions.
Sales Revenue & Growth Rate
This is the most fundamental retail KPI. It measures the total income from sales over a specific period. Tracking growth rate (week-over-week, month-over-month, year-over-year) shows your business's trajectory.
Sales Growth = ((Current Period Sales - Previous Period Sales) / Previous Period Sales) * 100
Conversion Rate (Online and In-Store)
Conversion rate measures the percentage of visitors who make a purchase. For a physical store, it's the number of buyers divided by total foot traffic. For an eCommerce site, it's buyers divided by total site visitors. A low conversion rate can indicate problems with pricing, product selection, or customer experience.
Conversion Rate = (Number of Sales / Number of Visitors) * 100
Average Transaction Value (ATV)
ATV measures the average amount a customer spends in a single transaction. Increasing your ATV is a powerful way to boost revenue without needing more customers. Strategies like upselling, cross-selling, and product bundling can effectively raise ATV.
ATV = Total Revenue / Number of Transactions
Units Per Transaction (UPT)
Closely related to ATV, UPT tracks the average number of items sold in each transaction. It is a key indicator of staff performance and the effectiveness of in-store promotions. Training employees on add-on selling can directly improve this kpi for a retail store manager.
Sales Per Square Foot
For brick-and-mortar stores, this metric measures revenue generated for every square foot of sales space. It helps retailers evaluate store layout, product placement, and overall store profitability. Underperforming areas can be redesigned or repurposed to improve this crucial retail store metric.
Essential Customer KPIs for Building Loyalty
Acquiring a new customer is significantly more expensive than retaining an existing one. Customer KPIs help you understand your customer base, measure their loyalty, and create experiences that keep them coming back.
Customer Lifetime Value (CLV)
CLV is the total profit a business can expect from a single customer account throughout their relationship. It is a forward-looking metric that helps prioritize marketing efforts and customer service investments. High-CLV customers are your most valuable asset.
Customer Retention Rate (CRR)
CRR measures the percentage of existing customers who remain customers over a period. A high CRR is a sign of a healthy business with strong brand loyalty. Small improvements in retention can lead to significant increases in profitability over time.
CRR = ((Customers at End of Period - New Customers) / Customers at Start of Period) * 100
Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC)
CAC is the total cost of sales and marketing efforts needed to acquire a new customer. It is crucial to compare CAC with CLV. A sustainable business model requires a CLV that is substantially higher than the CAC (often a 3:1 ratio is considered healthy).
Net Promoter Score (NPS)
NPS measures customer loyalty by asking a single question: "On a scale of 0-10, how likely are you to recommend our brand to a friend?" Customers are categorized as Promoters (9-10), Passives (7-8), or Detractors (0-6). The score helps gauge overall brand perception.
Customer Satisfaction (CSAT) Score
CSAT measures customer satisfaction with a specific product, service, or interaction. It is typically measured through surveys asking customers to rate their satisfaction on a scale. Tracking CSAT helps pinpoint and resolve specific issues in the customer journey.
Crucial Inventory KPIs to Optimize Stock and Cash Flow
Inventory is one of the largest assets for any retailer. Effective inventory management is a delicate balance. You need enough stock to meet demand but not so much that it ties up cash and increases holding costs. These KPIs help you strike that balance.
Inventory Turnover Ratio
This ratio shows how many times a company has sold and replaced its inventory during a given period. A high turnover rate is generally good. It indicates strong sales and efficient inventory management. A low rate may suggest overstocking or poor product demand.
Inventory Turnover = Cost of Goods Sold / Average Inventory
Sell-Through Rate
Sell-through rate compares the amount of inventory a retailer receives from a manufacturer to the amount of inventory sold to customers. It is usually calculated on a monthly basis. This metric is essential for evaluating the performance of individual products or product lines.
Sell-Through Rate = (Units Sold / Units Received) * 100
Gross Margin Return on Investment (GMROI)
GMROI tells you how much money you made back for every dollar you invested in inventory. A GMROI greater than 1 means you are selling the product for more than it costs you. It is a powerful metric for evaluating the profitability of your inventory.
