Every marketing report relies on accurate conversion data. But how do platforms track user interactions across websites and ads? The answer lies in tracking pixels. These small tools collect behavioral data. They attribute conversions and optimize campaign performance.
This article explains what tracking pixels are and how they work. It covers their benefits and crucial considerations for marketers in 2026. We'll also explore the legal landscape surrounding them and examine the privacy concerns they raise. We'll discuss what the future holds for this fundamental digital marketing tool.
What Is a Tracking Pixel?
The concept is often referred to as a “spy pixel”, as described on Wikipedia, emphasizing its role in tracking user behavior through invisible images. When a user loads a webpage or opens an email, the pixel triggers a server request. This request sends key interaction data. This allows marketers, advertisers, and website owners to analyze user activity, track conversions, and optimize ad spend.
Key insights provided by tracking pixels include:
- Pageviews: Tracks how often a specific webpage is visited.
- User Data: Captures IP addresses, device types, browsers, and geographic locations.
- Conversion Tracking: Identifies when a user completes key actions, such as submitting a form or making a purchase.
- Ad Performance: Measures impressions, clicks, and post-click conversions to assess the effectiveness of digital advertising campaigns.
How Does a Tracking Pixel Work?
Unlike regular images, tracking pixels are hosted on a remote server. This server could be owned by an advertising company, a social media platform, or any organization interested in collecting data.
The process unfolds in a few key steps.
1. Embedding the pixel with HTML code
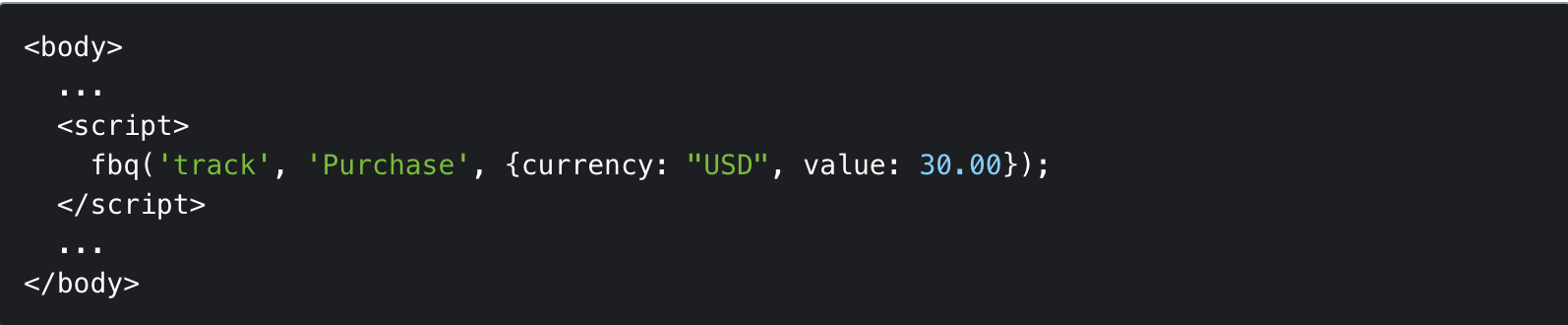
A tracking pixel is inserted into a webpage, email, or digital advertisement via a small HTML snippet. This snippet contains a URL pointing to the pixel’s location on the tracking server. Platforms like Google Ads, Meta (Facebook), and LinkedIn use this method to track ad impressions, email opens, and conversions.
Consider a Meta pixel code example. It triggers when users complete purchases. The pixel sends specific information to Meta's servers. This logs the conversion event. This embed method is foundational for all pixel tracking.
2. The browser requests and data transmission
When a user loads the webpage or email, their browser reads the HTML code. Upon encountering the pixel's code, the browser automatically sends a request to the server hosting the pixel.
This process works like loading any other image file. The pixel is transparent and tiny. Users remain unaware of it. During this request, various pieces of user information are transmitted to the server.
3. Server logging and analysis
Once the pixel server receives the request, it logs the interaction in its database. This log captures various user data points, including:
- IP Address: Determines approximate location and Internet Service Provider.
- User-Agent String: Identifies the browser, operating system, and device type (e.g., mobile, desktop).
