From the minute a prospect becomes aware of your brand, they enter a journey of learning, reading, watching, and engaging with your marketing efforts. While each interaction certainly has an impact on whether or not someone becomes a customer, not all touchpoints are equal.
Marketing teams are tasked with the challenge of determining which of these interactions have the greatest impact on an audience’s decision to buy.This is where marketing attribution models come into play.
Attribution models are the frameworks that allow you to assign value to each touchpoint and construct a clear narrative of what drives conversions. This will ultimately help you create more cost-effective and responsive campaigns.
Key Takeaways:
- Definition: Marketing attribution is the science of assigning credit to the marketing touchpoints a customer interacts with on their path to conversion.
- Model Categories: Attribution models are broadly categorized into Single-Touch (First, Last-Click) and Multi-Touch (Linear, Time-Decay, U-Shaped, W-Shaped, etc.), with advanced algorithmic models offering the most nuance.
- Choosing a Model: The best model depends on your business goals, sales cycle length, marketing channel complexity, and available data. There is no one-size-fits-all solution.
- Data is Paramount: Accurate attribution is impossible without clean, centralized, and granular data. A robust data infrastructure is the foundation of any successful attribution strategy.
- Beyond Reporting: The ultimate goal of attribution is not just to report on past performance but to generate actionable insights that inform future budget allocation, campaign optimization, and strategic decision-making.
What Is Marketing Attribution? The Foundation of ROI Measurement
Without attribution, marketers are flying blind. You might see that a customer converted after clicking a Google Ad, but you're missing the full story.
Did they first discover your brand through a LinkedIn post?
Did they read three blog posts before that ad?
Did a retargeting campaign on Facebook keep your brand top-of-mind?
Attribution connects these dots to paint a complete picture of influence.
Why Marketing Attribution is Non-Negotiable for Growth
Implementing a marketing attribution strategy is a powerful lever for growth, offering insights that extend far beyond simple ROI calculations. In fact, organizations that master attribution are better equipped to navigate competitive markets and allocate resources with precision. The core benefits are transformative.
1. Greater Data Integrity and a Single Source of Truth
A well-defined attribution strategy forces data hygiene. When you're using multiple tools for each touchpoint (Google Ads, Facebook Ads, an email platform), each platform will naturally take 100% of the credit for a conversion it was involved in. This leads to over-reporting and a fragmented view of performance.
A centralized attribution model de-duplicates these conversions and establishes a single source of truth, allowing you to accurately measure the true ROI of marketing campaigns.
2. Deeper Understanding for Smarter Campaigns
When you consistently assign credit across the entire journey, it becomes crystal clear what's driving conversions, what's causing drop-off, and what's having little to no effect. This knowledge empowers you to optimize campaigns with surgical precision, delivering high-impact touchpoints in the right sequence, to the right audience.
You can analyze the paths of your most valuable customers and build campaigns designed to attract more prospects just like them.
3. Higher ROI on Spend and Resources
With a clear understanding of what works, you can confidently eliminate low-performing channels and reallocate that budget to high-performers. More importantly, you can identify assist channels.
A channel might not be the last click before a conversion, but it may play a critical role in the awareness or consideration phase. Without multi-touch attribution, these valuable assisting channels might be cut, crippling your funnel without you realizing why.
4. A More Granular, Cohort-Level View of a Journey
Marketing attribution doesn’t just tell you how you moved a prospect down the funnel; it tells you when. You can analyze which messaging, visuals, and platforms resonated with specific customer cohorts.
This insight into their journey allows you to calculate more precise metrics like cohort-specific LTV:CAC, enabling you to streamline the acquisition of your most profitable customers.
5. Better Product and Market Alignment
Attribution data reveals trends about how your product is perceived in the market. By analyzing the effectiveness of each touchpoint, your data will show which features, benefits, and value propositions persuade a prospect to continue their journey.
If content about a specific feature consistently drives engagement and conversions, that's a strong signal of market fit. Conversely, if touchpoints about another feature fall flat, it may indicate a need to refine the product or its messaging.
Understanding Attribution Models: The Core Frameworks
If marketing attribution is the process of assigning credit, then marketing attribution models are the different rulesets or methods for distributing that credit.
Each model is a framework that determines precisely how you’ll weigh credit and which touchpoints receive it. There isn't a single best model; the right choice depends entirely on your business priorities, sales cycle, and the questions you're trying to answer.
Some models are simple, designed to quickly identify top-of-funnel drivers. Others are complex, built to provide a nuanced view of a long and intricate customer journey.
The key is to understand the assumptions and limitations of each before you commit to one.
Single-Touch vs. Multi-Touch Attribution: A Foundational Choice
At the highest level, all attribution models fall into one of two categories: single-touch or multi-touch. This is the first and most important decision you'll make in your attribution journey, as it dictates the fundamental lens through which you'll view your marketing performance.
- Single-Touch Attribution Models: These models assign 100% of the conversion credit to a single marketing touchpoint. They are simple to implement and understand, making them a common starting point for businesses new to attribution. However, their simplicity is also their biggest weakness, as they ignore the influence of all other interactions.
