Updated on
Nov 20, 2025
Custom SQL queries allow you to shape, filter, and optimize your data. Now, instead of pulling entire tables, you can write your query directly in the flat data extraction flow. This gives you more control to pre-filter or group your data before extraction, speeding up the process and reducing unnecessary load.
{%docs-informer info%} This feature is currently available only for Snowflake and Google BigQuery flat data ingestions. {%docs-informer-end%}
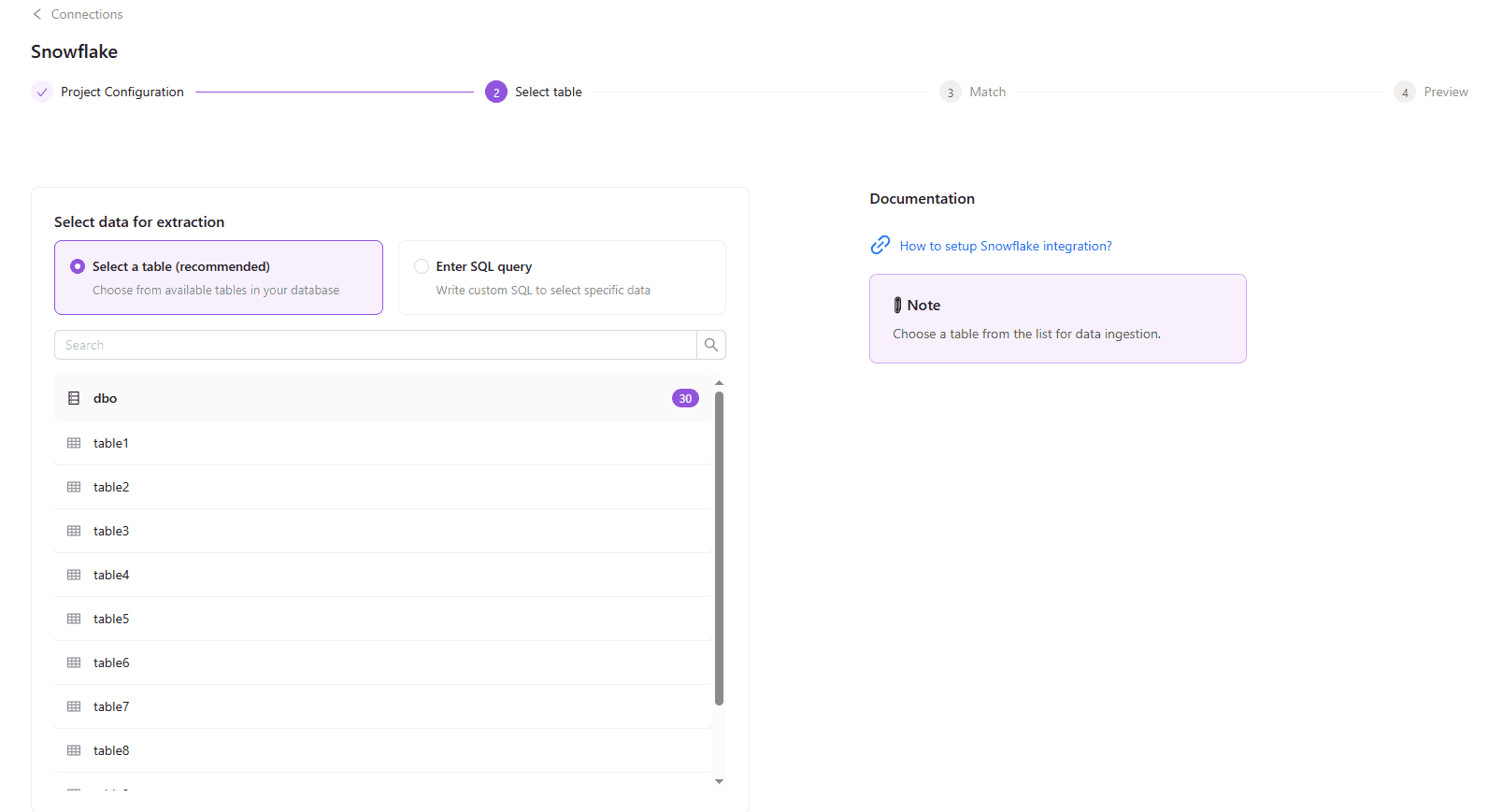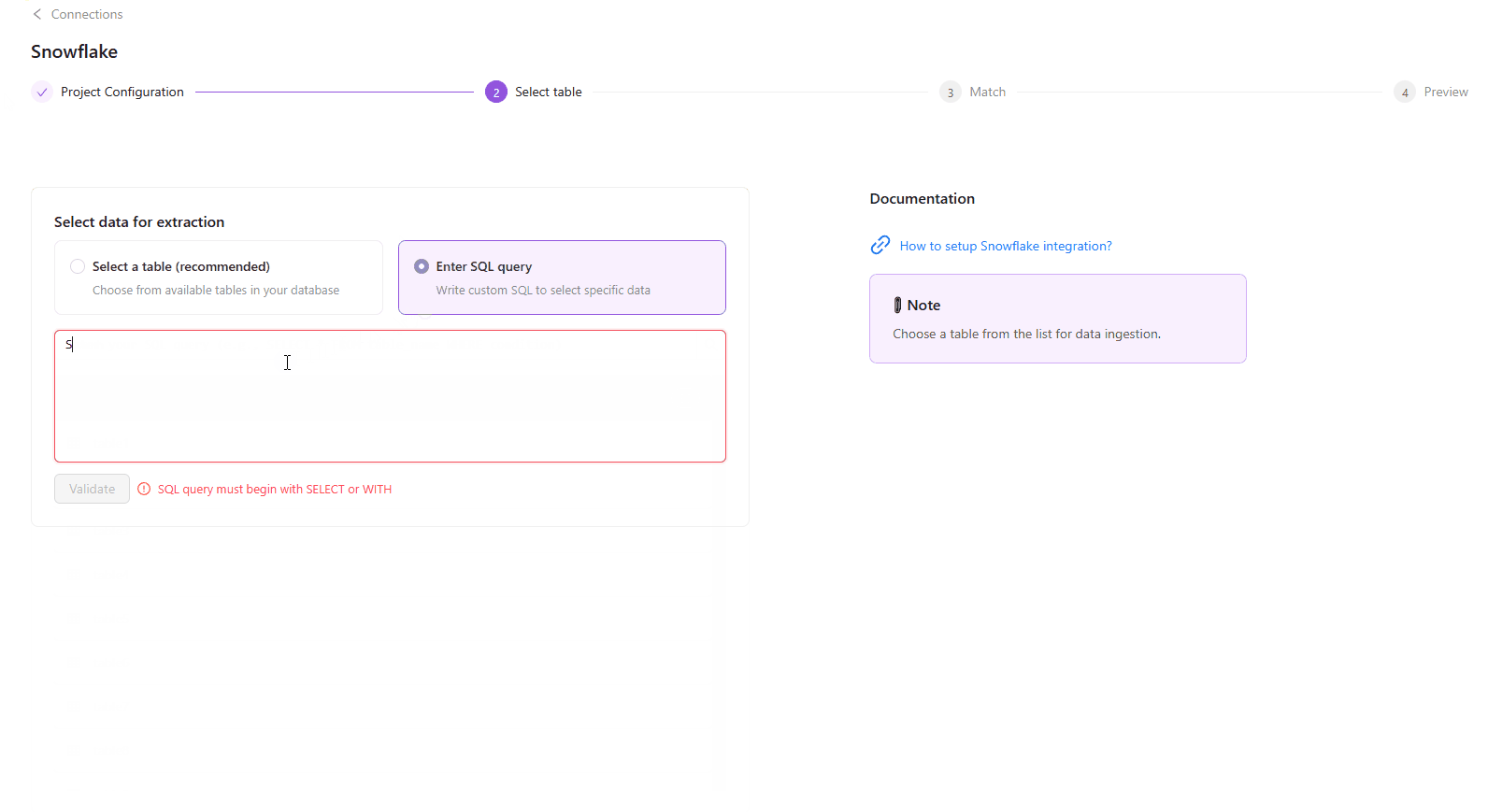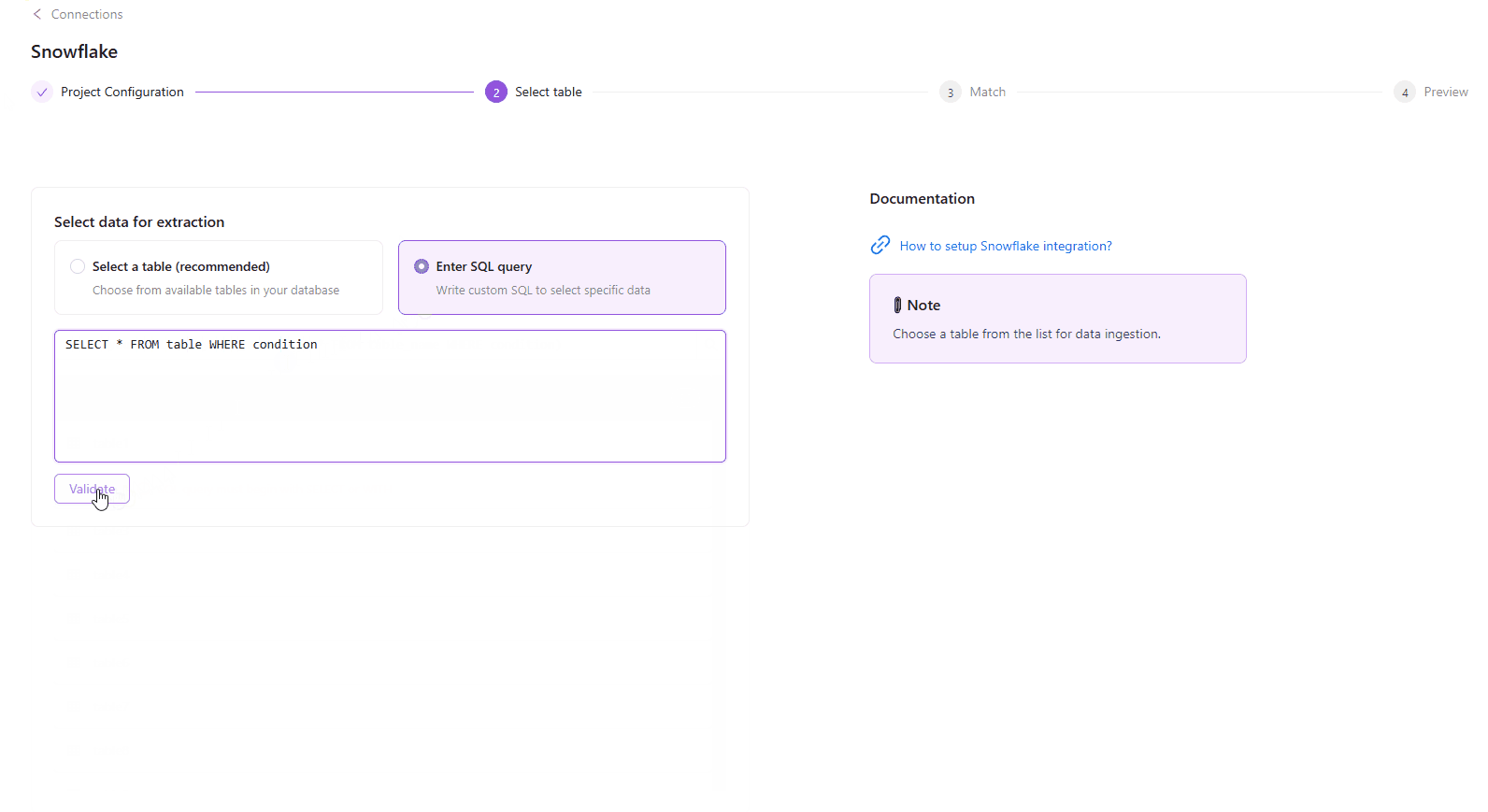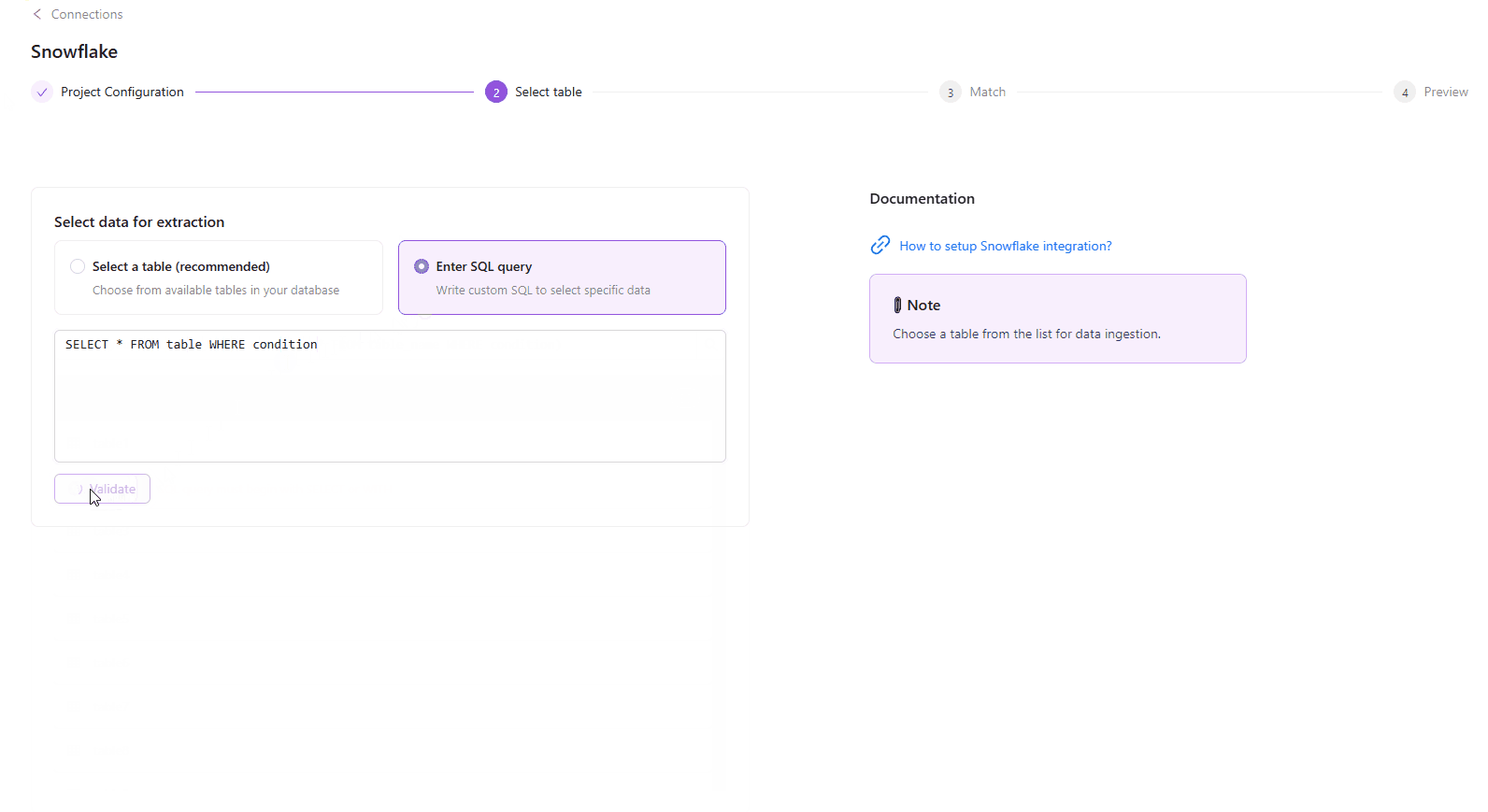