- Timestamp: Records the exact moment the pixel was triggered.
- Referrer URL: Indicates the webpage the user visited immediately before triggering the pixel, providing context for the interaction.
More sophisticated tracking pixels capture additional details. They record screen resolution and language settings. Language settings help with localization. Pixels also track specific user interactions. Examples include clicks, form submissions, and time spent on pages. This rich information enables advertisers to analyze user behavior in detail.
Tracking Pixel vs Cookies
Don't cookies do the same thing?
Well, not exactly. While both tracking pixels and cookies collect user data, they operate differently and serve distinct marketing purposes.
A tracking pixel is like a silent reporter that sends information directly to a server, providing real-time data about user interaction. Cookies, on the other hand, are small text files that store information on the user's web browser itself. Because tracking pixels report back to a server, they can often gather information from multiple devices if a user is logged into the same platform (like Facebook) across them, whereas cookies are typically browser-specific.
Here's a breakdown of their key differences.
| Aspect | Tracking Pixel | Cookies |
|---|---|---|
| Nature | Invisible image (usually 1x1 pixel) | Small text files |
| Location | Embedded in content (webpages, emails, ads) | Stored on user's device |
| Primary Use | Monitor interactions and gather data | Store user data and preferences |
| Data Collection | Sends data back when content is accessed | Gathers data over multiple sessions/interactions |
| Scope of Tracking | Specific to content where it's embedded | Tracks user behavior across various web pages/sites |
| Duration | Active as long as content is live | Can be session-based or persistent for a set duration |
| Retargeting | Commonly used for retargeting campaigns | Facilitates personalized experiences based on history |
| User Control | Hard for users to detect without specialized tools | Users can easily delete or block via browser settings |
With growing privacy regulations and the decline of third-party cookies, tracking pixels, particularly when deployed server-side, remain a more reliable method for marketers to measure engagement, optimize ad spend, and track conversions across multiple platforms.
Types of Tracking Pixels
Tracking pixels serve different purposes depending on the data they collect and how they are used in digital marketing and analytics. Below are the most common types:
- Retargeting Pixels: Retargeting pixels track user behavior on a website, such as pages visited, products viewed, or time spent, to serve relevant ads across other websites and platforms. For example, users might view a product on an e-commerce site. If they don't purchase, these pixels enable retargeting. Advertisers can show ads for that specific product or similar items later.
- Conversion Pixels: Conversion pixels trigger when a user completes a desired action, like making a purchase, submitting a form, or signing up for a newsletter. These pixels are critical for measuring advertising campaign effectiveness. They attribute specific conversions to the traffic sources that drove them. This provides valuable information on campaign performance.
- Analytics Pixels: Analytics pixels collect broad engagement data, including page views, session duration, bounce rates, and visitor demographics. Marketers often integrate these pixels with platforms like Google Analytics 4 (GA4). They provide a holistic view of website traffic and user behavior. This helps analyze overall website performance and user interaction. From an SEO and analytics standpoint, Ryte details how tracking pixels enable performance measurement and retargeting campaigns.
- Social Media Pixels (Meta, LinkedIn, etc.): Platforms like Facebook (Meta), LinkedIn, X (Twitter), and Pinterest use their proprietary pixels to track ad engagement, optimize audience targeting, and measure conversions within their respective ecosystems. These pixels help advertisers build custom audiences, create lookalike audiences, and understand the ROI of their social media ad campaigns.
- Email Tracking Pixels: Embedded in emails, these pixels monitor open rates, link clicks, and forwards, providing insights into email campaign engagement and audience interaction. They help email marketers understand how recipients interact with their content and refine their email marketing strategy. According to the BBC, “spy pixels in emails have become endemic,” illustrating how pervasive invisible tracking has become in everyday inboxes. With over 4.6 billion email users worldwide in 2026, even small changes in tracking practices can affect vast audiences.
- Affiliate Pixels: Used in affiliate marketing, these pixels track sales or leads generated through specific referral links. They ensure accurate commission payouts for affiliates by precisely attributing conversions to the correct partner, enabling a transparent method for performance-based marketing.