- Multi-Touch Attribution (MTA) Models: Also known as multi-channel attribution, these models distribute conversion credit across multiple touchpoints. While more complex to set up, they provide a far more realistic and holistic view of how your various marketing channels work together to drive conversions.
| Aspect | Single-Touch Attribution | Multi-Touch Attribution |
|---|---|---|
| Complexity | Low. Easy to implement and explain. | High. Requires sophisticated tracking and data integration. |
| Insight Level | Basic. Answers "what was the first/last touch?" | Deep. Shows how channels work together over time. |
| Best For | Short sales cycles, brand awareness campaigns, or teams new to attribution. | Longer sales cycles, complex multi-channel strategies, optimization focus. |
| Key Weakness | Oversimplifies the customer journey, ignoring other influential touchpoints. | Can be difficult to implement correctly and requires clean, unified data. |
| Data Requirement | Minimal. Only needs to identify one key touchpoint. | Extensive. Requires tracking every touchpoint for each user. |
| Example Models | First-Touch, Last-Touch, Last Non-Direct Click | Linear, Time-Decay, U-Shaped, W-Shaped, Data-Driven |
On top of that, marketing attribution models can take two forms: click-through attribution (CTA) and view-through attribution (VTA).
- Click-Through Attribution (CTA) models credit users’ conversion to the last ad or website they clicked on.
- View-Through Attribution (VTA) models, conversion is credited to the last touchpoint a user sees.
For example, you run an ad campaign in June, and your ideal customer clicks on the banner and browses through the website but doesn’t convert. In the next 30 days, you run retargeting campaigns and chase this same prospect on different platforms. Finally, in August, the user makes a purchase by going on your website.
In this situation, the CTA model will credit the customer’s conversion to the original ad they clicked on, the one they saw in June. While the VTA models will focus on the last ad the customer saw, even if they didn’t click on it, and attribute the conversion to this touchpoint.
A Deep Dive into Single-Touch Attribution Models
While limited, single-touch models can provide valuable directional insights, especially when your primary goal is simple and focused.
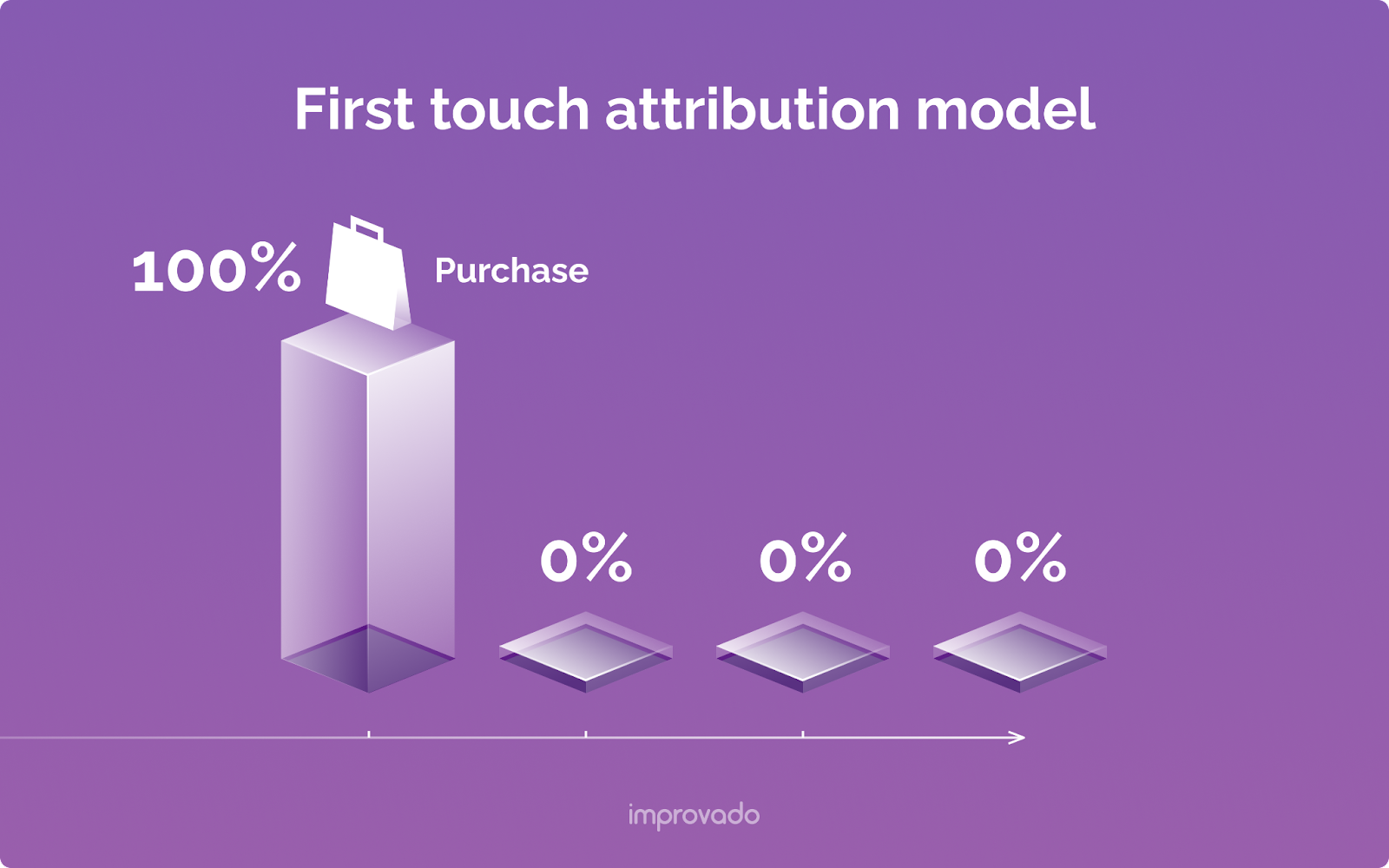
First-Touch Attribution
The First-Touch model gives 100% of the credit for a conversion to the very first interaction a customer had with your brand.