GMROI = Gross Margin / Average Inventory Cost
Stock-to-Sales Ratio
This ratio compares the amount of inventory on hand to the sales being generated. It helps retailers determine if they have too much or too little stock at any given time. This kpi in the retail industry is crucial for planning future purchases.
Days of Inventory Outstanding (DIO)
DIO measures the average number of days a company holds its inventory before selling it. The goal is generally to keep this number low. A lower DIO indicates that the company is converting its inventory into sales quickly, which improves cash flow.
Key Store Operations & Employee Performance KPIs
For brick-and-mortar retailers, the physical store is the heart of the business. Operational KPIs measure the efficiency and effectiveness of your physical locations and the staff who run them.
Foot Traffic and Dwell Time
Foot traffic measures the number of people entering your store. Dwell time measures how long they stay. Analyzing these metrics can reveal peak shopping hours and help evaluate the effectiveness of window displays and in-store marketing. Modern sensors can provide this data in real time.
Employee Turnover Rate
High employee turnover can be costly and disruptive. This KPI tracks the rate at which employees leave your company. A high rate might indicate issues with management, compensation, or company culture. Investing in employee satisfaction can reduce turnover and improve customer service.
Sales Per Employee
This metric measures the revenue generated by each employee. It is a useful indicator of staff productivity and the effectiveness of sales training. It helps managers identify top performers and those who may need additional support.
Average Basket Size
Basket size refers to the number of items a customer purchases in a single transaction, the same as Units Per Transaction (UPT). Analyzing basket size can inform product placement and promotional strategies. For example, placing complementary items near each other can encourage larger basket sizes.
Measuring Digital Success: Marketing & eCommerce KPIs
In an omnichannel world, your digital presence is as important as your physical one. These KPIs help you measure the performance of your eCommerce site and digital marketing campaigns.
Website Traffic & Bounce Rate
Website traffic measures the number of visitors to your online store. Bounce rate is the percentage of visitors who leave after viewing only one page. High traffic is good, but a high bounce rate suggests your landing page isn't engaging visitors or meeting their expectations.
Cart Abandonment Rate
This is the percentage of online shoppers who add items to their cart but leave without completing the purchase. A high cart abandonment rate can indicate problems with the checkout process, such as unexpected shipping costs or a complicated form.
Return on Ad Spend (ROAS)
ROAS measures the revenue generated for every dollar spent on advertising. It is a critical metric for evaluating the profitability of your marketing campaigns. Understanding ROAS helps you allocate your marketing budget to the most effective channels and strategies. Proper marketing attribution models are essential for accurately calculating ROAS across complex customer journeys.
Social Media Engagement & Analytics
For brands that use social media, tracking engagement is vital. Metrics like likes, shares, comments, and follower growth indicate how well your content resonates with your audience. Effective social media analytics can link these engagement metrics to website traffic and sales, demonstrating the channel's impact on the bottom line.
How to Select and Implement the Right KPIs for Your Business
Tracking dozens of KPIs is not practical or effective. The key is to select a handful of metrics that are most relevant to your specific business goals. A structured approach ensures your chosen KPIs will drive meaningful action.
Aligning KPIs with Strategic Business Goals
Start with your high-level business objectives. Do you want to increase market share, improve profitability, or enhance customer loyalty? Each goal will have a different set of relevant KPIs. For example, a goal to improve customer loyalty would prioritize metrics like CRR and NPS.
The SMART Framework for KPI Setting
Once you have identified relevant KPIs, use the SMART framework to set targets:
- Specific: Clearly define what you want to achieve. (e.g., "Increase online conversion rate.")
- Measurable: Ensure you can track progress with a concrete metric. (e.g., "Increase it from 2.5% to 3.5%.")
- Achievable: Set a realistic and attainable target.
- Relevant: The goal should be important to your overall business strategy.
- Time-bound: Set a deadline for achieving the goal. (e.g., "by the end of Q4.")
Establishing Baselines and Setting Realistic Targets
Before you can set targets, you need to know your starting point. Collect historical data to establish a baseline for each KPI. This baseline provides context and helps you set targets that are challenging yet achievable. Compare your baselines to industry benchmarks to understand your competitive position.