Benefits and ROI of Pixel Tracking
The data harvested by tracking pixels is like a treasure chest for businesses. This invaluable information translates into tangible benefits and a strong return on investment (ROI) for digital marketing efforts.
1. Personalized web experiences
Imagine visiting a website that instantly understands your interests. That's what tracking pixels enable.
By collecting data on user behavior, these pixels help businesses understand what each visitor is interested in. This means the next time the same user visits, businesses can show more relevant content, products, or offers. This makes the entire website experience more engaging and effective.
This personalization boosts user satisfaction and conversion rates.
2. Optimized advertising campaigns & ad spend
Tracking pixels are essential for understanding which ad campaigns are performing well and which aren't. They allow marketers to measure impressions, clicks, and conversions with precision.
This clarity enables businesses to stop spending money on underperforming ads. They can reallocate budgets to campaigns that deliver the best results. It's like having a super-smart advisor. The advisor tells you exactly where to invest your advertising dollars for the highest ROI. This ensures every dollar of ad spend is optimized.
3. Enhanced website analytics
Beyond just ad performance, tracking pixels provide a granular view of user activity across your website. They contribute to comprehensive website analytics by capturing page views, session durations, scroll depth, and specific user interactions.
This detailed user behavior data allows businesses to identify pain points in the user journey. They can optimize site navigation and improve overall website usability. This leads to higher engagement and better conversion funnels.
4. Cross-platform measurement
In today's multi-channel marketing landscape, users interact with brands across numerous platforms and devices. Tracking pixels facilitate cross-platform measurement by linking user activity from an initial ad click on one platform to a conversion on your website, or even an email open. This capability provides a more complete picture of the customer journey. It helps marketers understand the true impact of their integrated campaigns. It enables more accurate attribution modeling.
How Does Tracking Pixel Data Become Actionable?
Tracking pixels power attribution, audience segmentation, and performance measurement. But raw pixel data is disorganized and incomplete on its own. To extract meaningful insights, it must go through several processing stages before appearing in reports or dashboards.
Here’s how tracking pixel data flows through the marketing analytics pipeline and how platforms help organize it for advanced reporting.
1. Data capture across multiple platforms
Each platform logs pixel-tracked user interactions independently, leading to multiple versions of the same event in different environments:
- Google Ads & Meta Ads: Store pixel data related to clicks, impressions, and conversion events (purchases, sign-ups, form fills).
- Google Analytics 4 (GA4): Captures site-wide user activity, including page views, scroll depth, and engagement metrics, but doesn’t automatically connect ad-driven conversions to revenue.
- Email marketing platforms (HubSpot, Marketo, Mailchimp): Use tracking pixels to log email opens, link clicks, and post-email website behavior, but this data is often separate from advertising performance.
- CRM & ecommerce systems (Salesforce, Shopify, Magento): House customer transactions and offline conversions, but don’t natively connect with ad platform tracking.
These platforms don't natively communicate. Marketing teams must manually reconcile cross-channel conversion paths. This leads to reporting inefficiencies and lost insights. The alternative is to integrate data automatically with a data platform.
2. Data aggregation & cross-platform identity matching
To analyze cross-channel performance, marketers need a unified data pipeline that integrates pixel data from different sources. This process includes:
- ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) pipelines: Platforms like Improvado pull raw event data from ad networks, analytics tools, and CRM systems into a single environment.
- Cross-platform identity matching: Using UTM parameters, first-party cookies, and user IDs to link interactions across touchpoints (e.g., a Google Ads click that led to an email conversion).
- Data processing and standardization: Different event names (Google Ads “Purchase” vs. GA4 “Transaction”) are aligned to create a consistent dataset by a data transformation engine, and duplicate conversions logged by multiple tracking pixels across platforms are removed.
- Offline & online attribution: Matching pixel-based conversions with offline sales data from Salesforce or other CRMs, ensuring all revenue contributions are accounted for.
Without automated data integration, marketers risk double-counting conversions, failing to track multi-touch journeys, or misattributing revenue to the wrong channels. The real power of pixel data is unlocked when it's combined with data from every other marketing source.
3. Data modeling & BI integration
Once aggregated and standardized, pixel data is prepared for analysis and strategic decision-making. Depending on the analytics requirements, marketers can:
- Apply attribution models: Use last-click, first-click, linear, or data-driven attribution to understand how different campaigns contribute to conversions.