This model is excellent for marketers whose primary goal is demand generation and filling the top of the funnel. It answers the question: "Which channels are best at introducing new prospects to our brand?"
The major shortcoming is that it completely ignores everything that happens after that initial discovery, providing no insight into what actually nurtured the lead and drove the conversion.
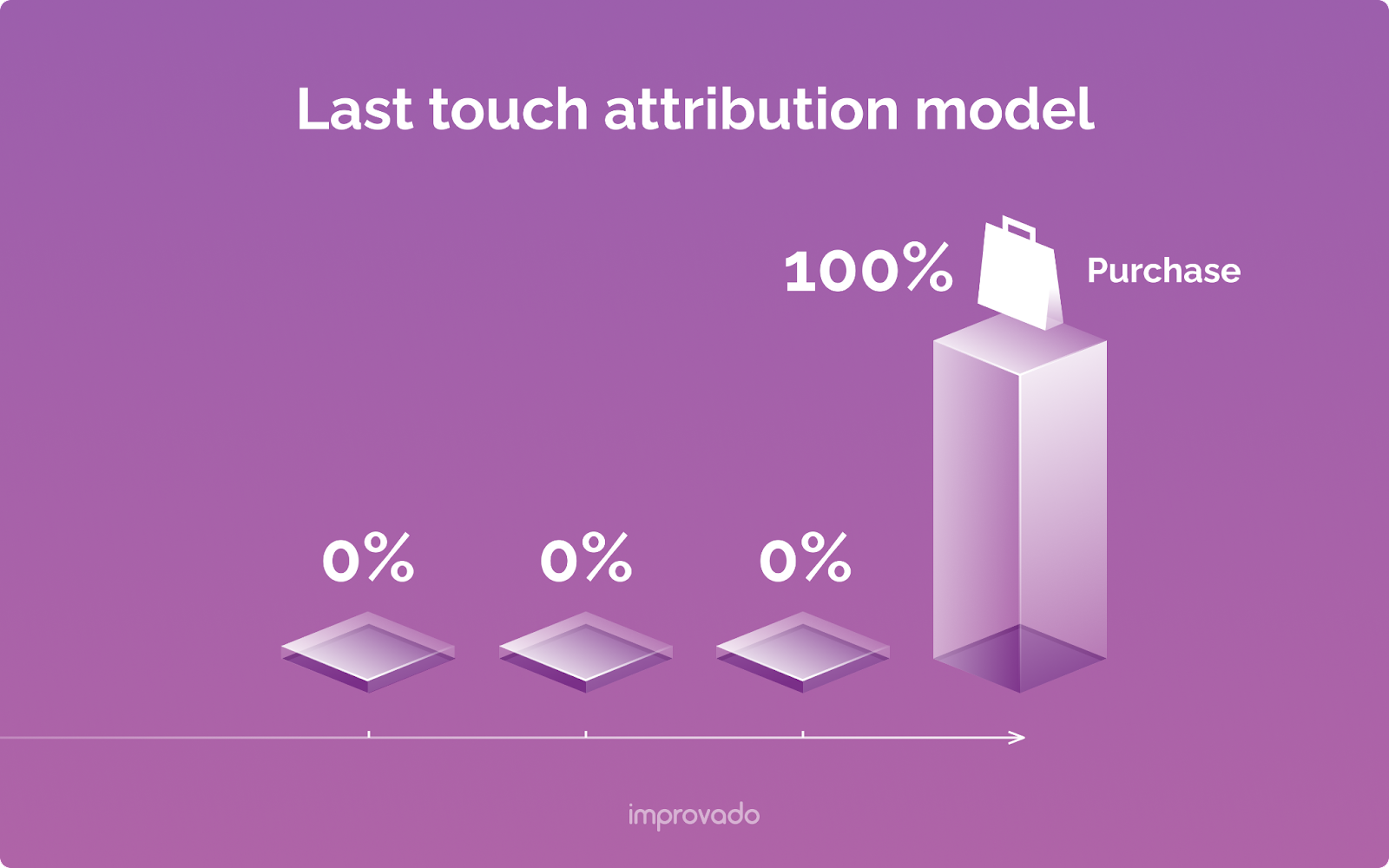
Last-Touch Attribution Model
As its name suggests, the Last-Touch model assigns 100% of the credit to the final touchpoint before a conversion.
This is often the default model in many analytics platforms (like Google Analytics' default setting for many years). It's useful for identifying your "closers" – the channels that are most effective at tipping prospects over the edge.
However, it completely devalues all the preceding marketing efforts that built awareness and consideration, often over-crediting channels like branded search or direct traffic.
