Updated on
Jul 17, 2025
Attribution models are designed to work in both ways for B2B and B2C.
B2B considers customer journey at the account level, while B2C attributes single user journey.
We can also implement any attribution model for your needs.
First-touch attribution assigns all credit to the first touchpoint in the customer journey. However, it ignores all further interactions after the first touch with the brand.
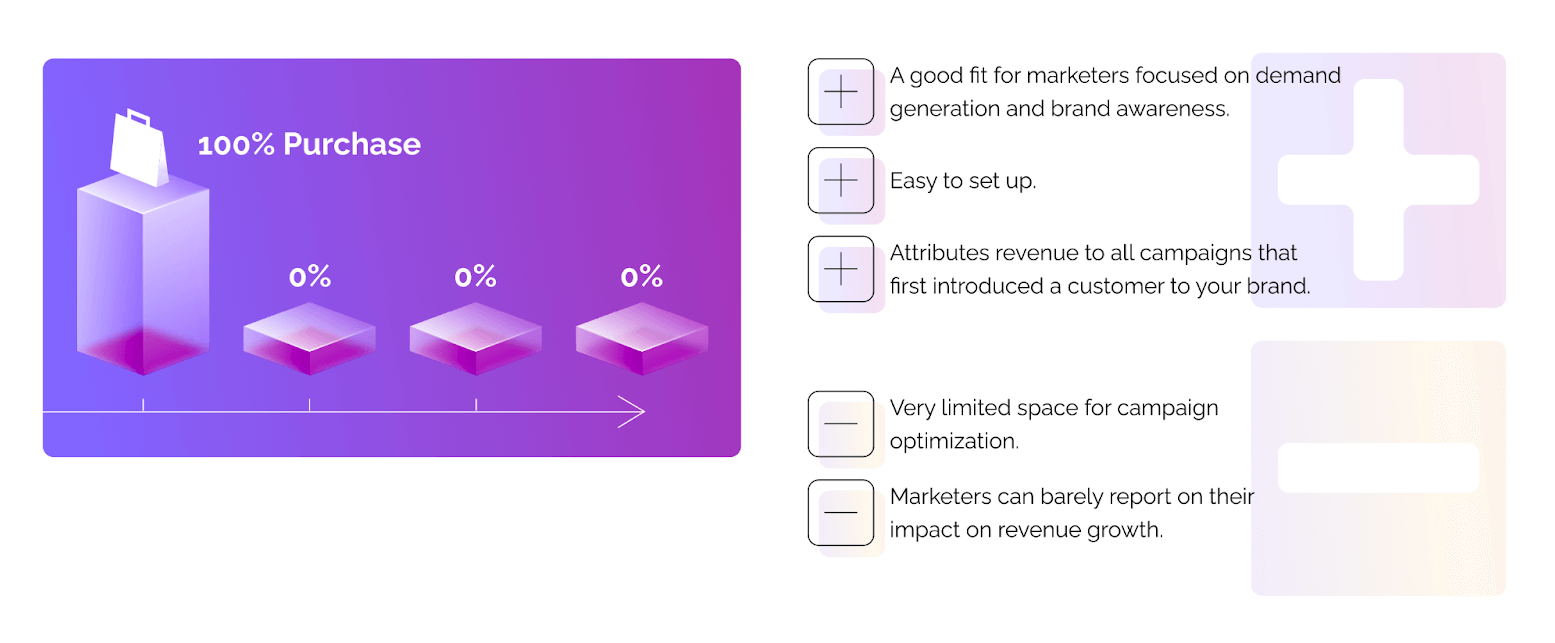
Last-touch attribution is the exact oposite of a first-touch model. It assigns 100% credit to the last step in the customer journey. In contrast to first-touch attribution, this model ignores all steps in the customer journey prior to the purchase.