Communicating KPIs Across Your Organization
KPIs are most effective when they are understood and used by everyone in the organization. Share performance data transparently. Help employees understand how their individual roles contribute to the key metrics. When everyone is aligned and focused on the same goals, the entire organization moves forward together.
Common Challenges in Tracking Retail KPIs (And How to Solve Them)
While the benefits of tracking KPIs are clear, many retailers face significant challenges in doing so effectively. Identifying these hurdles is the first step toward overcoming them.
Data Silos and Disparate Sources
Retailers generate massive volumes of data across POS systems, ecommerce platforms, inventory systems, loyalty programs, CRMs, and dozens of marketing channels. But because these systems don’t speak the same language, teams end up with fragmented insights and incomplete visibility into performance.
This makes it difficult to understand the full customer journey, attribute revenue accurately, or coordinate marketing and merchandising decisions.
To solve this, retailers need a unified data foundation, and this is exactly what Improvado delivers.
Improvado centralizes every retail data source into a governed, analytics-ready environment, eliminating silos and providing teams with a single, reliable view of marketing, sales, and customer behavior. Retailers gain consistent, standardized, and continuously updated data that supports attribution, forecasting, merchandising, and omnichannel reporting.
How Improvado solves retail data fragmentation:
- 500+ prebuilt connectors covering ad platforms, ecommerce tools, POS systems, CRM, analytics tools, and retail media networks.
- Cross-channel data normalization that standardizes naming, taxonomies, product IDs, campaign structures, and attributes across all sources.
- Marketing, CRM, and retail data unification to connect shopper behavior, loyalty metrics, transactions, and campaign influence in one model.
- Real-time or near real-time ingest for accurate pacing, inventory-linked campaigns, and up-to-date performance monitoring.
- Retail-specific schema alignment for orders, SKUs, product catalogs, and customer segments.
- AI-ready data models that support advanced analytics like MMM, MTA, demand forecasting, and customer lifetime value prediction.
- Automated reporting workflows that feed BI dashboards, spreadsheets, and internal analytics environments without manual intervention.
By consolidating everything into a single source of truth, Improvado enables retail teams to finally see the complete picture: what’s selling, who’s buying, and which campaigns are driving incremental revenue.
Ensuring Data Accuracy and Consistency
Inaccurate data leads to flawed decisions. Manual data entry errors, inconsistent naming conventions, and system glitches can all compromise data quality. Implementing data governance policies and automating data collection processes are essential for maintaining data integrity.
Lack of Real-Time Insights
The retail environment changes quickly. Relying on weekly or monthly reports means you are always looking in the rearview mirror. To make agile, proactive decisions, you need access to real-time data. This requires a modern analytics infrastructure that can process and display information as it happens.
Translating Data into Actionable Strategies
Collecting data is only half the battle. The real challenge is translating that data into actionable insights and strategic initiatives. This requires a combination of the right tools for data visualization and a data-literate culture where employees are trained to interpret and act on data.