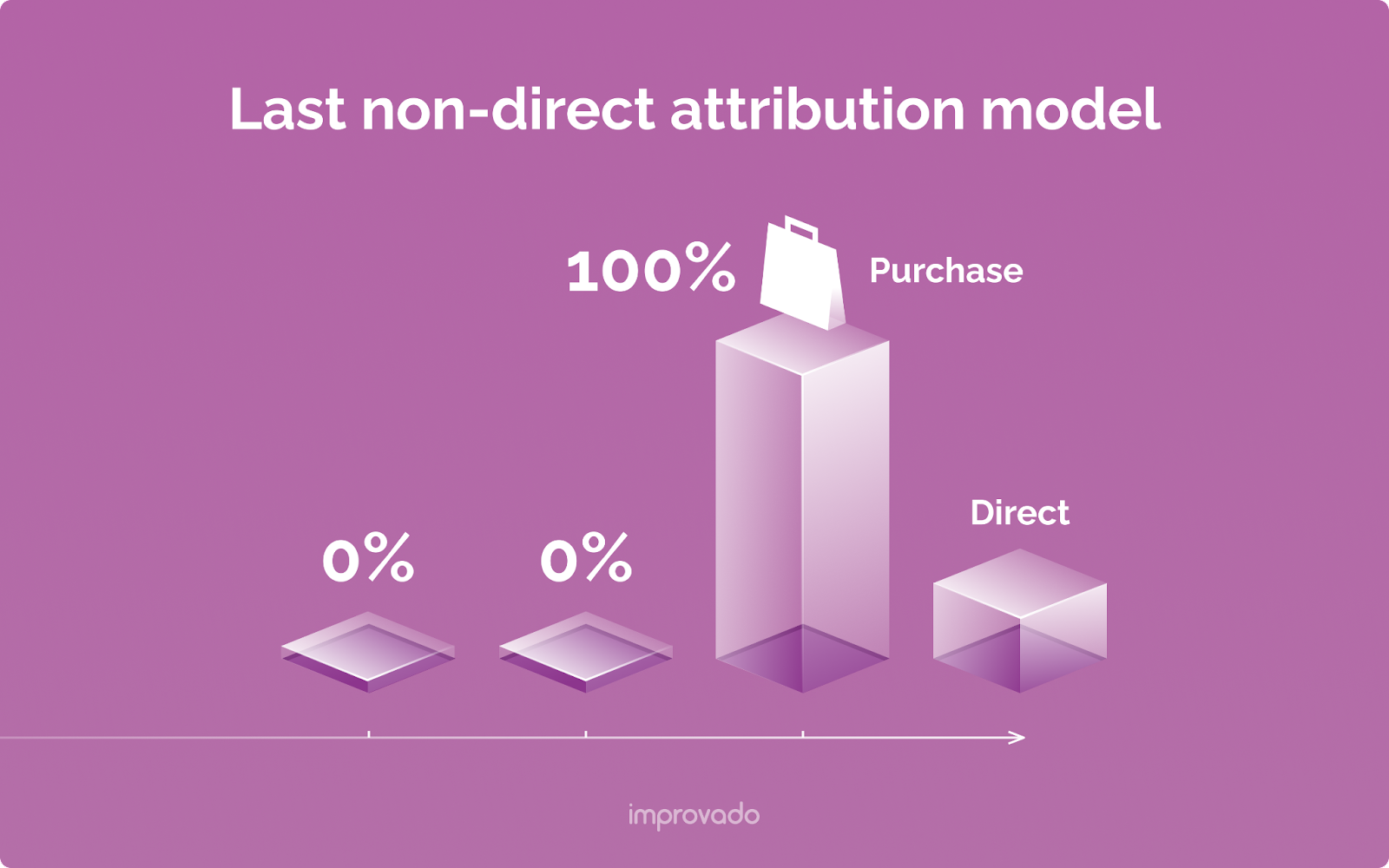
Last Non-Direct Attribution
This is a slightly more sophisticated version of the Last-Touch model. It gives 100% of the credit to the last marketing channel a user engaged with before converting, but it ignores direct traffic.
The logic is that a user typing your URL directly into their browser was likely influenced by a prior marketing touchpoint. This model attempts to find that last influential touch.
For example, if a user clicks a Facebook ad, leaves, and then comes back a day later by typing your website address and converts, the Facebook ad gets the credit. It helps solve the problem of direct traffic stealing credit but still suffers from the fundamental flaw of being a single-touch model.
Exploring the Nuances of Multi-Touch Attribution (MTA) Models
Multi-touch models acknowledge the reality that conversions are the result of a sequence of interactions. They distribute credit across these touchpoints, providing a more balanced view of performance.
These are often called rules-based models because you define the rules for how credit is distributed.
Linear Attribution Model
The Linear model is the simplest form of MTA. It distributes credit equally across every single touchpoint in the customer's journey. If there were five touchpoints, each gets 20% of the credit.
This model is great for valuing every interaction and highlighting the importance of a sustained marketing presence. Its weakness is that it assumes all touchpoints are equally important, which is rarely the case.
The first discovery touchpoint is not the same as the final decision-enabling touchpoint.