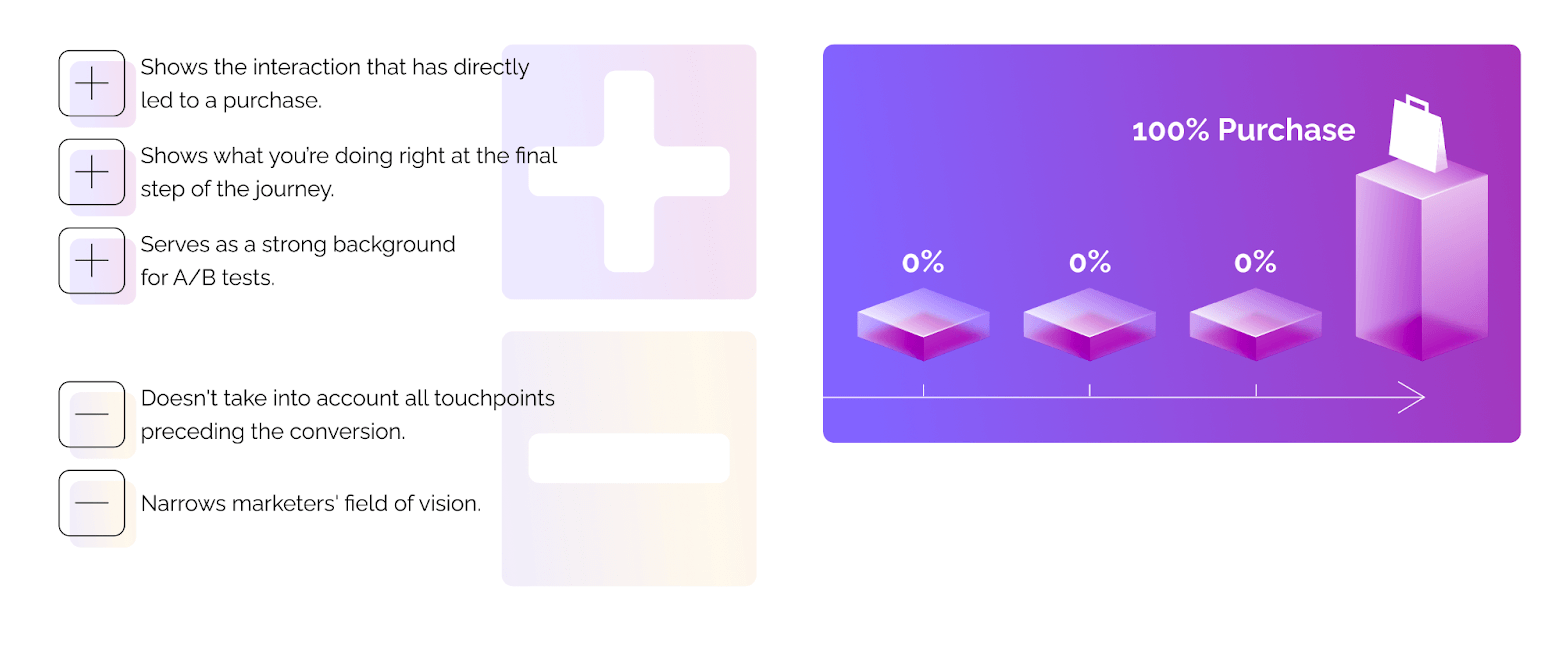
Imagine a prospect that has already discovered your brand and decided on the purchase. The next day, they enter your website's URL and make a purchase. The last-touch model attributes this conversion to direct, leaving you with no information about the stage where the prospect has made a purchase decision.
The linear attribution model is the first model on our list that assigns credit to interactions between first and last touches.
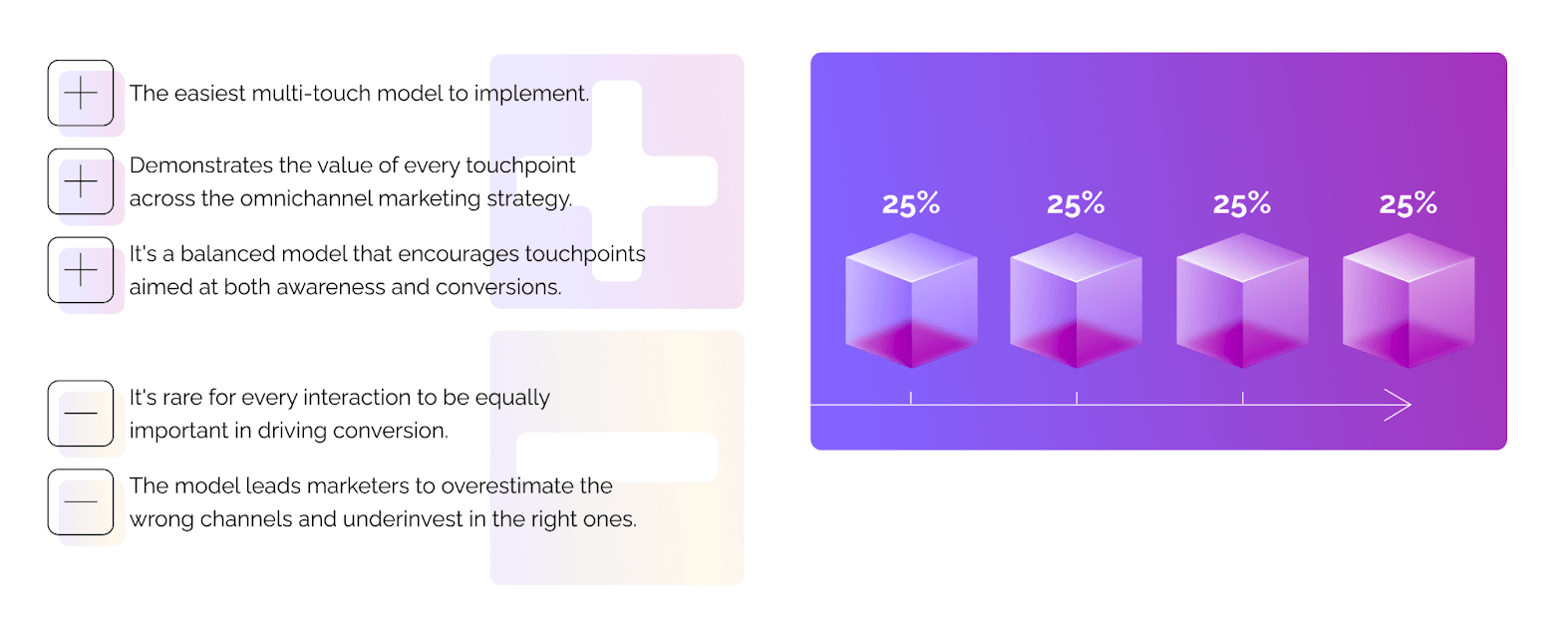
The linear model might be an entry point to a more advanced model. Accumulated data allows you to investigate touches that occur most frequently for a group of successful prospects. Then, you can shift your attribution model toward assigning more credit to more successful touchpoints.