Step 1. Select the SQL query option, while setting up your flat data extraction.
Step 2. Enter custom SQL in the field.
Step 3. Click the Validate button to start the SQL query check.
Step 4. Click on the Continue button.
{%docs-informer info%} You can modify your custom SQL queries at any time in Order Settings tab. {%docs-informer-end%}
Below are common use cases and best practices for using custom SQL effectively.
You can use the Custom SQL query feature to extract data via cross-project queries directly, without going through GBQ manually. This enables you to pull data from another project or dataset seamlessly.
Step 1. Enter your GBQ project ID:```your-project-id``` and any dataset name in this project, e.g.: ```your-dataset```.
Step 2. Select the Enter SQL query option and enter the query to fetch data from a different project.
Example:
Use cases:
Many data warehouses store time-partitioned tables with naming conventions like ```events_2024_10``` or ```orders_2025_01```.
Custom SQL lets you query these tables dynamically using wildcards or pattern matching.
Example:
Use cases:
Instead of pulling raw event-level data, you can aggregate metrics directly in SQL to reduce data volume and improve performance.
Example:
Use cases:
You can derive new metrics or KPIs using SQL expressions. This allows you to add calculated fields that don’t exist in the source schema.
Example:
Use cases:
To reduce data load and processing time, apply filters directly in SQL. This ensures that only the most relevant subset of data is extracted.
Example:
Use cases:
CTEs allow you to structure complex queries for readability and modularity. They’re especially useful when multiple intermediate steps are needed.
Example:
Use cases:
Improvado team is always happy to help with any other questions you might have! Send us an email.
Contact your Customer Success Manager or raise a request in Improvado Service Desk.