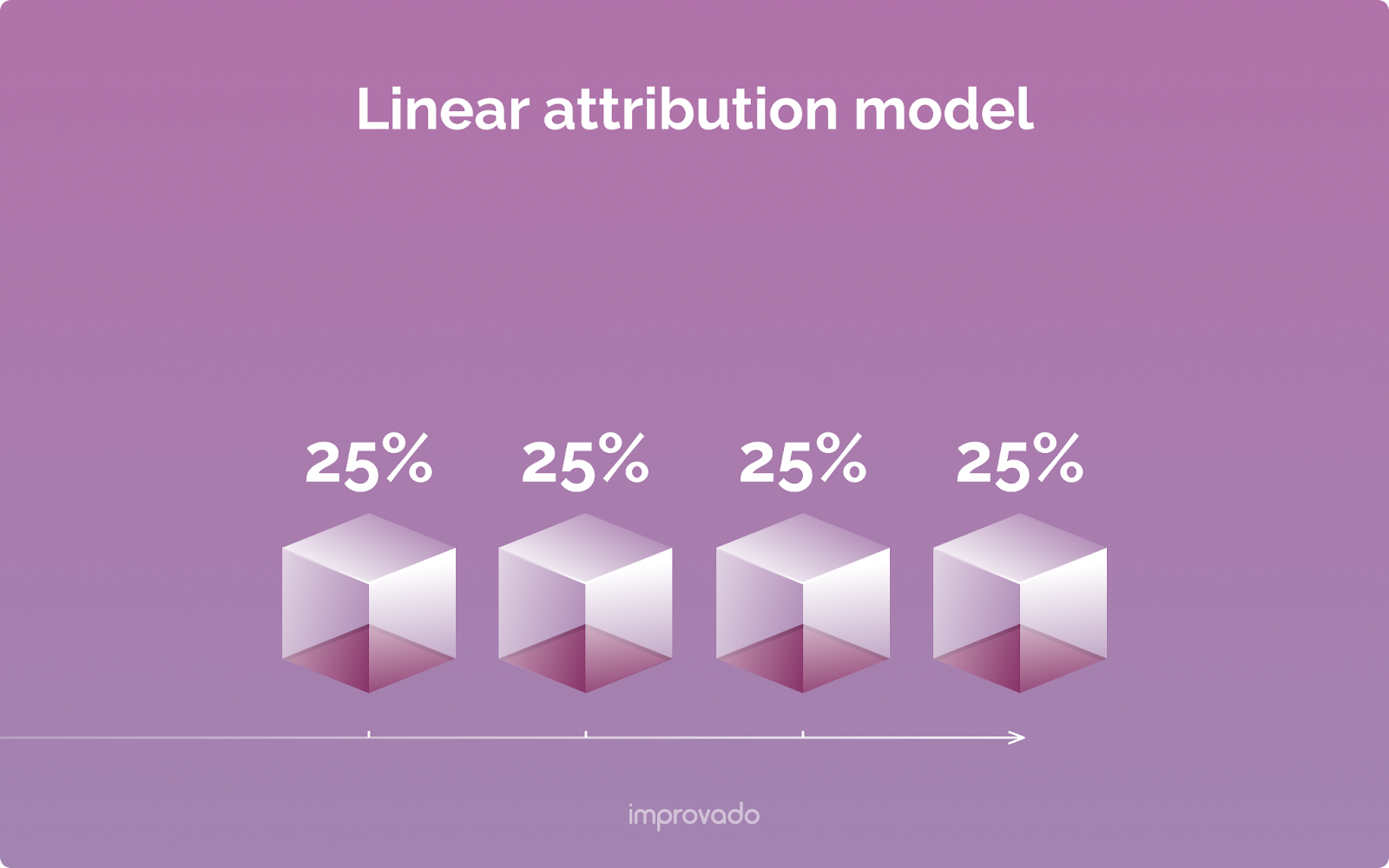
Position-Based (U-Shaped) Attribution Model
The Position-Based model, also known as the U-Shaped model, is a hybrid that gives special importance to two key moments: the first touch (the discovery) and the last touch (the conversion).
A common configuration assigns 40% of the credit to the first touch, 40% to the last touch, and distributes the remaining 20% evenly among all the touchpoints in the middle. This model values both what brought a customer in the door and what closed the deal, making it a popular and balanced choice for many businesses.
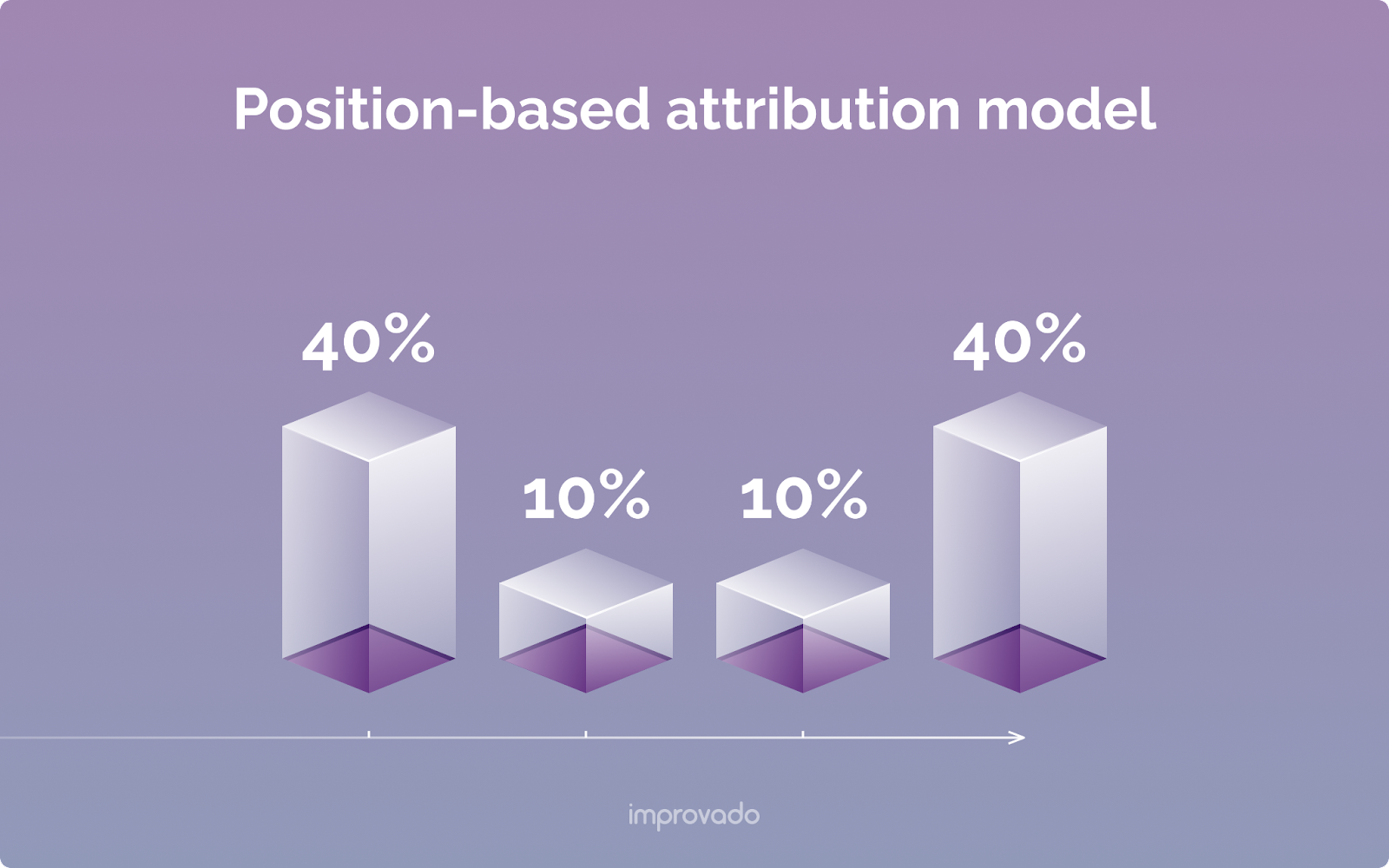
Time-Decay Attribution Model
The Time-Decay model gives more credit to touchpoints that happened closer in time to the conversion. The interaction that occurred just hours before the sale gets more credit than the one that happened weeks earlier.
This model is based on the assumption that the most recent touchpoints were the most influential. It’s particularly useful for businesses with longer consideration phases or B2B sales cycles where relationship-building and nurturing activities closer to the deal closing are critical.
Its main downside is that it can undervalue critical top-of-funnel activities that started the journey.
W-Shaped Attribution Model
The W-Shaped model is an evolution of the U-Shaped model. It also gives credit to the first and last touches but adds a third major milestone: the point where a prospect becomes a qualified lead (for example, when they sign up for a demo or create an account).
A common credit distribution is 30% to the first touch, 30% to the lead creation touch, 30% to the final conversion touch, and the remaining 10% is split among the other interactions.
This is a powerful model for B2B companies with a defined sales funnel and MQL/SQL stages.