- Incorporate predictive analytics: Leverage historical pixel data to forecast trends and optimize spend allocation.
- Push data to BI and reporting tools: Export structured pixel data into Looker, Tableau, Power BI, or Google Data Studio for advanced reporting and visualization. An AI-powered marketing intelligence platform like Improvado automates the entire data pipeline—from extraction and cleaning to transformation—creating a single, reliable source of truth that feeds directly into BI tools like Tableau or Looker for advanced analysis and reporting.
The Risks and Privacy Concerns of Pixel Tracking
While incredibly useful, tracking pixels are not without controversy. The main issue revolves around user privacy and the ethical implications of data collection.
Understanding these risks is crucial for both marketers and users.
Invasion of user privacy & lack of transparency
One of the biggest concerns is that tracking pixels collect data about users without their explicit knowledge or consent. This unseen collection of personal and behavioral information can feel like an invasion of privacy.
While some pixels are declared in privacy policies, the average user often doesn't realize the extent to which their online activities are being monitored by various trackers embedded across the web.
This lack of transparency erodes trust and raises significant ethical questions about data collection practices.
Misuse of data and intrusive advertising
The data collected by tracking pixels can be extensive, including browsing history, interests, demographics, and even purchase intent. There's a risk that this highly detailed information could be misused by third parties.
This might include sharing data with other companies without user awareness, or using it to create highly intrusive and persistent advertising that feels overly personalized or even manipulative.
Even seemingly anonymized data, such as "hashed" identifiers, can sometimes be de-anonymized, leading to a loss of true user privacy.
Data security risks and breaches
Any system that collects and stores vast amounts of user data is a target for cyber threats. Tracking pixel data, if not adequately secured, can be vulnerable to data breaches. If this sensitive information falls into the wrong hands, it can lead to identity theft, fraud, or other malicious activities.
Businesses deploying tracking pixels have a significant responsibility to ensure robust data security measures are in place to protect the user information they collect.
Are Tracking Pixels Legal? (GDPR, CCPA, & HIPAA)
The legality of tracking pixels is a complex and evolving landscape, primarily governed by data privacy regulations designed to protect user information. Academic research has explored mitigation strategies for tracking beacons. One paper, Email Tracking Beacon: Concerns and Solutions, analyzes privacy implications and user protection methods.
Compliance is critical for any organization utilizing pixels.
Compliance with GDPR & CCPA
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) are two of the most significant data privacy laws impacting tracking pixels.
Both require businesses to:
- Obtain explicit consent: For most tracking activities, especially those involving personal data or targeting, users must provide clear, affirmative consent before a pixel starts collecting data. This usually takes the form of cookie consent banners or privacy notices.
- Be transparent: Companies must inform users about what data is being collected, why it's being collected, and how it will be used.
- Provide user rights: Users have rights to access, rectify, and delete their data, and to opt out of its sale or sharing.
Failure to comply with GDPR or CCPA can result in hefty fines, emphasizing the importance of a well-defined privacy strategy for pixel deployment.
Implications for Healthcare and HIPAA
For healthcare organizations, the stakes are even higher due to the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) in the United States.
HIPAA governs the protection of Protected Health Information (PHI). If a tracking pixel collects or transmits data that could be considered PHI, the organization must ensure strict HIPAA compliance. PHI can include visits to pages about medical conditions, appointment bookings, or prescription refills.
This often means carefully scrutinizing all pixels. Organizations must prevent PHI transmission or obtain specific patient authorizations. This can be very challenging in a typical digital marketing context. Many healthcare providers opt for highly restricted or server-side tracking solutions. This helps them avoid compliance pitfalls.
FTC Guidance and Enforcement
In the United States, the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) plays a role in enforcing consumer protection laws, including those related to online privacy. The FTC provides guidance on transparency and fairness in data collection practices.
While not a specific data privacy law like GDPR or CCPA, the FTC can take action against companies. It targets companies that engage in deceptive or unfair practices regarding tracking. Examples include undisclosed pixel use or misleading privacy policies.
This means organizations must not only comply with specific laws but also adhere to broader principles of ethical data handling.