Unlike all previous models, linear attribution takes into account all of the touchpoints across the journey. It distributes credit equally between all campaigns or channels. For example, if your omnichannel strategy consists of four different channels, each one of them gets 25% credit.
The position-based (also known as U-Shaped) attribution model considers the first and last interactions the most important within the customer journey. These two touchpoints get a fixed credit for every conversion.
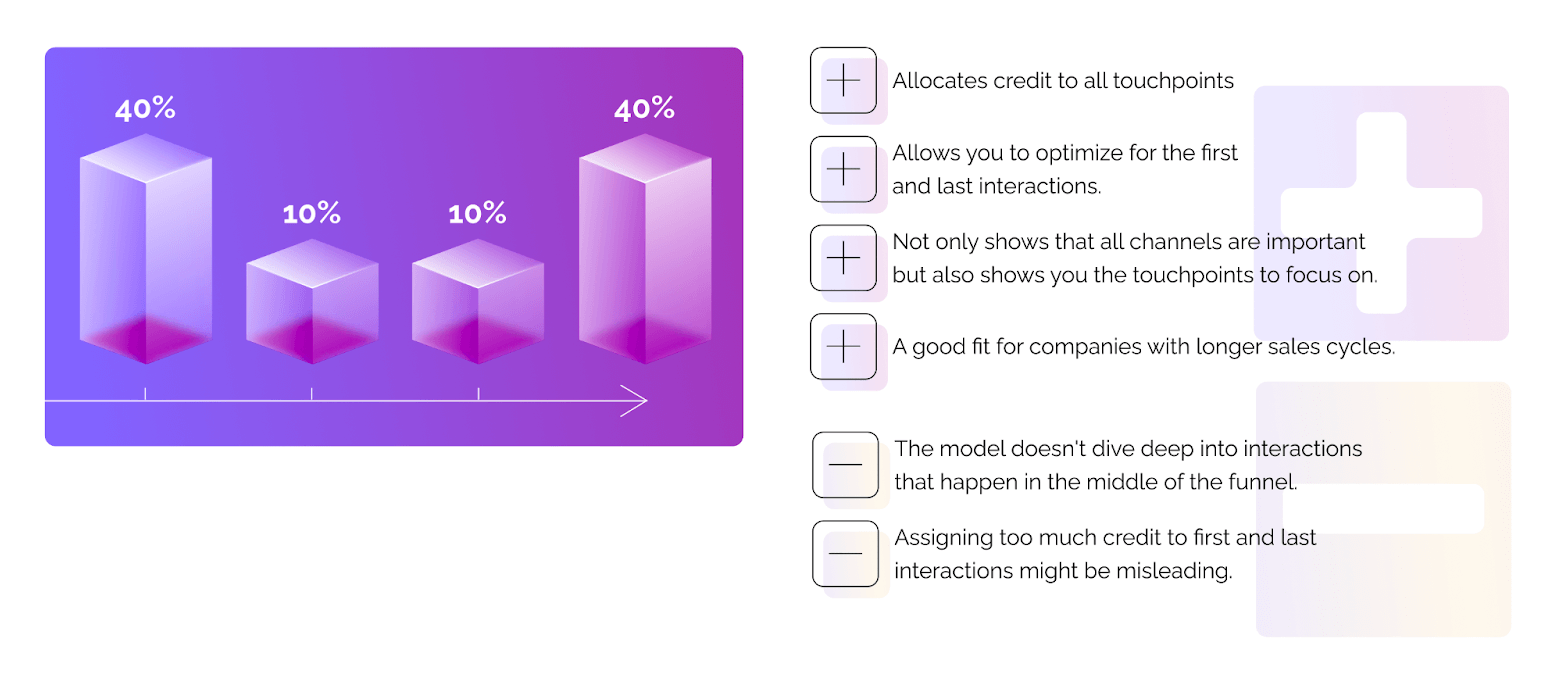
The position-based model also has a varition that is slightly different from the original.