| Multi-Touch Model | Credit Distribution | Key Assumption | Best For... | Primary Weakness |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Linear | Equal credit to all touchpoints. | Every interaction is equally important. | Valuing the entire customer journey and long sales cycles. | Doesn't differentiate impact; first and last touches are often more critical. |
| Time-Decay | More credit to touchpoints closer to conversion. | The most recent touchpoints are the most influential. | Shorter promotional campaigns or relationship-based B2B sales. | Devalues critical top-of-funnel, awareness-building activities. |
| Position-Based (U-Shaped) | 40% first, 40% last, 20% split in the middle. | The first and last interactions are the most important. | Businesses focused on both lead generation and conversion optimization. | Can undervalue crucial mid-funnel nurturing touchpoints. |
| W-Shaped | 30% first, 30% lead creation, 30% last, 10% split elsewhere. | First touch, lead creation, and close are the three pivotal moments. | Companies with a distinct lead-to-opportunity sales process (e.g., SaaS). | More complex to implement as it requires tracking the lead creation event. |
Advanced and Algorithmic Attribution Models: Beyond the Rules
While rules-based models are a massive leap forward from single-touch attribution, they still rely on human assumptions. The most advanced stage of attribution maturity involves leveraging machine learning to move beyond these assumptions.
Data-Driven (Algorithmic) Attribution
Data-Driven Attribution (DDA) uses machine learning algorithms to analyze all converting and non-converting paths in your data. It compares the paths of customers who converted to those who didn't to identify the patterns and determine which touchpoints truly had the most impact.
The model assigns credit based on the incremental lift provided by each interaction. This is the most accurate and unbiased approach, but it requires a very large volume of data to work effectively and often relies on sophisticated platforms like a dedicated marketing analytics platform or tools like Google Analytics 4's DDA model.