How to Block Pixel Tracking?
For users concerned about their privacy, several methods exist to minimize or block tracking pixels. While complete blocking can sometimes impact website functionality or personalization, these steps provide significant control.
Adjusting email client settings (Gmail, Outlook, Apple Mail)
Many email tracking pixels rely on the automatic loading of images within an email. You can prevent this by configuring your email client settings:
- Gmail: Go to Settings > See all settings > General. Under "Images," select "Ask before displaying external images."
- Outlook: Go to File > Options > Trust Center > Trust Center Settings > Automatic Download. Check "Don't download pictures automatically in HTML email messages or RSS items."
- Apple Mail: On macOS, go to Mail > Settings > Privacy. Deselect "Protect Mail Activity" or uncheck "Load Remote Content in Messages." On iOS, go to Settings > Mail > Privacy Protection and toggle off "Protect Mail Activity" or "Load Remote Content."
By disabling automatic image loading, you prevent the pixel from being "fired" unless you explicitly choose to display images for a specific email.
Using browser extensions and privacy plugins
Various browser extensions are designed to detect and block tracking pixels and other trackers:
- Privacy Badger (EFF): Automatically learns to block invisible trackers based on sites you visit.
- Ghostery: Identifies and blocks tracking technologies on websites, giving you control over which trackers to allow.
- uBlock Origin: Primarily an ad blocker, but also highly effective at blocking a wide range of trackers.
- Disconnect: Visualizes and blocks invisible tracking on websites.
Install these extensions from your browser's official store (Chrome Web Store, Firefox Add-ons, etc.) and configure them to block known trackers.
Configuring Browser Tracking Protection
Modern web browsers offer built-in privacy features that can help block tracking pixels:
- Mozilla Firefox: Enhanced Tracking Protection (ETP) blocks trackers by default. You can customize the level of protection (Standard, Strict, Custom) in the browser's privacy settings.
- Google Chrome: While Chrome has been slower to implement aggressive tracking prevention, it offers features like "Do Not Track" requests (though not widely enforced) and Incognito Mode, which prevents sites from storing cookies locally. Chrome is also phasing out third-party cookies.
- Apple Safari: Intelligent Tracking Prevention (ITP) automatically blocks cross-site tracking by limiting third-party cookies and other tracking methods.
- Microsoft Edge: Offers "Tracking prevention" settings with different levels (Basic, Balanced, Strict) to block trackers.
Regularly review your browser's privacy settings and enable the strongest tracking protection available to limit the data collected by pixels.
The Future of Pixel Tracking
The landscape of digital tracking is rapidly evolving, driven by increasing privacy regulations, consumer demand for data control, and technological advancements. The future of pixel tracking will likely be defined by a shift towards more privacy-centric and sophisticated methods.
The decline of third-party cookies, led by browsers like Safari and Firefox and soon by Chrome, is a major catalyst. This shift is pushing marketers to explore alternative tracking solutions that are less reliant on persistent cross-site identifiers.
One significant trend is the rise of server-side tracking. Instead of pixels directly sending data from the user's browser to third-party servers, server-side tracking routes data through the brand's own server first. This allows the brand to control, filter, and anonymize data before sending it to advertising platforms. This provides better data governance and potentially mitigates some privacy concerns. It also improves data accuracy and load times.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are also set to play a transformative role. AI can help refine tracking by:
- Probabilistic Matching: Using various data points (IP address, user agent, timestamps, device type) to probabilistically identify users across different sessions and devices without relying on traditional identifiers.
- Modeling Conversions: In scenarios where direct tracking is limited, AI can use historical data and other signals to model conversions and predict campaign performance, helping marketers optimize ad spend even with incomplete data.
- Enhanced Personalization: AI-powered systems can analyze collected pixel data to create more dynamic and relevant content delivery and advertising, moving beyond simple retargeting to truly intelligent, real-time personalization.
Ultimately, the future of pixel tracking points towards a more sophisticated, privacy-aware ecosystem. Brands prioritize first-party data. They leverage server-side solutions and utilize AI/ML to extract insights. They deliver personalized experiences while respecting user consent and regulatory requirements.
.png)

%20(1).png)


.png)