For example, when this model is used in Google Analytics, it assigns 40% to the first and last interactions and splits the remaining 20% evenly among all other touchpoints.
Time decay attribution assigns credit to touchpoints based on their timespan proximity to the conversion. The closer the interaction is to the conversion, the more credit it gets.
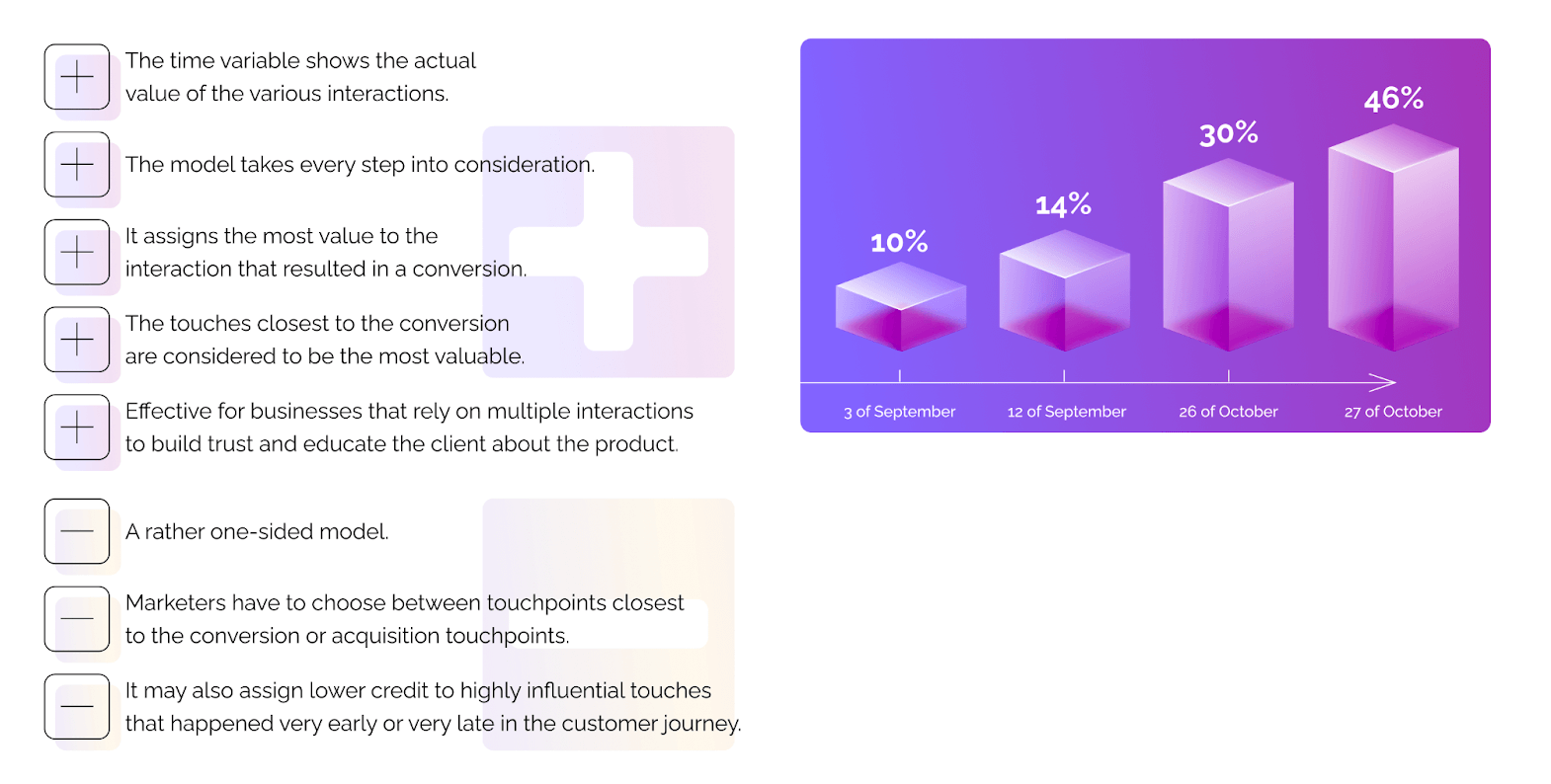
Highly influential touches are the ones that most frequently occur throughout the customer journey of your successful customers.
Improvado team is always happy to help with any other questions you might have! Send us an email.
Contact your Customer Success Manager or raise a request in Improvado Service Desk.