Marketing Mix Modeling (MMM)
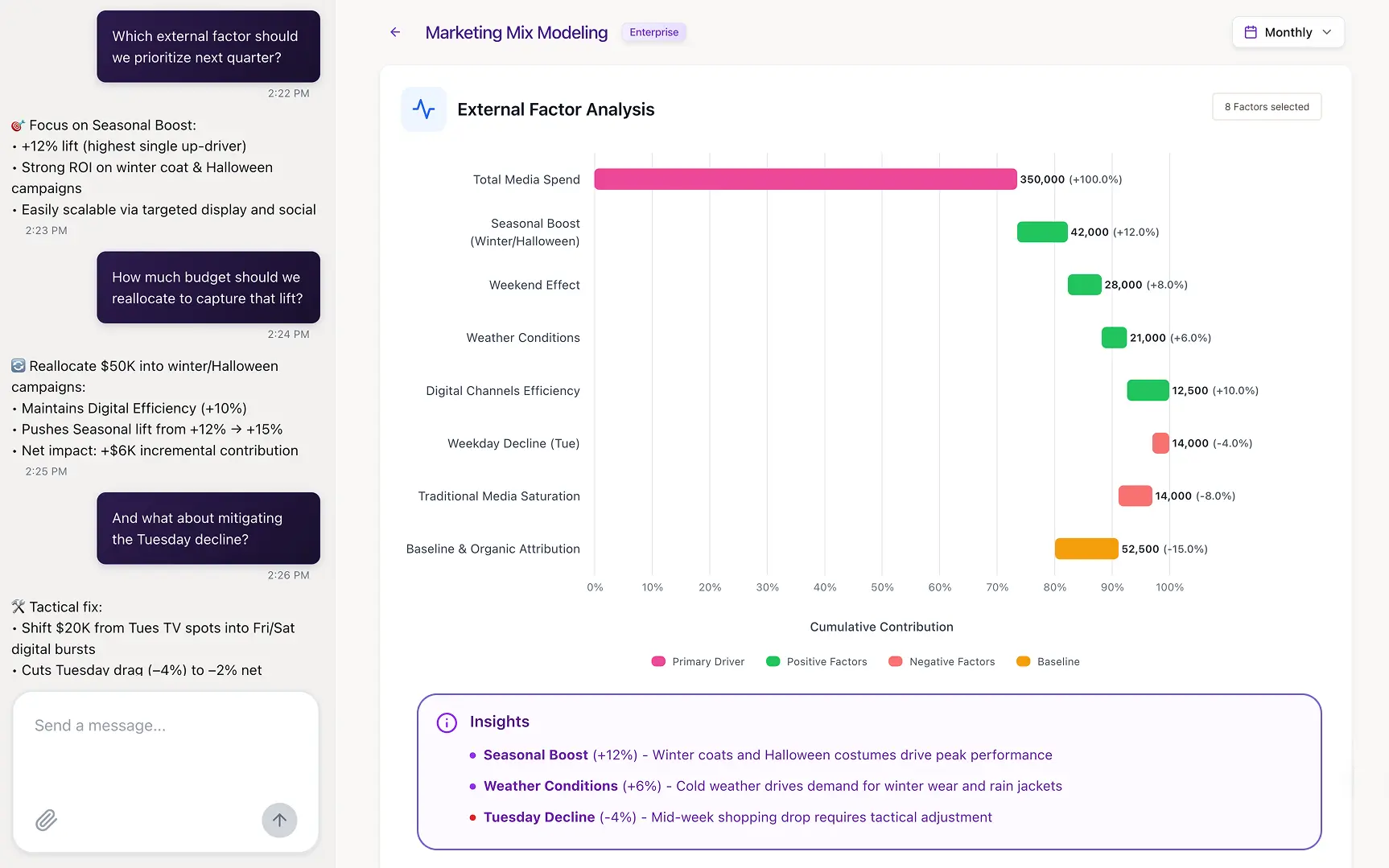
Marketing Mix Modeling takes a different, top-down approach.
Instead of tracking individual user journeys, MMM uses statistical analysis (like multivariate regression) on aggregate historical data to quantify the impact of various marketing inputs on a specific outcome, usually sales or revenue.
It can measure the impact of both online and offline channels (like TV, radio, and print) and account for external factors like seasonality, economic conditions, and competitor actions.
While less granular than user-level attribution, MMM is becoming increasingly important in a privacy-focused world where user-level tracking is more difficult.
How to Choose the Right Attribution Model for Your Business
Selecting the right model is not a technical decision; it's a strategic one. It requires introspection about your business, your customers, and your goals. Here’s a framework to guide your choice:
- Define Your Business Goals: What are you trying to achieve? If your primary goal is brand awareness and new lead acquisition, a First-Touch model might be a good starting point. If you're focused on optimizing a complex funnel for conversions, a multi-touch model like U-Shaped or W-Shaped is necessary.
- Analyze Your Sales Cycle Length: For businesses with very short, transactional sales cycles (for example, low-cost e-commerce), a Last-Touch model might be sufficient. For B2B SaaS with a 6-month sales cycle involving multiple decision-makers, a Time-Decay or W-Shaped model will provide far more valuable insights.
- Assess Your Channel Mix: If you only market on two channels, a simple model will do. If you're running coordinated campaigns across a dozen channels (paid search, social, content, email, webinars, etc.), you absolutely need a multi-touch model to understand how they interact.
- Evaluate Your Resources and Technical Capabilities: Be realistic. Do you have the data volume for a data-driven model? Do you have the technical expertise to implement cross-domain and cross-device tracking? It's better to implement a simpler model correctly than a complex model poorly. Start with what's feasible and build from there.
Don't be afraid to experiment. Use a tool (like Google Analytics' Model Comparison Tool) to compare how different models would assign credit based on your existing data. This can reveal biases in your current reporting and highlight which model best aligns with your business logic.
Implementing Your Attribution Model: A Step-by-Step Guide
Moving from theory to practice is where the real work begins. Successful implementation hinges on a solid data foundation.
Step 1: Unify Your Data Sources
Attribution only works if your data speaks the same language.
Marketing data lives in silos — ad platforms, CRM systems, website analytics, offline touchpoints, call tracking, and product usage data all sit in separate environments. Before you can assign credit accurately, you need a single, centralized view of every customer interaction. That means standardizing naming conventions, aligning timestamps, reconciling identities, and ensuring every source feeds into one destination.
This is where Improvado streamlines the process. Instead of juggling APIs, spreadsheets, and manual mapping, Improvado automatically consolidates and prepares cross-channel marketing and sales data for attribution analysis.