Automating Your Retail Analytics with Improvado
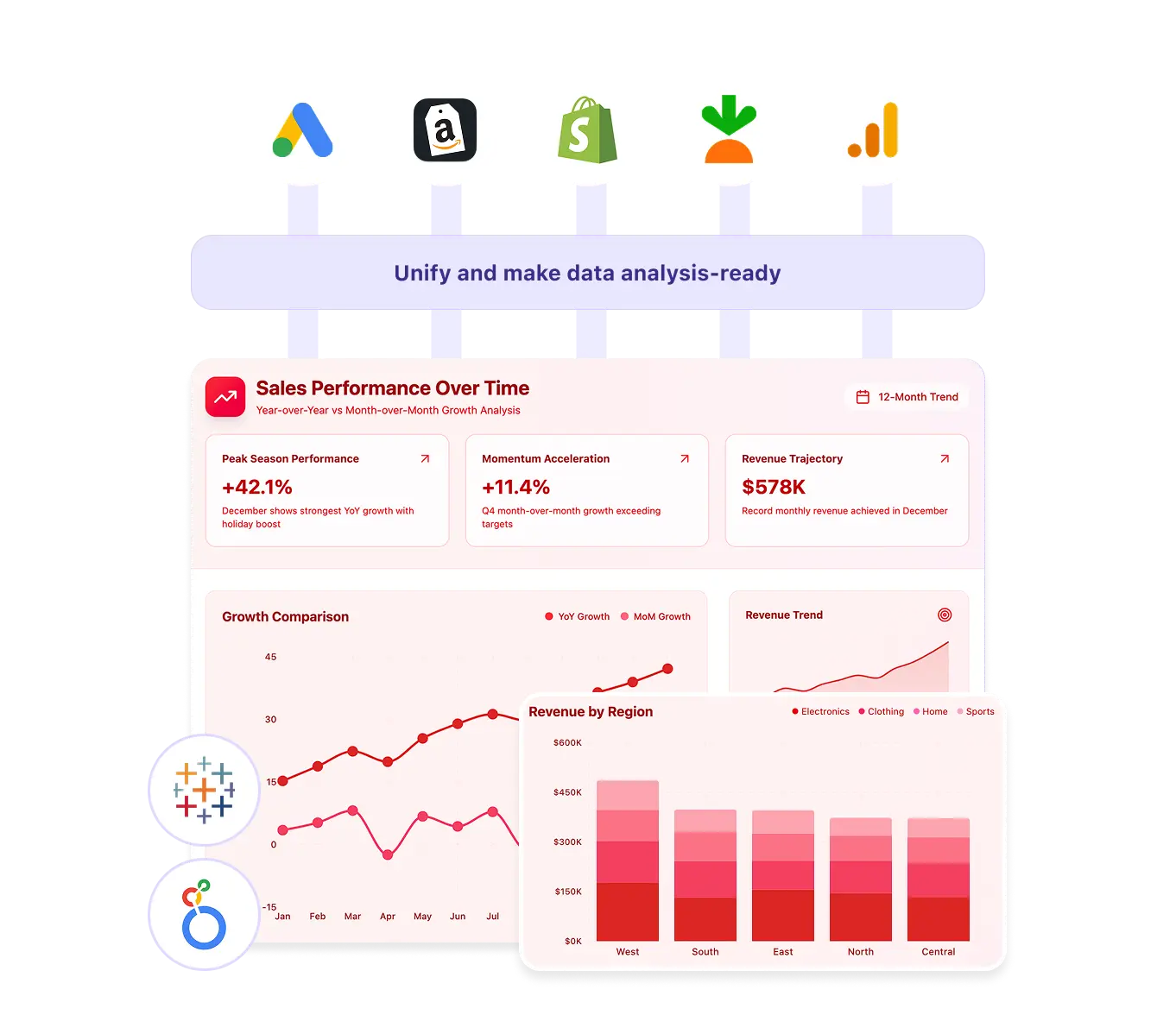
Improvado is a platform designed to solve the data challenges modern retailers face. It provides an end-to-end solution for automating data collection, integration, and visualization, so you can focus on what truly matters: growing your business.
Unifying Online and Offline Data Sources
Improvado connects to over 500 data sources out of the box, from Shopify and Amazon to Google Analytics and your brick-and-mortar POS system. Each Improvado package includes customization credits a company can use to build a custom connection and integrate data from any niche, legacy, and in-house system with the rest of the stack.
It seamlessly pulls all retail data together, breaking down silos and providing a truly unified view of your customer and business performance.
From Raw Data to Actionable Insights
The platform doesn't just collect data, it transforms it into an analysis-ready format.
Improvado handles data cleaning, mapping, and normalization, delivering a pristine dataset to your business intelligence tool or data warehouse. The whole process is no-code and AI-powered.
This process includes powerful reporting automation, saving countless hours of manual work.
Measuring the True ROI of Marketing Campaigns
With a complete view of both marketing spend and sales data, you can accurately measure the true ROI of marketing campaigns. Improvado helps you connect the dots between your marketing efforts and your bottom line, enabling you to optimize spend and maximize profitability.
Book a demo with Improvado to get a full view of your retail marketing data ecosystem.
.png)
.jpeg)



.png)