With Improvado, you can:
- Connect and extract data from over 500 of ad, CRM, and analytics tools, online and offline sources, in-house systems and any niche platforms
- Normalize fields, naming conventions, and taxonomies across sources
- Resolve identity and unify touchpoints for every customer journey
- Apply pre-built and custom attribution models across centralized datasets
- Push clean, attribution-ready data to your warehouse or BI tool or build attribution models with AI Agent
By starting with a unified foundation, you eliminate reporting blind spots, reduce attribution errors, and give your models the context they need to reveal true impact across the funnel.
Step 2: Ensure Consistent Tracking
Consistent tracking is non-negotiable. This means implementing a rigorous UTM tagging strategy across all your campaigns.
Every URL used in your marketing should have clear, consistent tags for source, medium, campaign, content, and term. Without this, your data will be a mess, and your attribution model will be built on a faulty foundation.
You can learn more about UTM tracking best practices to get started.
Step 3: Stitch User Identities
A user might interact with you on their phone, their laptop, and their work computer. They might use different browsers or clear their cookies.
Identity stitching is the process of resolving these different interactions back to a single, unique user profile. This is a complex technical challenge that often requires a Customer Data Platform (CDP) or advanced identity resolution solutions.
Step 4: Choose Your Modeling Environment
Where will you run your model?
This could be within a platform like Google Analytics 4, a dedicated attribution tool, or a custom model you build yourself in a BI tool or data warehouse. The latter provides the most flexibility but requires the most technical resources.
The goal is to feed your clean, unified data into this environment to be processed according to the rules of your chosen model.
Step 5: Visualize and Activate the Insights
Data is useless if it isn't accessible. The final step is to visualize your attribution results in intuitive KPI dashboards. These dashboards should allow your team to slice and dice the data, compare model outputs, and identify optimization opportunities.
Setting up automated reporting ensures these insights are delivered consistently, enabling your team to make data-driven decisions part of their regular workflow.
Common Challenges and Pitfalls in Attribution Modeling (And How to Avoid Them)
The path to attribution mastery is fraught with challenges. Being aware of them is the first step to overcoming them.
Ignoring Offline Channels
Many customer journeys include offline touchpoints like events, direct mail, or even word-of-mouth. Standard digital attribution models miss these entirely.
To get a more complete picture, you need to find ways to incorporate this data, either through methods like custom coupon codes, "how did you hear about us?" survey fields, or by using a broader MMM approach.
Data Silos and Integration Issues
The most common failure point is data. Overcoming data integration challenges is paramount. If your ad platform data doesn't talk to your CRM data, you can't connect campaign spend to revenue. This is where a robust, automated data integration platform becomes a critical piece of your marketing technology stack.
The Walled Gardens of Major Platforms
Platforms like Facebook and Google operate as "walled gardens," making it difficult to track users once they leave their ecosystem. This can lead to gaps in the customer journey. Cross-device tracking and probabilistic modeling can help fill some of these gaps, but it remains a persistent challenge.
Navigating Privacy Regulations and Cookie Deprecation
With GDPR, CCPA, and the impending deprecation of third-party cookies, user-level tracking is becoming harder. This is a major headwind for granular attribution. Marketers must adapt by relying more on first-party data, cohort analysis, and privacy-centric modeling techniques like MMM. A strong first-party data strategy is no longer optional.
Analysis Paralysis and Lack of Action
Don't let perfect be the enemy of good. It's easy to get lost in the data and endlessly debate which model is "right." The goal isn't to find a perfect model but to find a model that is directionally correct and provides actionable insights. Pick a model, use it to make decisions, measure the results, and iterate. The value of attribution comes from the actions you take based on its insights.
The Future of Marketing Attribution: Trends to Watch
The world of attribution is constantly evolving. Staying ahead of the curve means understanding the forces that are shaping its future.
- The Rise of AI and Machine Learning: Algorithmic attribution will become more accessible. AI will not only help assign credit more accurately but will also provide prescriptive recommendations, suggesting budget shifts and campaign optimizations automatically.
- Unified Measurement Frameworks: The future isn't about choosing between MTA and MMM. It's about combining them. Unified measurement frameworks use the granularity of MTA for day-to-day digital optimization and the breadth of MMM for high-level strategic planning and offline channel measurement.
- Focus on Incrementality: The key question is not "what channel got the credit?" but "what would have happened if I didn't run this campaign?" Incrementality testing and conversion lift studies, which use control groups to measure the true causal impact of marketing, will become a standard part of the attribution toolkit.
- Privacy-Centric Solutions: Expect to see more innovation in privacy-enhancing technologies (PETs) and data clean rooms, which allow for aggregated analysis without exposing individual user data.
Conclusion: Activating Your Insights with a Unified Data Strategy
Attribution modeling can transform how you allocate budget, optimize campaigns, and understand the true value of each channel but only when it’s built on complete, trustworthy data.
If touchpoints are missing, identities aren’t matched, or platforms don’t share a common language, even the most advanced attribution framework will deliver skewed insights.
Improvado provides the foundation required for attribution modeling done right. It centralizes marketing, sales, and revenue data; normalizes naming and taxonomies; resolves identities across platforms; and ensures every interaction flows into a single analytics environment.
With clean, cross-channel data structured for analysis, teams can layer any attribution model with confidence. Improvado removes the data engineering burden, enabling marketers to focus on insight, not infrastructure.
.png)



.png)
